Yonsei Med J.
2008 Aug;49(4):553-562. 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.4.553.
Antenatal Cognitive-behavioral Therapy for Prevention of Postpartum Depression: A Pilot Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University, Seoul, Korea. itslife@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Psychology, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Soon Chun Hyang University Hospital, Soon Chun Hyang University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1793190
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2008.49.4.553
Abstract
- PURPOSE
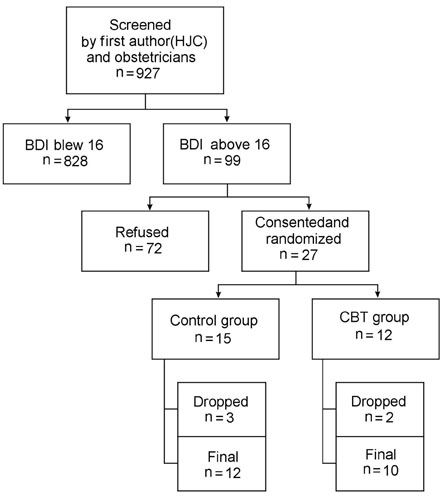
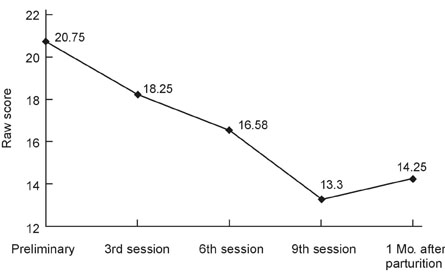
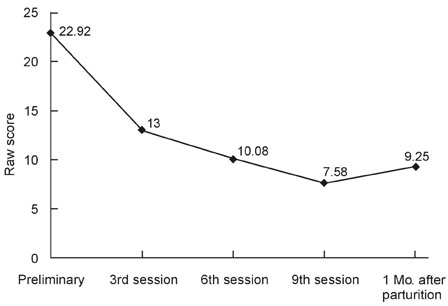
To examine the efficacy of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for the prevention of postpartum depression (PPD) in "at risk" women. MATERIALS and METHODS: We recruited 927 pregnant women in 6 obstetric and gynecology clinics and screened them using Beck Depression Inventory (BDI). Ninety-nine of the screened women who had significantly high scores in BDI (a score above 16) were selected for the study. They were contacted through by telephone, and 27 who had consented to participate in the study were interviewed via SCID-IV-I. Twenty-seven eligible women were randomly assigned to the CBT intervention (n = 15) and control condition (n = 12). All participants were required to complete written questionnaires, assessing demographic characteristics, depressive symptoms, negative thoughts, dyadic communication satisfaction, and global marital satisfaction prior to treatment and approximately 1 month postpartum. The 15 women in the CBT condition received 9 bi-weekly 1-hour individual CBT sessions, targeting and modifying negative patterns of thinking and behaviors occurring in the context of the dyadic relationship. RESULTS: The analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) showed that there were significant differences in all postpartum measures between the 2 groups, indicating that our antenatal intervention with CBT was effective in reducing depressive symptoms and improving marital satisfaction, which lasted until the postpartum period. CONCLUSION: Our pilot study has provided preliminary empirical evidence that antenatal CBT intervention can be an effective preventive treatment for PPD. Further study in this direction was suggested.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. O'Hara M, Swain AM. Rates and risks of postpartum depression: A meta-analysis. Int Rev Psychiatry. 1996. 8:37–54.2. Cooper PJ, Murray L, Wilson A, Romaniuk H. Controlled trial of the short- and long-term effect of psychological treatment of post-partum depression. Br J Psychiatry. 2003. 182:412–419.
Article3. Cornish AM, McMahon CA, Ungerer JA, Barnett B, Kowalenko N, Tennant C. Postnatal depression and infant cognitive and motor development in the second postnatal year: The impact of depression chronicity and infant gender. Infant Behav Dev. 2005. 28:407–417.
Article4. Goodman SH, Gotlib IH. Risk for psychopathology in the children of depressed mothers: a developmental model for understanding mechanisms of transmission. Psychol Rev. 1999. 106:458–490.5. Beardslee WR, Keller MB, Lavori PW, Staley J, Sacks N. The impact of parental affective disorder on depression in offspring: a longitudinal follow-up in a nonreferred sample. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1993. 32:723–730.6. Beardslee WR, Versage EM, Gladston TR. Children of affectively ill parents: a review of the past 10 years. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1998. 37:1134–1141.
