Korean J Urol.
2014 Jul;55(7):496-498. 10.4111/kju.2014.55.7.496.
Vesicoenteric Fistula due to Bladder Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea. honda400@dreamwiz.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea.
- KMID: 1794581
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.7.496
Abstract
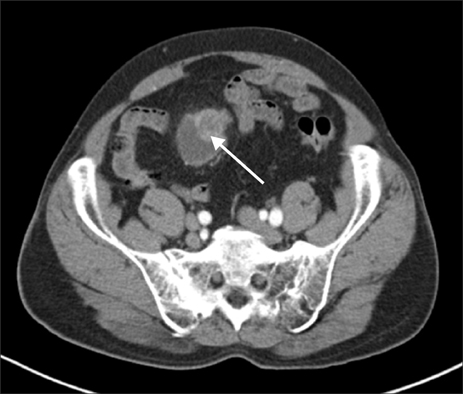
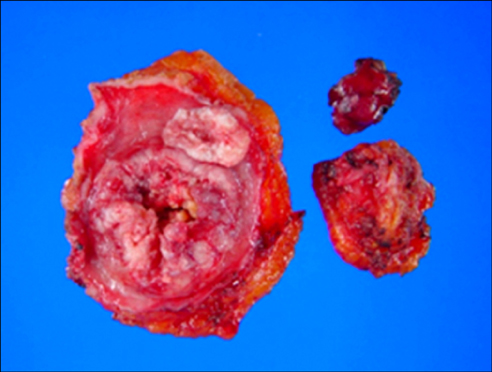
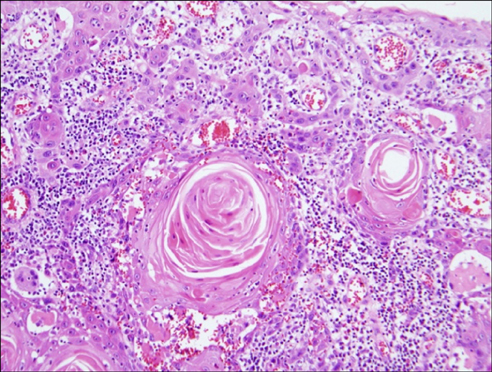
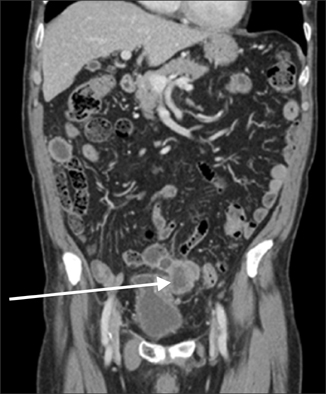
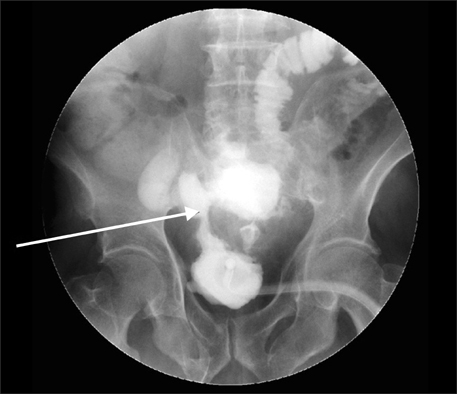
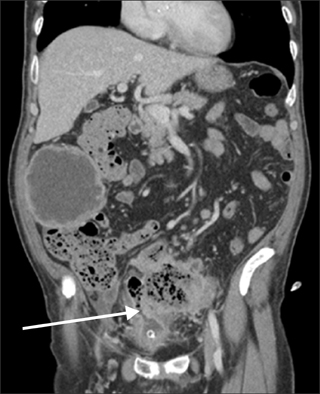
- Vesicoenteric fistula is a rare complication of bladder squamous cell carcinoma. We report the case of a 70-year-old male who complained of painless, total gross hematuria. Abdominopelvic computed tomography (CT) revealed an approximately 2.7-cm lobulated and contoured enhancing mass in the bladder dome. We performed partial cystectomy of the bladder dome after transurethral resection of the bladder. The biopsy result was bladder squamous cell carcinoma, with infiltrating serosa histopathologically, but the resection margin was free. Postoperatively, follow-up CT was done after 3 months. Follow-up CT revealed an approximately 4.7-cmx4.0-cm lobulated, contoured, and heterogeneous mass in the bladder dome. A vesicoenteric fistula was visible by cystography. Here we report this case of a vesicoenteric fistula due to bladder squamous cell carcinoma.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Karamchandani MC, West CF Jr. Vesicoenteric fistulas. Am J Surg. 1984; 147:681–683.2. Kirsh GM, Hampel N, Shuck JM, Resnick MI. Diagnosis and management of vesicoenteric fistulas. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1991; 173:91–97.3. Dawam D, Patel S, Kouriefs C, Masood S, Khan O, Sheriff MK. A "urological" enterovesical fistula. J Urol. 2004; 172:943–944.4. Larsen A, Bjerklund Johansen TE, Solheim BM, Urnes T. Diagnosis and treatment of enterovesical fistula. Eur Urol. 1996; 29:318–321.5. Rovner ES. Urinary tract fistulae. In : Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, Peters CA, editors. Campbell-Walsh urology. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;2011. p. 2252–2254.6. Carson CC, Malek RS, Remine WH. Urologic aspects of vesicoenteric fistulas. J Urol. 1978; 119:744–746.7. Shinjo T, Kondo Y, Harada K, Yamazaki J, Okada M. Treatment of malignant enterovesical fistula with octreotide. J Palliat Med. 2009; 12:965–967.8. Mizushima T, Ikeda M, Sekimoto M, Yamamoto H, Doki Y, Mori M. Laparoscopic bladder-preserving surgery for enterovesical fistula complicated with benign gastrointestinal disease. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2012; 6:279–284.9. Whiteley HW Jr, Grabstald H. Conservative management of distal large bowel cancer invading the urinary bladder. Clin Bull. 1975; 5:99–101.10. Vidal Sans J, Pradell Teigell J, Palou Redorta J, Villagrasa Serrano M, Banus Gassol JM. Review of 31 vesicointestinal fistulas: diagnosis and management. Eur Urol. 1986; 12:21–27.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Bladder Diverticulum: A Report of One Case
- A Case of Synchronous Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder and Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Ureter
- Verrucous Carcinoma of the Bladder Unassociated with Bilharzial Cystitis: A Case Report
- A Case of Reconstruction of Abdominal Wall Defect using Tensor Fascia Lata Myocutaneous Flap: The Defect Caused by a Wide Resection of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Bladder Invading Abdominal Wall
- Primary Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Gallbladder Forming a Cholecystogastric Fistula