J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2015 Mar;22(1):13-19. 10.4184/jkss.2015.22.1.13.
Neurophysiologic Mechanism of Pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, South Korea. wkmin@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1800389
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2015.22.1.13
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: A review of the literature regarding neurophysiologic mechanism of pain.
OBJECTIVES
To review and discuss neurophysiologic mechanism of pain, including neuropathic pain. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: The neurophysiology of pain has been established at the cellular and molecular biology level through many studies. Also, multiple modalities to manage pain have been developed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A literature review.
RESULTS
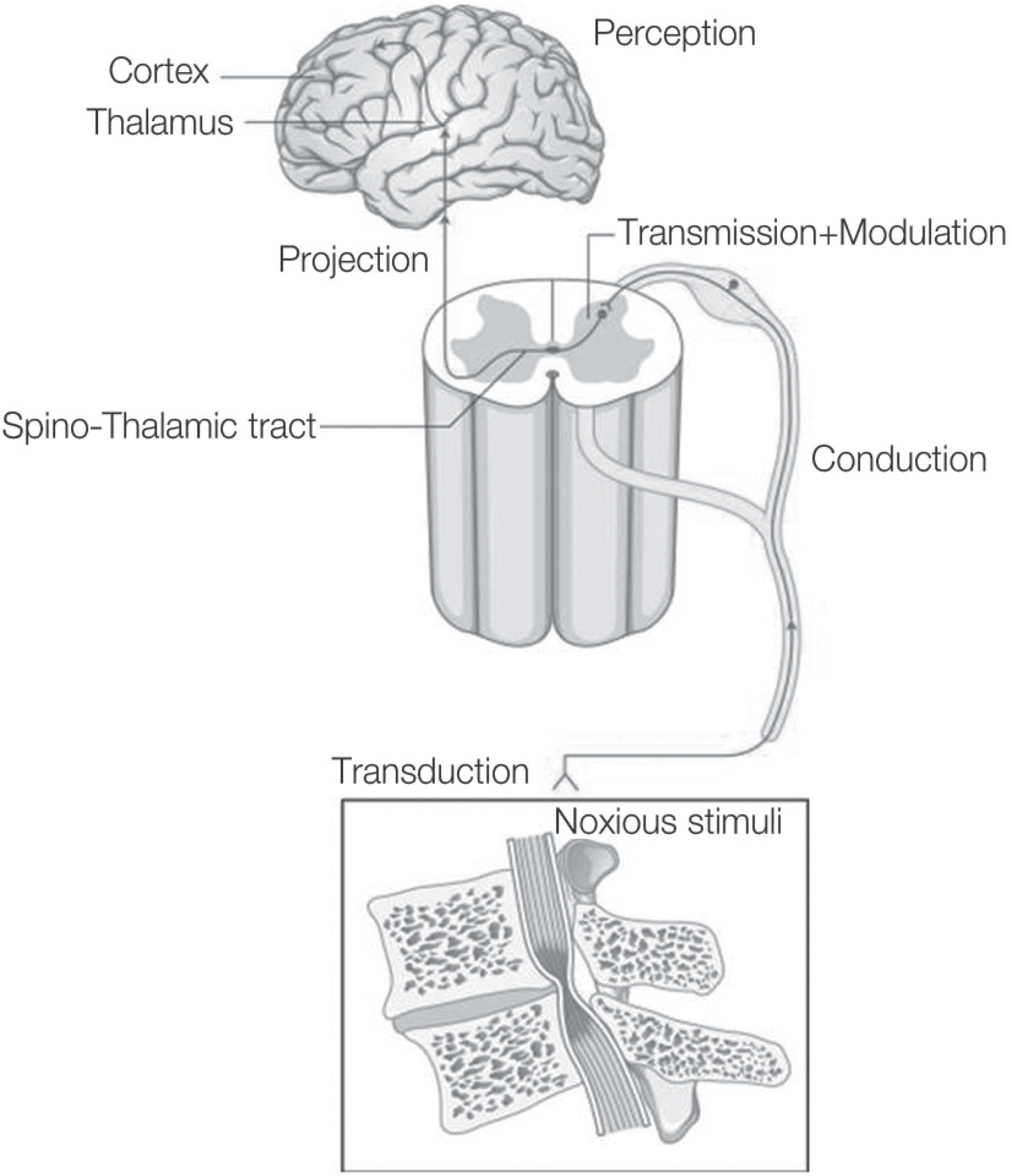
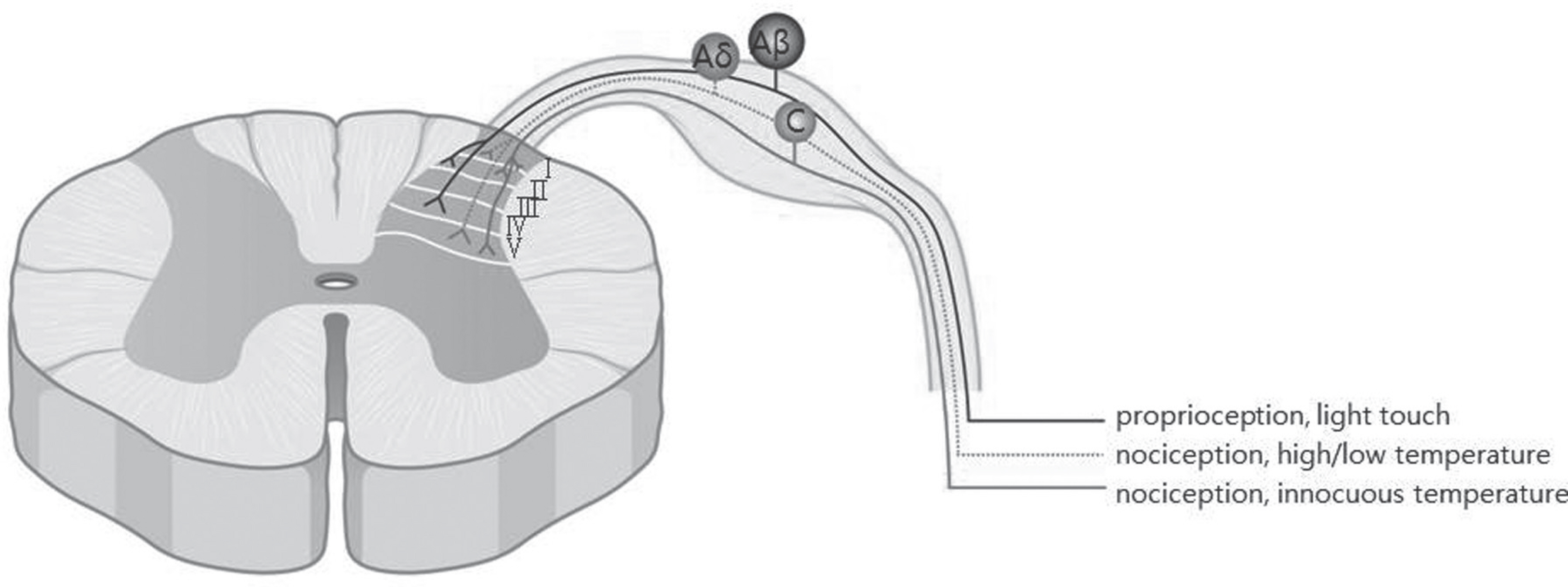
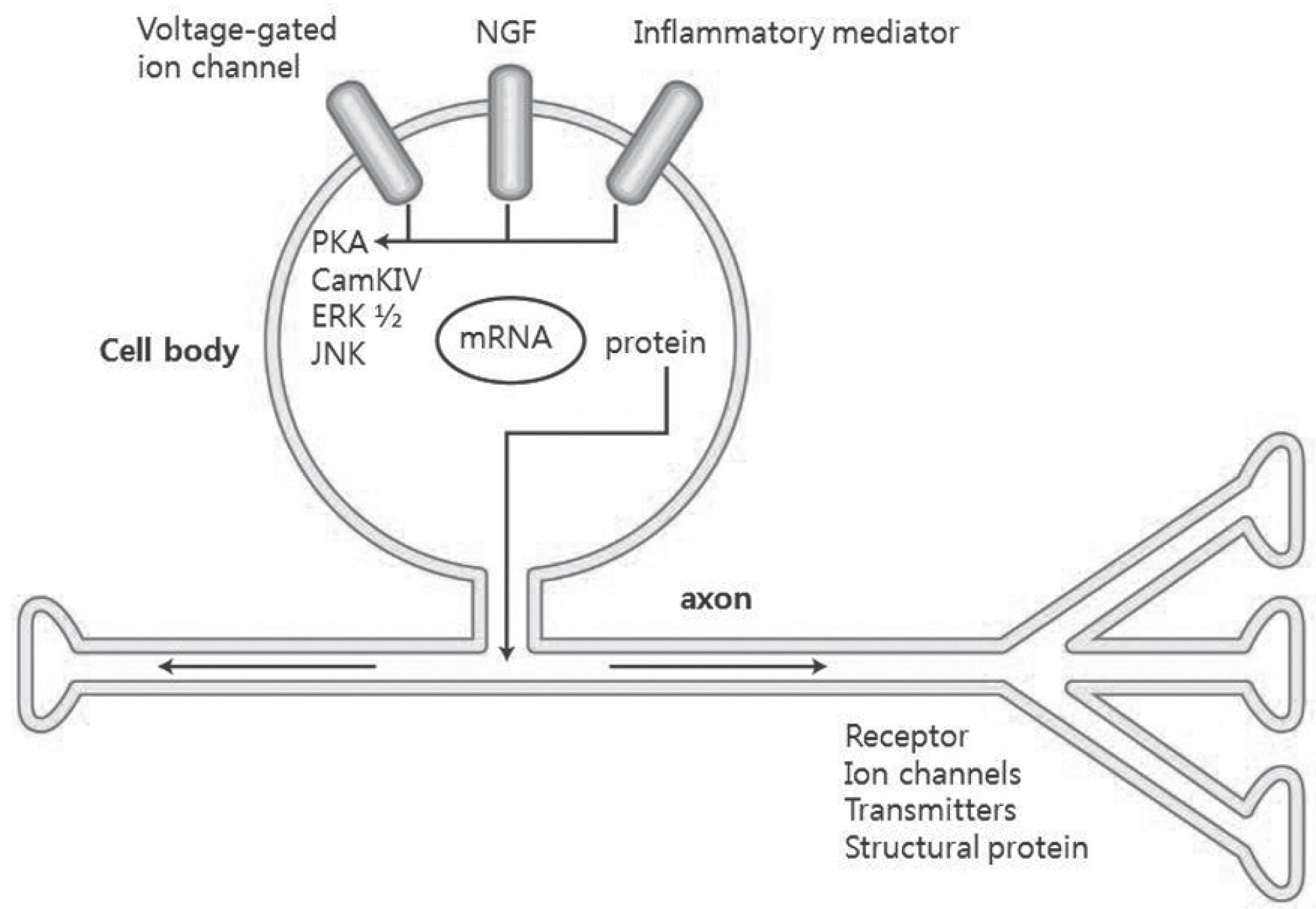
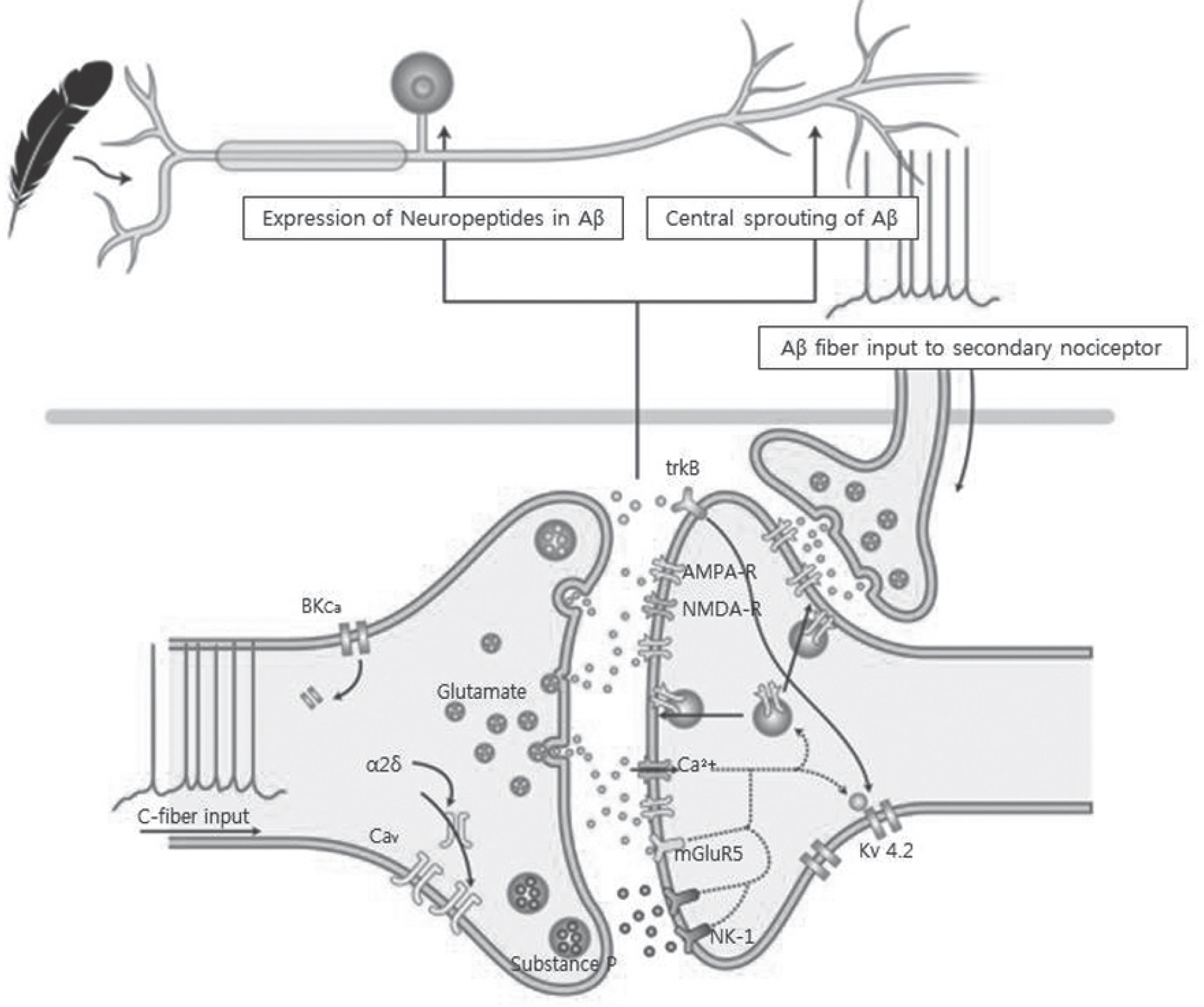
