Clin Endosc.
2015 Mar;48(2):112-120. 10.5946/ce.2015.48.2.112.
Endoscopic Management of Dieulafoy's Lesion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. doc0224@pusan.ac.kr
- KMID: 1801201
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.2.112
Abstract
- A Dieulafoy's lesion is a vascular abnormality consisting of a large caliber-persistent tortuous submucosal artery. A small mucosal defect with the eruption of this protruding vessel can cause bleeding. In fact, a Dieulafoy's lesion is a relatively rare but potentially life-threatening condition. It accounts for 1% to 2% of cases of acute gastrointestinal bleeding. Although there is no consensus on the treatment of Dieulafoy's lesions; treatment options depend on the mode of presentation, site of the lesion, and available expertise. Endoscopic therapy is usually successful in achieving primary hemostasis, with hemostasis success rates reaching 75% to 100%. Although various therapeutic endoscopic methods are used to control bleeding in Dieulafoy's lesions, the best method for endoscopic intervention is not clear. Combination endoscopic therapy is known to be superior to monotherapy because of a lower rate of recurrent bleeding. In addition, mechanical therapies including hemostatic clipping and endoscopic band ligation are more effective and successful in controlling bleeding than other endoscopic methods. Advances in endoscopic techniques have reduced mortality in patients with Dieulafoy's lesion-from 80% to 8%-and consequently, the need for surgical intervention has been reduced. Currently, surgical intervention is used for cases that fail therapeutic endoscopic or angiographic interventions.
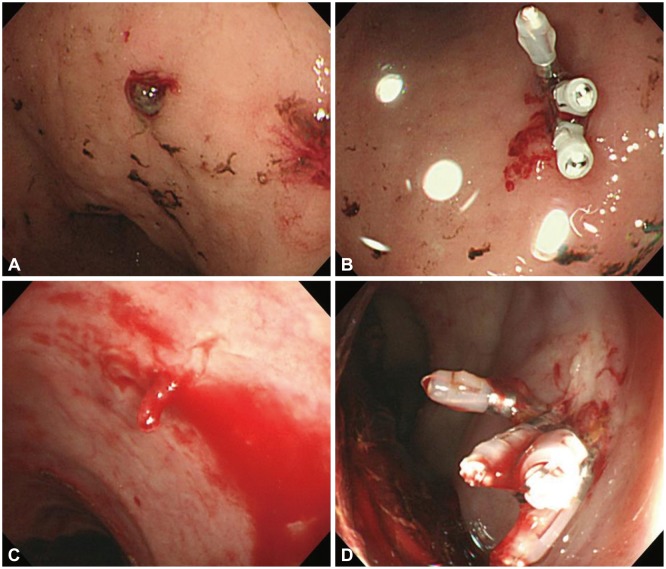
Figure
Reference
-
1. Baxter M, Aly EH. Dieulafoy's lesion: current trends in diagnosis and management. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2010; 92:548–554. PMID: 20883603.
Article2. Amaro R, Petruff CA, Rogers AI. Rectal Dieulafoy's lesion: report of a case and review of the literature. Dis Colon Rectum. 1999; 42:1339–1341. PMID: 10528775.3. Veldhuyzen van Zanten SJ, Bartelsman JF, Schipper ME, Tytgat GN. Recurrent massive haematemesis from Dieulafoy vascular malformations: a review of 101 cases. Gut. 1986; 27:213–222. PMID: 3485070.4. Kasapidis P, Georgopoulos P, Delis V, Balatsos V, Konstantinidis A, Skandalis N. Endoscopic management and long-term follow-up of Dieulafoy's lesions in the upper GI tract. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55:527–531. PMID: 11923766.
Article5. Jain R, Chetty R. Dieulafoy disease of the colon. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009; 133:1865–1867. PMID: 19886725.
Article6. Chaer RA, Helton WS. Dieulafoy's disease. J Am Coll Surg. 2003; 196:290–296. PMID: 12595057.
Article7. Stark ME, Gostout CJ, Balm RK. Clinical features and endoscopic management of Dieulafoy's disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 1992; 38:545–550. PMID: 1397908.
