Yonsei Med J.
2013 Nov;54(6):1511-1515. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.6.1511.
Is There Relationship between Brain Atrophy and Higher Incidence of Hip Fracture in Old Age?: A Preliminary Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Konkuk University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. osjinho@naver.com
- KMID: 1798151
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.6.1511
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The studies on the correlation between incidence of fall and brain atrophy have been going on to find out the cause of fall and its prevention. The purpose of this study was to explore the relationship between incidence of hip fracture and brain volume, measured by magnetic resonance image.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
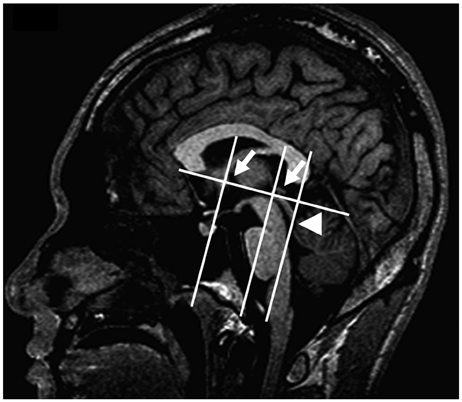
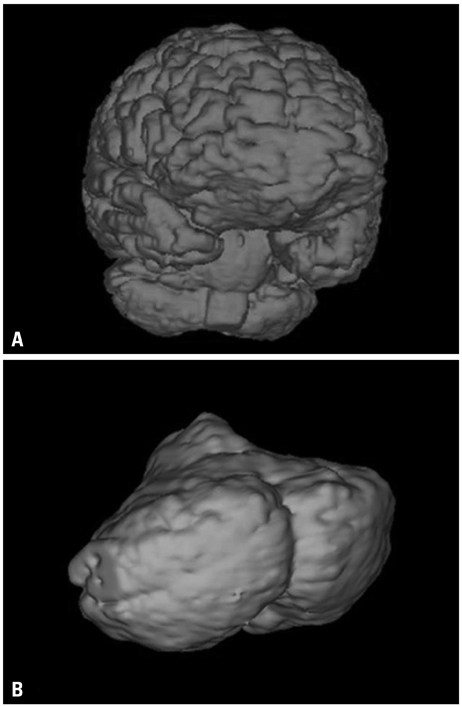
A total of 14 subjects with similar conditions (age, height, weight, and past history) were selected for this study. Fracture group (FG) was consisted of 5 subjects with intertrochanteric fracture. Control group (CG) had 9 subjects without intertrochanteric fracture. MRI-based brain volumetry was done in FG and CG with imaging software (V-works, CyberMed Co., Korea). Total brain (tBV), absolute cerebellar volumes (aCV) and relative cerebellar volumes (rCV) were compared between two groups. Student t-test was used to statistically analyze the results.
RESULTS
In FG, average tBV, aCV and rCV were 1034.676+/-38.80, 108.648+/-76.80 and 10.50+/-0.72 cm3, respectively. In CG, average tBV, aCV and rCV were found to be 1106.459+/-89.15, 114.899+/-98.06 and 10.39+/-0.53 cm3, respectively, having no statistically significant difference (p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
There was no significant difference between the fracture and control groups. Patients with neurologic disease such as cerebellar ataxia definitely have high incidence of fall that causes fractures and have brain changes as well. However, FG without neurologic disease did not have brain volume change. We consider that high risk of fall with hip fracture might decrease brain function which is not obvious to pickup on MRI.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gullberg B, Johnell O, Kanis JA. World-wide projections for hip fracture. Osteoporos Int. 1997; 7:407–413.
Article2. Cummings SR, Kelsey JL, Nevitt MC, O'Dowd KJ. Epidemiology of osteoporosis and osteoporotic fractures. Epidemiol Rev. 1985; 7:178–208.
Article3. Munger RG, Cerhan JR, Chiu BC. Prospective study of dietary protein intake and risk of hip fracture in postmenopausal women. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999; 69:147–152.
Article4. Richmond J, Aharonoff GB, Zuckerman JD, Koval KJ. Mortality risk after hip fracture. 2003. J Orthop Trauma. 2003; 17:8 Suppl. S2–S5.5. Sernbo I, Johnell O. Consequences of a hip fracture: a prospective study over 1 year. Osteoporos Int. 1993; 3:148–153.
Article6. Stevens JA, Olson S. Reducing falls and resulting hip fractures among older women. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2000; 49:3–12.
Article7. Nevitt MC, Cummings SR, Kidd S, Black D. Risk factors for recurrent nonsyncopal falls. A prospective study. JAMA. 1989; 261:2663–2668.