Pain develops by actions of multiple receptors, ion channels and neurotransmitters along the pain pathway. Pathologic states, such as persistent pain, allodynia, and hyperalgesia, arise from alteration of the pain pathway. Especially, neuropathic pain results from nerve injury and its pathology is rather different from the neuroplasty of normal individuals.
CONCLUSION
Multiple modalities, including individualized pain treatment based on pain phenotype, are introduced. However, optimal treatment is uncertain, therefore, further studies are needed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Woolf CJ. American Colle�e of P�ysicians; American P�ysiolo�ical Society. Pain: movin� from symptom control toward mec�anism�specific p�armacolo�ic mana�ement. Ann Intern �ed. 2004; 140:441–51.2. Julius �, Basbaum AI. �olecular mec�anisms of nocicep�tion. Nature. 2001; 413:203–10.3. von He�n CA, Baron R, Woolf CJ. �econstructin� t�e neuropat�ic pain p�enotype to reveal neural mec�anisms. Neuron. 2012; 73:638–52.4. Basbaum AI, Bautista ��, Sc�errer �, Julius �. Cellular and molecular mec�anisms of pain. Cell. 2009; 139:267–84.5. Zeil�ofer HU. T�e �lyciner�ic control of spinal pain pro� cessin�. Cell �ol Life Sci. 2005; 62:2027–35.6. �illan � J. T�e induction of pain: an inte�rative review. Pro� Neurobiol. 1999; 57:1–164.7. Boos N, Aebi �. Pat�ways of Spinal Pain in t�e Spinal �is� orders. 