Article8. Strong RW. Dieulafoy's disease: a distinct clinical entity. Aust N Z J Surg. 1984; 54:337–339. PMID: 6333234.9. Marangoni G, Cresswell AB, Faraj W, Shaikh H, Bowles MJ. An uncommon cause of life-threatening gastrointestinal bleeding: 2 synchronous Dieulafoy lesions. J Pediatr Surg. 2009; 44:441–443. PMID: 19231553.
Article10. Park CH, Joo YE, Kim HS, Choi SK, Rew JS, Kim SJ. A prospective, randomized trial of endoscopic band ligation versus endoscopic hemoclip placement for bleeding gastric Dieulafoy's lesions. Endoscopy. 2004; 36:677–681. PMID: 15280971.
Article11. Sone Y, Kumada T, Toyoda H, Hisanaga Y, Kiriyama S, Tanikawa M. Endoscopic management and follow up of Dieulafoy lesion in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Endoscopy. 2005; 37:449–453. PMID: 15844024.
Article12. Lara LF, Sreenarasimhaiah J, Tang SJ, Afonso BB, Rockey DC. Dieulafoy lesions of the GI tract: localization and therapeutic outcomes. Dig Dis Sci. 2010; 55:3436–3441. PMID: 20848205.
Article13. Schmulewitz N, Baillie J. Dieulafoy lesions: a review of 6 years of experience at a tertiary referral center. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001; 96:1688–1694. PMID: 11419815.
Article14. Lee YT, Walmsley RS, Leong RW, Sung JJ. Dieulafoy's lesion. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 58:236–243. PMID: 12872092.
Article15. Juler GL, Labitzke HG, Lamb R, Allen R. The pathogenesis of Dieulafoy's gastric erosion. Am J Gastroenterol. 1984; 79:195–200. PMID: 6199971.16. Morowitz MJ, Markowitz R, Kamath BM, von Allmen D. Dieulafoy's lesion and segmental dilatation of the small bowel: an uncommon cause of gastrointestinal bleeding. J Pediatr Surg. 2004; 39:1726–1728. PMID: 15547843.
Article17. Fockens P, Tytgat GN. Dieulafoy's disease. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 1996; 6:739–752. PMID: 8899405.
Article18. Parra-Blanco A, Takahashi H, Méndez Jerez PV, et al. Endoscopic management of Dieulafoy lesions of the stomach: a case study of 26 patients. Endoscopy. 1997; 29:834–839. PMID: 9476766.
Article19. Alshumrani G, Almuaikeel M. Angiographic findings and endovascular embolization in Dieulafoy disease: a case report and literature review. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2006; 12:151–154. PMID: 16972222.20. al-Mishlab T, Amin AM, Ellul JP. Dieulafoy's lesion: an obscure cause of GI bleeding. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1999; 44:222–225. PMID: 10453143.21. Dulic-Lakovic E, Dulic M, Hubner D, et al. Bleeding Dieulafoy lesions of the small bowel: a systematic study on the epidemiology and efficacy of enteroscopic treatment. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:573–580. PMID: 21802676.
Article22. Yoshikumi Y, Mashima H, Suzuki J, et al. A case of rectal Dieulafoy's ulcer and successful endoscopic band ligation. Can J Gastroenterol. 2006; 20:287–290. PMID: 16609760.
Article23. Firat O, Karaköse Y, Calişkan C, Makay O, Ozütemiz O, Korkut MA. Dieulafoy's lesion of the anal canal: report of a case. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2007; 18:265–267. PMID: 18080926.24. Baettig B, Haecki W, Lammer F, Jost R. Dieulafoy's disease: endoscopic treatment and follow up. Gut. 1993; 34:1418–1421. PMID: 8244112.
Article25. Reilly HF 3rd, al-Kawas FH. Dieulafoy's lesion. Diagnosis and management. Dig Dis Sci. 1991; 36:1702–1707. PMID: 1748038.26. Ibrarullah M, Wagholikar GD. Dieulafoy's lesion of duodenum: a case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 2003; 3:2. PMID: 12581456.
Article27. Carvalho R, Almeida N, Ferreira M, et al. An unusual endoscopic image of a submucosal angiodysplasia. Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2012; 2012:186065. PMID: 23050173.
Article28. Fockens P, Meenan J, van Dullemen HM, Bolwerk CJ, Tytgat GN. Dieulafoy's disease: endosonographic detection and endosonography-guided treatment. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996; 44:437–442. PMID: 8905365.
