Korean J Gastroenterol.
2011 May;57(5):309-314. 10.4166/kjg.2011.57.5.309.
A Case of Acute Phlegmonous Gastritis Causing Gastroparesis and Cured with Medical Treatment Alone
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Bundang Jesaeng General Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. parkjs@dmc.or.kr
- KMID: 1792788
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2011.57.5.309
Abstract
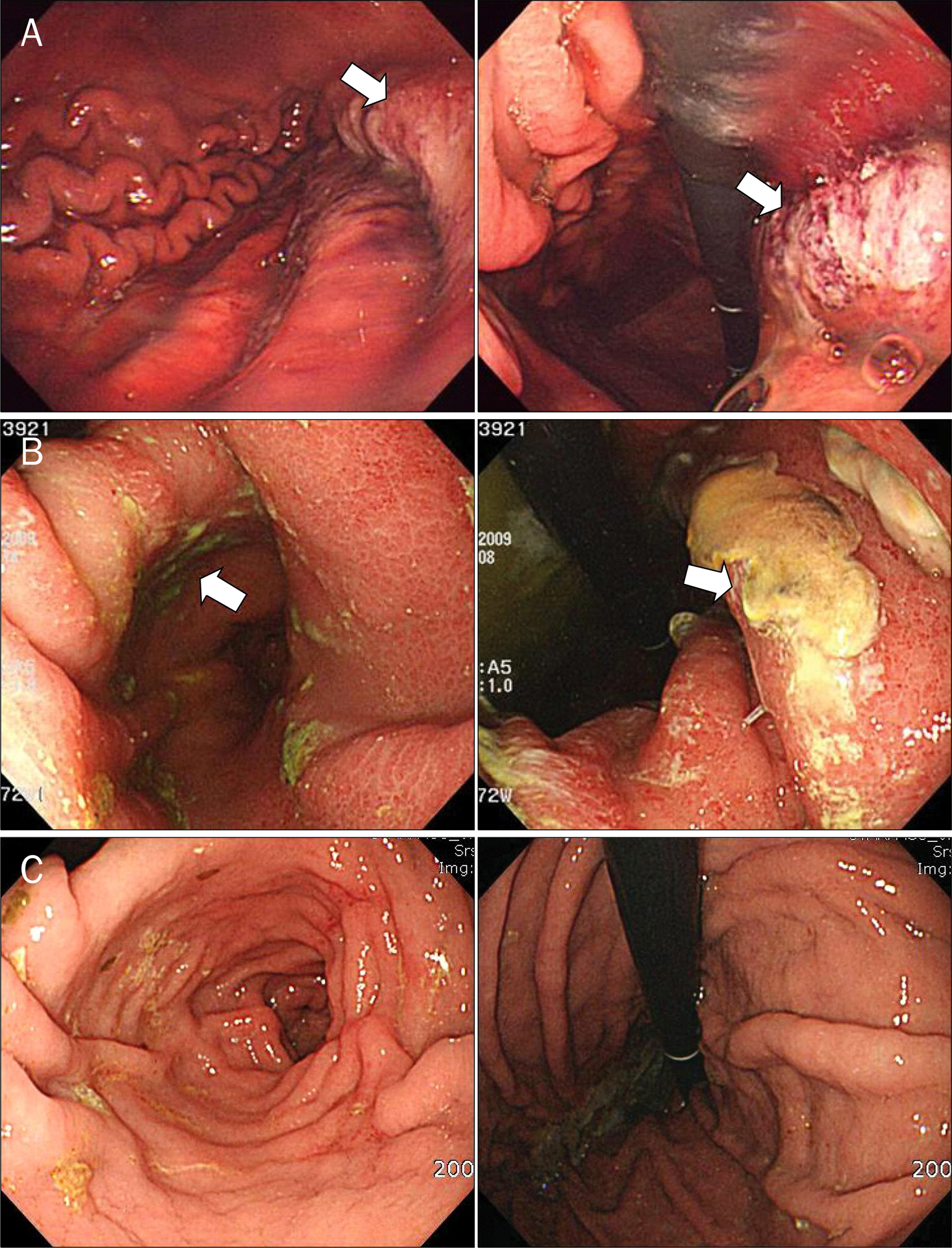
- Acute phlegmonous gastritis is an uncommon disease, often fatal condition characterized by suppurative bacterial infection of the gastric wall. It has a high mortality rate mainly because the diagnosis is usually made late. Until recently, gastrectomy in combination with antibiotics was recommended. We had experienced a case of 66-year-old man presented with epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, and hematemesis, followed by aspiration pneumonia. At upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, the gastric lumen was narrow, and the mucosa was severely inflamed, which was erythematous, swelled, and showed necrotic areas covered with purulent exudate. Klebsiella oxytoca and Acinetobacter lwoffii were isolated in the gastric tissue culture. Contrast-enhanced computerized tomography scan of abdomen demonstrated diffuse gastric wall thickening and an intramural abscess in the gastric antral wall. Although delayed gastric emptying by gastroparesis prolonged the in-hospital period, the only medical treatment with antibiotics alone successfully cured the patient without gastrectomy.