1sted.Berlin: Sprin�er Co;2008. .131� 7.8. �illespie P�, Walker R�. �olecular basis of mec�anosen� sory transduction. Nature. 2001; 413:194–202.9. Katano T, Nakazawa T, Nakatsuka T, Watanabe �, Yamamoto T, Ito S. Involvement of spinal p�osp�oryla�tion cascade of Tyr1472�NR2B, T�r286�Ca�KII, and Ser831��luR1 in neuropat�ic pain. Neurop�armacolo�y. 2011; 60:609–16.10. Porreca F, Ossipov � H, �eb�art � F. C�ronic pain and medullary descendin� facilitation. Trends Neurosci. 2002; 25:319–25.11. Binder A, �ay �, Baron R, et al. Transient receptor poten� tial c�annel polymorp�isms are associated wit� t�e somato� sensory function in neuropat�ic pain patients. PLoS One. 2011; 6:�. 17387.12. Watabiki T, Kiso T, Kuramoc�i T, et al. Amelioration of neuropat�ic pain by novel transient receptor potential vanil� loid 1 anta�onist AS1928370 in rats wit�out �ypert�ermic effect. J P�armacol �xp T�er. 2011; 336:743–50.13. Ta L�, Bieber AJ, Carlton S�, Loprinzi CL, Low PA, Windebank AJ. Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 is essential for cisplatin�induced �eat �yperal�esia in mice. �ol Pain. 2010; 6:15.14. �anty� PW, Koltzenbur� �, �endell L�, Tive L, S�elton � L. Anta�onism