Article29. Sai Prasad TR, Lim KH, Lim KH, Yap TL. Bleeding jejunal Dieulafoy pseudopolyp: capsule endoscopic detection and laparoscopic-assisted resection. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2007; 17:509–512. PMID: 17705738.
Article30. Lai LH. Obscure GI bleeding: is capsule endoscopy sufficient? Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 68:1128–1130. PMID: 19028221.
Article31. Goldenberg SP, DeLuca VA Jr, Marignani P. Endoscopic treatment of Dieulafoy's lesion of the duodenum. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990; 85:452–454. PMID: 2248637.32. Mumtaz R, Shaukat M, Ramirez FC. Outcomes of endoscopic treatment of gastroduodenal Dieulafoy's lesion with rubber band ligation and thermal/injection therapy. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003; 36:310–314. PMID: 12642736.
Article33. Park CH, Sohn YH, Lee WS, et al. The usefulness of endoscopic hemoclipping for bleeding Dieulafoy lesions. Endoscopy. 2003; 35:388–392. PMID: 12701008.
Article34. Norton ID, Petersen BT, Sorbi D, Balm RK, Alexander GL, Gostout CJ. Management and long-term prognosis of Dieulafoy lesion. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999; 50:762–767. PMID: 10570333.
Article35. Alis H, Oner OZ, Kalayci MU, et al. Is endoscopic band ligation superior to injection therapy for Dieulafoy lesion? Surg Endosc. 2009; 23:1465–1469. PMID: 19125307.
Article36. Iacopini F, Petruzziello L, Marchese M, et al. Hemostasis of Dieulafoy's lesions by argon plasma coagulation (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:20–26. PMID: 17591469.
Article37. Ahn DW, Lee SH, Park YS, et al. Hemostatic efficacy and clinical outcome of endoscopic treatment of Dieulafoy's lesions: comparison of endoscopic hemoclip placement and endoscopic band ligation. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 75:32–38. PMID: 22100302.
Article38. Nikolaidis N, Zezos P, Giouleme O, et al. Endoscopic band ligation of Dieulafoy-like lesions in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Endoscopy. 2001; 33:754–760. PMID: 11558028.
Article39. Chung IK, Kim EJ, Lee MS, et al. Bleeding Dieulafoy's lesions and the choice of endoscopic method: comparing the hemostatic efficacy of mechanical and injection methods. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 52:721–724. PMID: 11115902.
Article40. Yamaguchi Y, Yamato T, Katsumi N, et al. Short-term and long-term benefits of endoscopic hemoclip application for Dieulafoy's lesion in the upper GI tract. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 57:653–656. PMID: 12709692.
Article41. Lim W, Kim TO, Park SB, et al. Endoscopic treatment of dieulafoy lesions and risk factors for rebleeding. Korean J Intern Med. 2009; 24:318–322. PMID: 19949729.
Article42. Asaki S, Sato H, Nishimura T, et al. Endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of Dieulafoy's ulcer. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1988; 154:135–141. PMID: 3289138.
Article43. Matsui S, Kamisako T, Kudo M, Inoue R. Endoscopic band ligation for control of nonvariceal upper GI hemorrhage: comparison with bipolar electrocoagulation. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55:214–218. PMID: 11818925.
Article44. Romãozinho JM, Pontes JM, Lérias C, Ferreira M, Freitas D. Dieulafoy's lesion: management and long-term outcome. Endoscopy. 2004; 36:416–420. PMID: 15100950.
Article45. Cheng CL, Liu NJ, Lee CS, et al. Endoscopic management of Dieulafoy lesions in acute nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Dig Dis Sci. 2004; 49:1139–1144. PMID: 15387335.
Article46. Walmsley RS, Lee YT, Sung JJ. Dieulafoy's lesion: a case series study. World J Gastroenterol. 2005; 11:3574–3577. PMID: 15962378.
Article47. Ljubicic N. Efficacy of endoscopic clipping and long-term follow-up of bleeding Dieulafoy's lesions in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Hepatogastroenterology. 2006; 53:224–227. PMID: 16608029.48. De Palma GD, Patrone F, Rega M, Simeoli I, Masone S, Persico G. Actively bleeding Dieulafoy's lesion of the small bowel identified by capsule endoscopy and treated by push enteroscopy. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:3936–3937. PMID: 16804987.49. Pointner R, Schwab G, Königsrainer A, Dietze O. Endoscopic treatment of Dieulafoy's disease. Gastroenterology. 1988; 94:563–566. PMID: 3257449.