Article7. Cutrona CE. Social support and stress in the transition to parentghood. J Abnorm Psychol. 1984. 93:378–390.8. Phillipps LHC, O'Hara MW. Prospective study of postpartum depression: 4 1/2 year follow up of women and children. J Abnorm Psychol. 1991. 100:151–155.9. Zelkowitz P, Milet TH. Postpartum psychiatric disorders: their relationship to psychological adjustment and marital satisfaction in the spouses. J Abnorm Psychol. 1996. 105:281–285.
Article10. Brown GW, Bifulco A, Andrew B. Self-esteem and depression III. Aetiological issues. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 1990. 25:235–243.11. Spinelli MG. Interpersonal psychotherapy for depressed antepartum women: a pilot study. Am J Psychiatry. 1997. 154:1028–1030.
Article12. Brugha TS, Wheatley S, Taub NA, Culverwell A, Friedman T, Kirwan P, et al. Pragmatic randomized trial of antenatal intervention to prevent post-natal depression by reducing psychosocial risk factors. Psychol Med. 2000. 30:1273–1281.
Article13. Zlotnick C, Johnson SL, Miller IW, Pearlstein T, Howard M. Postpartum depression in women receiving public assistance: pilot study of an interpersonal therapy-oriented group intervention. Am J Psychiatry. 2001. 15:638–640.14. Cascardi M, O'Leary KD, Lawrence EE, Schlee KA. Characteristics of women physically abused by their spouses and who seek treatment regarding marital conflict. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1995. 63:616–623.
Article15. Beach SRH, Sandeen EE, O'Leary KD. Depession in marriage: A model for etiology and treatment. 1990. New York: Guilford;53–83.16. Butler AC, Chapman JE, Forman EM, Beck AT. The empirical status of cognitive-behavioral therapy: a review of meta-analyses. Clin Psychol Rev. 2006. 26:17–31.
Article17. Epstein N, Baucom DH, Rankin LA. Treatment of marital conflict: a cognitive-behavioral approach. Clin Psychol Rev. 1993. 13:45–57.18. Beach SR, Sandeen EE, O'leary KD. Depression in marriage: a model for etiology and treatment. New York: The Guilfrord Press.19. Horowitz JA, Damato E, Solon L, Von Metzsch G, Gill V. Postpartum depression: issues in clinical assessment. J Perinatol. 1995. 15:268–278. quiz 279-80.20. Posner NA, Unterman RR, Williams KN, Williams GH. Screening for postpartum depression. An antepartum questionnaire. J Reprod Med. 1997. 42:207–215.21. Beck AT, Rush AJ, Shaw BF, Emery G. Cognitive Therapy of Depression. 1979. New York: Guilford Press.22. Hollen SD, Kendall PC. Cognitive self-statements in depression: Development of an automatic thoughts questionnaire. Cognit Ther Res. 1980. 4:383–395.
Article23. Snyder DK. Marital satisfaction inventory (MSI) Manual. 1997. Los Angeles: Western Psychological Service.24. Kwon JH, Chae PK. A validation study of Korean marital satisfaction inventory. Korean J Clin Psychol. 1999. 18:123–139.25. Brugha TS, Wheatley S, Taub NA, Culverwell A, Friedman T, Kirwan P, et al. Pragmatic randomized trial of antenatal intervention to prevent post-natal depression by reducing psychosocial risk factors. Psychol Med. 2000. 30:1273–1281.
Article26. Hayes BA, Muller R, Bradley BS. Perinatal depression: a randomized controlled trial of an antenatal education intervention for primiparas. Birth. 2001. 28:28–35.27. Dennis CL. Psychosocial and psychological interventions for prevention of postnatal depression: systematic review. BMJ. 2005. 331:1–8.
Article28. Affonso DD, De AK, Horowitz JA, Mayberry LJ. An international study exploring levels of postpartum depressive symptomatology. J Psychosom Res. 2000. 49:207–216.
Article29. Beck CT. Maternal depression and child behaviour problems: a meta-analysis. J Adv Nurs. 1999. 29:623–629.
Article30. Lovejoy MC, Graczyk PA, O'Hare E, Neuman G. Maternal depression and parenting behavior: a meta-analytic review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2000. 20:561–592.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Diabetic Patients
- The Effects of Postpartum Depression on the Development of Children
- Development of a Home-Based Multimedia Tutoring System for Postpartum Depression Management
- Effect of a Telephone-administered Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for the Management of Depression, Anxiety, and Chronic Illness Anticipated Stigma in Parkinson's Disease
- Psychotherapy and Psychosocial Therapy for the Geriatric Mood Disorders