of nerve �rowt� factor�TrkA si�nalin� and t�e relief of pain. Anest�esiolo�y. 2011; 115:189–204.15. Wu �, Rin�kamp �, �urinson BB, et al. �e�eneration of myelinated efferent fibers induces spontaneous activity in uninjured C�fiber afferents. J Neurosci. 2002; 22:7746–53.16. He XH, Zan� Y, C�en X, et al. TNF�alp�a contributes to up�re�ulation of Nav1.3 and Nav1.8 in �R� neurons fol� lowin� motor fiber injury. Pain. 2010; 151:266–79.17. �mery � C, Youn� � T, Berrocoso ��, C�en L, �cNau��� ton PA. HCN2 ion c�annels play a central role in inflam� matory and neuropat�ic pain. Science. 2011; 333:1462–6.18. Nitzan�Luques A, �evor �, Tal �. �enotype�selective p�enotypic switc� in primary afferent neurons contributes to neuropat�ic pain. Pain. 2011; 152:2413–26.19. Tan A�, C�an� YW, Z�ao P, Hains BC, Waxman S�. Rac1�re�ulated dendritic spine remodelin� contributes to neuropat�ic pain after perip�eral nerve injury. �xp Neurol. 2011; 232:222–33.20. Leon� � L, �u �, Speltz�Paiz R, et al. Neuronal loss in t�e rostral ventromedial medulla in a rat model of neuropat�ic pain. J Neurosci. 