Article50. Skok P. Endoscopic hemostasis in exulceratio simplex-Dieulafoy's disease hemorrhage: a review of 25 cases. Endoscopy. 1998; 30:590–594. PMID: 9826135.51. Lin HJ, Tsai YT, Lee SD, et al. A prospectively randomized trial of heat probe thermocoagulation versus pure alcohol injection in nonvariceal peptic ulcer hemorrhage. Am J Gastroenterol. 1988; 83:283–286. PMID: 3278595.52. Shudo R, Yazaki Y, Sakurai S, Uenishi H, Yamada H, Sugawara K. Diffuse antral vascular ectasia: EUS after argon plasma coagulation. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 54:623. PMID: 11677481.
Article53. Canard JM, Vedrenne B. Clinical application of argon plasma coagulation in gastrointestinal endoscopy: has the time come to replace the laser? Endoscopy. 2001; 33:353–357. PMID: 11315899.
Article54. Valera JM, Pino RQ, Poniachik J, et al. Endoscopic band ligation of bleeding dieulafoy lesions: the best therapeutic strategy. Endoscopy. 2006; 38:193–194. PMID: 16479429.
Article55. Kim KB, Yoon SM, Youn SJ. Endoscopy for nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Clin Endosc. 2014; 47:315–319. PMID: 25133117.
Article56. Gimeno-García AZ, Parra-Blanco A, Nicolás-Pérez D, Ortega Sánchez JA, Medina C, Quintero E. Management of colonic Dieulafoy lesions with endoscopic mechanical techniques: report of two cases. Dis Colon Rectum. 2004; 47:1539–1543. PMID: 15486754.
Article57. Lee BI, Kim BW, Choi H, et al. Hemoclip placement through a forward-viewing endoscope for a Dieulafoy-like lesion in a duodenal diverticulum. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 58:813–814. PMID: 14997904.
Article58. Brown GR, Harford WV, Jones WF. Endoscopic band ligation of an actively bleeding Dieulafoy lesion. Gastrointest Endosc. 1994; 40:501–503. PMID: 7926548.
Article59. Xavier S. Band ligation of Dieulafoy lesions. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2005; 24:114–115. PMID: 16041104.60. Kirschniak A, Kratt T, Stüker D, Braun A, Schurr MO, Königsrainer A. A new endoscopic over-the-scope clip system for treatment of lesions and bleeding in the GI tract: first clinical experiences. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:162–167. PMID: 17591492.
Article61. Gomez V, Kyanam Kabir, Lukens FJ, Woodward T. Novel treatment of a gastric Dieulafoy lesion with an over-the-scope clip. Endoscopy. 2013; 45(Suppl 2 UCTN):E71. PMID: 23526524.
Article62. Mangiavillano B, Arena M, Morandi E, Viaggi P, Masci E. Successful treatment with an over-the-scope clip of Dieulafoy's gastric lesion resistant to conventional endoscopic treatment. Endoscopy. 2012; 44(Suppl 2 UCTN):E387. PMID: 23135974.
Article63. Jamanca-Poma Y, Velasco-Guardado A, Piñero-Pérez C, et al. Prognostic factors for recurrence of gastrointestinal bleeding due to Dieulafoy's lesion. World J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:5734–5738. PMID: 23155314.
Article64. Katsinelos P, Paroutoglou G, Mimidis K, et al. Endoscopic treatment and follow-up of gastrointestinal Dieulafoy's lesions. World J Gastroenterol. 2005; 11:6022–6026. PMID: 16273618.
Article65. Pathan NF, El-Fanek H. A 70-year-old man with episodes of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Dieulafoy lesion/malformation. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006; 130:e27–e29. PMID: 16454577.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Life-threatening Gastrointestinal Bleeding from a Dieulafoy’s Lesion in the Duodenum: A Case Report
- A Dieulafoy's Lesion of the Rectum Treated by Endoscopic Band Ligation: A case report
- A Case of Endoscopic Management of Dieulafoy's Lesion in the Ampulla of Vater
- Endoscopic Hemoclipping Treatment for Gastric Dieulafoy Lesion in a Newborn
- Endoscopic " 0 " Band Ligation Treatment for 3 Cases with Dieulafoy Lesion