MeSH Terms
-
Acinetobacter/isolation & purification
Acute Disease
Aged
Anti-Bacterial Agents/*therapeutic use
Anti-Infective Agents/therapeutic use
Cefotaxime/therapeutic use
Ceftriaxone/therapeutic use
Ciprofloxacin/therapeutic use
Drug Resistance, Multiple, Bacterial
Drug Therapy, Combination
Gastritis/*diagnosis/drug therapy/microbiology
Gastroparesis/*diagnosis/microbiology
Gastroscopy
Humans
Imipenem/therapeutic use
Klebsiella oxytoca/isolation & purification
Male
Ofloxacin/therapeutic use
Pneumonia/diagnosis/drug therapy
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Acute Phlegmonous Esophagogastritis
Taehoon Kim, Yeon Namgung, Sun Young Jeong, Sun-Jin Boo
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2019;73(4):239-241. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2019.73.4.239.Two Cases of Phlegmonous Esophagogastritis in New Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Jae Woong Yoon, Chei Won Kim, Min Ju Kim, Hae Yoon Kwon, Shin Il Kim, Si Nae Lee, Seongbin Hong, Kyung-Hee Lee, Ju Young Han, So Hun Kim, Moonsuk Nam, Yong Seong Kim
J Korean Diabetes. 2015;16(2):153-159. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2015.16.2.153.
Reference
-
References
1. Miller AI, Smith B, Rogers AI. Phlegmonous gastritis. Gastroenterology. 1975; 68:231–238.
Article2. Wakayama T, Watanabe H, Ishizaki Y, et al. A case of phlegmonous esophagitis associated with diffuse phlegmonous gastritis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994; 89:804–806.3. Kim GY, Ward J, Henessey B, et al. Phlegmonous gastritis: case report and review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 61:168–174.
Article4. Lee TH, Lee GS, Im EH, et al. A case of acute phlegmonous gastritis treated with antibiotics alone. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 31:44–48.5. Choong NW, Levy MJ, Rajan E, Kolars JC. Intramural gastric abscess: case history and review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 58:627–629.6. Joko T, Tanaka H, Hirakata H, et al. Phlegmonous gastritis in a haemodialysis patient with secondary amyloidosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999; 14:196–198.
Article7. Radhi J, Kamouna M, Nyssen J. Phlegmonous gastritis following coronary bypass surgery. Can J Gastroenterol. 1999; 13:837–839.
Article8. Yu QQ, Tariq A, Unger SW, Cabello-Inchausti B, Robinson MJ. Phlegmonous gastritis associated with Kaposi sarcoma: a case report and review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2004; 128:801–803.
Article9. Lee BS, Kim SM, Seong JK, et al. Phlegmonous gastritis after endoscopic mucosal resection. Endoscopy. 2005; 37:490–493.
Article10. Min JS, Cho CH, Cho KS, et al. Diffuse phlegmonous gastritis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1980; 12:73–77.11. Choi KM, Kwon YJ, Park MG, et al. Two cases of acute phlegmonous gastritis. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 1995; 15:79–83.12. Lee BK, Park KT, Kim ES, et al. A case of phlegmonous gastritis. Korean J Med. 1988; 34:421–425.13. Lee GW, Lee OJ, Jung KW, et al. Acute phlegmonous gastritis diagnosed early endoscopically and treated successfully with antibiotics. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 23:225–229.14. Waseem S, Moshiree B, Draganov PV. Gastroparesis: current diagnostic challenges and management considerations. World J Gastroenterol. 2009; 15:25–37.
Article15. Kanno Y, Irisawa A, Takagi T, et al. Endosonographic diagnosis and follow-up of phlegmonous gastritis. J Clin Ultrasound. 2007; 35:524–526.16. Iwakiri Y, Kabemura T, Yasuda D, et al. A case of acute phlegmonous gastritis successfully treated with antibiotics. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1999; 28:175–177.
Article17. Hu DC, McGrath KM, Jowell PS, Killenberg PG. Phlegmonous gastritis: successful treatment with antibiotics and resolution documented by EUS. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 52:793–795.
Article18. Kim HS, Jang WI, Lee SS, et al. Two cases of phlegmonous gastritis secondary to corrosive gastritis caused by formalin. Korean J Med. 1991; 40:268–273.19. Jung JH, Choi HJ, Yoo J, Kang SJ, Lee KY. Emphysematous gastritis associated with invasive gastric mucormycosis: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 2007; 22:923–927.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Phlegmonous Gastritis Diagnosed Early Endoscopically and Treated Successfully with Antibiotics
- A Case of Acute Phlegmonous Gastritis Diagnosed with Endoscopic Submucosal Biopsy and Bacterial Culture and Improved by Antibiotics Treatment
- Two Cases of Acute Phlegmonous Gastritis
- Acute Phlegmonous Gastritis Developing after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection That Was Successfully Treated by Antibiotics Alone
- Treatment of phlegmonous esophagitis in various patients: a case series