2011; 31:17028–39.21. A�rawal S�, Silva C, Tourtellotte WW, Yon� VW. ���PRIN: a novel re�ulator of leukocyte transmi�ration into t�e CNS in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoim� mune encep�alomyelitis. J Neurosci. 2011; 31:669–77.22. �oulton �A, �lman I, Pendse �, Sc�ma�mann J, Becerra L, Borsook �. Aversion�related circuitry in t�e cerebellum: responses to noxious �eat and unpleasant ima�es. J Neuro� sci. 2011; 31:3795–804.23. Apkarian AV, Has�mi JA, Baliki � N. Pain and t�e brain: specificity and plasticity of t�e brain in clinical c�ronic pain. Pain. 2011; 152:49–64.24. Baliki � N, Sc�nitzer TJ, Bauer WR, Apkarian AV. Brain morp�olo�ical si�natures for c�ronic pain. PLoS One. 2011; 6:�. 26010.25. Baron R, Tolle TR, �ockel U, Brosz �, Freyn�a�en R. A cross�sectional co�ort survey in 2100 patients wit� painful diabetic neuropat�y and post�erpetic neural�ia: �iffer� ences in demo�rap�ic data and sensory symptoms. Pain. 2009; 146:34–40.26. Ranoux �, Attal N, �orain F, Bou�assira �. Botulinum toxin type A induces direct anal�esic effects in c�ronic neuropat�ic pain. Ann Neurol. 2008; 64:274–83.27. �dwards RR, Hayt�ornt�waite JA, Tella P, �ax � B, Raja S. Basal �eat pain t�res�olds predict opioid anal�e� sia in patients wit� post�erpetic neural�ia. Anest�esiol� o�y. 2006; 104:1243–8.