J Korean Soc Radiol.
2015 May;72(5):364-367. 10.3348/jksr.2015.72.5.364.
Three-Dimensional Fusion Angiography of a Giant Basilar Aneurysm for Coil Embolization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. dcsuh@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 1793895
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.72.5.364
Abstract
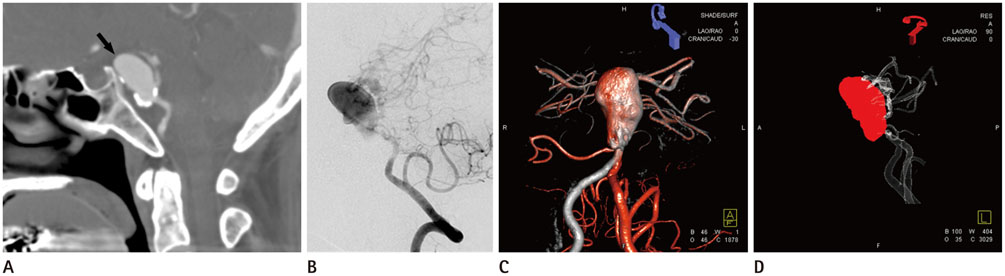
- A giant aneurysm was unexpectedly found on computed tomography angiogram in a 54-year-old female. Cerebral angiogram showed a giant aneurysm at the ventral side of the lower basilar artery trunk. However, it was difficult to demonstrate the precise relationship between the aneurysmal sac and the parent artery because of the incomplete filling of the contrast medium secondary to the preferential flows from a well-balanced development of both vertebral arteries. Three-dimensional (3D) fusion angiography revealed complete filling of the aneurysm as well as the basilar trunk itself beyond the aneurysm, which was dysplastic. Coiling of the aneurysm was safely and completely accomplished based on the fusion images. In this report, we demonstrate a case of giant basilar aneurysm with 3D fusion angiography proving useful in assisting with treatment planning.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hoit DA, Malek AM. Fusion of three-dimensional calcium rendering with rotational angiography to guide the treatment of a giant intracranial aneurysm: technical case report. Neurosurgery. 2006; 58:1 Suppl. ONS–E173. discussion ONS-E173.2. Ojemann RG, Ogilvy CS, Heros RC, Crowell RM. Surgical Management of Cerebrovascular Disease. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;1988.3. Sughrue ME, Saloner D, Rayz VL, Lawton MT. Giant intracranial aneurysms: evolution of management in a contemporary surgical series. Neurosurgery. 2011; 69:1261–1270.4. Nurminen V, Lehecka M, Chakrabarty A, Kivisaari R, Lehto H, Niemelä M, et al. Anatomy and morphology of giant aneurysms--angiographic study of 125 consecutive cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2014; 156:1–1.5. Schnell S, Ansari SA, Vakil P, Wasielewski M, Carr ML, Hurley MC, et al. Three-dimensional hemodynamics in intracranial aneurysms: influence of size and morphology. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014; 39:120–131.6. Oishi S, Murphy KJ, Oka M, Gailloud P. [Bone fusion algorithm: a new tool to support decision making]. Nihon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi. 2007; 63:843–851.7. Mikhal J, Kroon DJ, Slump CH, Geurts BJ. Flow prediction in cerebral aneurysms based on geometry reconstruction from 3D rotational angiography. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2013; 29:777–805.8. Schneiders JJ, Marquering HA, Antiga L, van den Berg R, VanBavel E, Majoie CB. Intracranial aneurysm neck size overestimation with 3D rotational angiography: the impact on intra-aneurysmal hemodynamics simulated with computational fluid dynamics. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013; 34:121–128.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stent Assisted Coil Embolization of Unruptured Aneurysm Associated with Basilar Artery Fenestration: A Case Report
- Giant Vertebrobasilar Junction Aneurysm Treated with Proximal Occlusion of Parent Artery Followed by Coil Embolization of Partially Thrombosed Aneurysm: A Case Report
- Dual Stent-Assisted Coil Embolization for Fusiform Aneurysm Arising From Persistent Trigeminal Artery
- Endovascular Treatment of Giant Basilar Trunk Aneurysm: Case Report
- Staged Y-shaped Stent Assisted Coil Embolization in a Wide-Neck Basilar Tip Aneurysm: Case Report