Article8. Tinetti ME, Speechley M, Ginter SF. Risk factors for falls among elderly persons living in the community. N Engl J Med. 1988; 319:1701–1707.
Article9. Adams RD, Victor M, Ropper AH. Principles of Neurology. New York: McGraw-Hill;1977. p. 405.10. Critchley M. On senile disorders of gait, including the so-called senile paraplegia. Geriatrics. 1948; 3:364–370.11. Fisher CM. Hydrocephalus in walking problems of the elderly. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1980; 105:29–33.12. Kim HJ, Yoon HR, Kim KD, Kang MK, Kwak HH, Park HD, et al. Personal-computer-based three-dimensional reconstruction and simulation of maxillary sinus. Surg Radiol Anat. 2003; 24:393–399.
Article13. Hutchinson S, Lee LH, Gaab N, Schlaug G. Cerebellar volume of musicians. Cereb Cortex. 2003; 13:943–949.
Article14. Press GA, Murakami J, Courchesne E, Berthoty DP, Grafe M, Wiley CA, et al. The cerebellum in sagittal plane--anatomic-MR correlation: 2. The cerebellar hemispheres. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989; 153:837–846.
Article15. Filipek PA, Richelme C, Kennedy DN, Caviness VS Jr. The young adult human brain: an MRI-based morphometric analysis. Cereb Cortex. 1994; 4:344–360.
Article16. Luft AR, Skalej M, Welte D, Kolb R, Bürk K, Schulz JB, et al. A new semiautomated, three-dimensional technique allowing precise quantification of total and regional cerebellar volume using MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1998; 40:143–151.
Article17. Witelson SF. Hand and sex differences in the isthmus and genu of the human corpus callosum. A postmortem morphological study. Brain. 1989; 112(Pt 3):799–835.
Article18. Peters M. Sex differences in human brain size and the general meaning of differences in brain size. Can J Psychol. 1991; 45:507–522.
Article19. Park IS, Han JW, Lee KJ, Lee NJ, Lee WT, Park KA, et al. Evaluation of morphological plasticity in the cerebella of basketball players with MRI. J Korean Med Sci. 2006; 21:342–346.
Article20. Rhyu IJ, Cho TH, Lee NJ, Uhm CS, Kim H, Suh YS. Magnetic resonance image-based cerebellar volumetry in healthy Korean adults. Neurosci Lett. 1999; 270:149–152.
Article21. Fisher CM. Hydrocephalus as a cause of disturbances of gait in the elderly. Neurology. 1982; 32:1358–1363.
Article22. Koller WC, Wilson RS, Glatt SL, Huckman MS, Fox JR. Senile gait: correlation with computed tomographic scans. Ann Neurol. 1983; 13:343–344.
Article23. Sudarsky L, Ronthal M. Gait disorders among elderly patients. A survey study of 50 patients. Arch Neurol. 1983; 40:740–743.24. Masdeu JC, Lantos G, Wolfson L. Hemispheric white matter lesions in the elderly prone to falling. Acta Radiol Suppl. 1986; 369:392.25. Paradiso S, Andreasen NC, O'Leary DS, Arndt S, Robinson RG. Cerebellar size and cognition: correlations with IQ, verbal memory and motor dexterity. Neuropsychiatry Neuropsychol Behav Neurol. 1997; 10:1–8.26. Koh I, Lee MS, Lee NJ, Park KW, Kim KH, Kim H, et al. Body size effect on brain volume in Korean youth. Neuroreport. 2005; 16:2029–2032.
Article27. Spann W, Dustmann HO. [Weight of the human brain and its dependence on age, body length, cause of death and occupation]. Dtsch Z Gesamte Gerichtl Med. 1965; 56:299–317.28. Lord SR, Clark RD, Webster IW. Postural stability and associated physiological factors in a population of aged persons. J Gerontol. 1991; 46:M69–M76.
Article29. Lichtenstein MJ, Shields SL, Shiavi RG, Burger MC. Clinical determinants of biomechanics platform measures of balance in aged women. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1988; 36:996–1002.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Second hip fracture in Hong Kong e Incidence, demographics, and mortality
- Intertrochanteric fracture associated with posterior hip dislocation
- Incidence, Morbidity and Mortality in Patients Older than 50 Years with Second Hip Fracture in a Jeju Cohort Study
- The Relationship between the Variation of the femoral neckshaft angle according to Age and the Fracture of the Hip
- The Relationship between the Fracutures of the Hip and the Bone Mineral Density over Fifty years