Ann Lab Med.
2014 Jul;34(4):300-306. 10.3343/alm.2014.34.4.300.
Comparison of ABO Antibody Titers on the Basis of the Antibody Detection Method Used
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. limyoung@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Green Cross Laboratories, Yongin, Korea.
- KMID: 1791938
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2014.34.4.300
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Detection methods for ABO antibody (Ab) titers vary across laboratories, and the results are different depending on the method used. We aimed to compare titer values using different detection methods for the measurement of ABO Ab titers.
METHODS
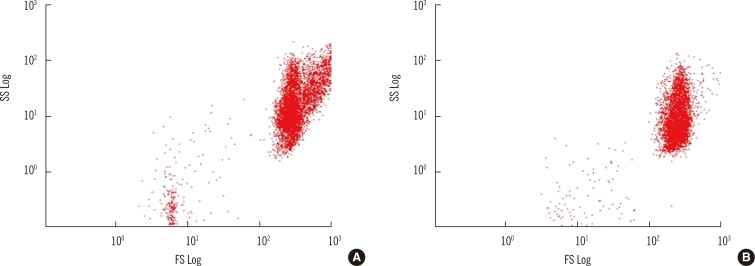
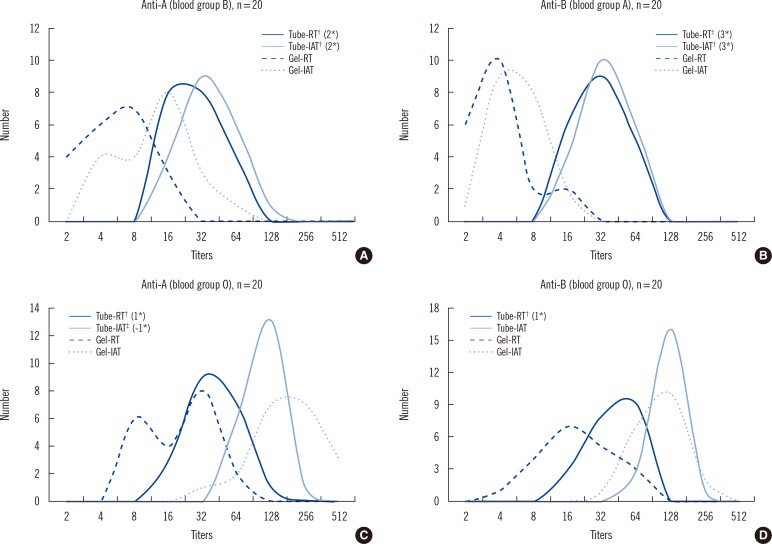
For ABO Ab detection, pooled group A or B red blood cells (RBCs) were reacted with each of 20 sera from blood groups A, B, or O without dithiothreitol treatment. The room-temperature (RT) incubation technique and the indirect antiglobulin test (IAT) were used in the tube test and gel card test. Flow cytometry (FCM) was performed by using anti-IgM and anti-IgG Abs.
RESULTS
Regardless of the blood groups tested, the FCM assay with anti-IgM showed the highest titer compared to the tube test and gel card test with RT incubation in both. The tube test with IAT showed a higher titer than the gel card test with IAT (Gel-IAT) or FCM with anti-IgG in blood group A and B, while Gel-IAT showed the highest titer relative to the other tests, only for the anti-A Ab in blood group O.
CONCLUSIONS
There were significant differences in the titers depending on the detection method used, and each method showed a different detection capacity for each ABO Ab depending on the ABO blood group tested. Therefore, caution should be exercised in interpreting ABO Ab titer results, taking into consideration the detection method used and the blood group.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Investigation of Discrepant ABO Blood Grouping Results from an Autoanalyzer
Young Ae Lim, Seo-Jin Park, Hyun Soo Cho
Ann Lab Med. 2022;42(6):650-658. doi: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.6.650.Application of Geometric Mean Criteria for Anti-Blood Group Antibody Proficiency Testing in the Korean External Quality Assurance Program
John Jeongseok Yang, Hee-Jeong Youk, Yousun Chung, Hyungsuk Kim, Sang-Hyun Hwang, Heung-Bum Oh, Dae-Hyun Ko
Lab Med Qual Assur. 2022;44(1):48-54. doi: 10.15263/jlmqa.2022.44.1.48.
Reference
-
1. Tobian AA, Shirey RS, King KE. ABO antibody titer monitoring for incompatible renal transplantation. Transfusion. 2011; 51:454–457. PMID: 21388388.
Article2. Kumlien G, Wilpert J, Säfwenberg J, Tydén G. Comparing the tube and gel techniques for ABO antibody titration, as performed in three European centers. Transplantation. 2007; 84(12 Suppl):S17–S19. PMID: 18162980.
Article3. Kobayashi T, Saito K. A series of surveys on assay for anti-A/B antibody by Japanese ABO-incompatible Transplantation Committee. Xenotransplantation. 2006; 13:136–140. PMID: 16623808.
Article4. Roback JD, editor. Technical Manual. 17th ed. Bethesda: American Association of Blood Banks;2011. p. 369.5. Stussi G, Huggel K, Lutz HU, Schanz U, Rieben R, Seebach JD. Isotype-specific detection of ABO blood group antibodies using a novel flow cytometric method. Br J Haematol. 2005; 130:954–963. PMID: 16156865.
Article6. Yung GP, Valli PV, Starke A, Mueller RJ, Fehr T, Cesar-Ozpamir M, et al. Flow cytometric measurement of ABO antibodies in ABO-incompatible living donor kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 2007; 84(12 Suppl):S20–S23. PMID: 18162982.
Article7. Tanabe K. Interinstitutional variation in the measurement of anti-A/B antibodies: the Japanese ABO-incompatible Transplantation Committee survey. Transplantation. 2007; 84(12 Suppl):S13–S16. PMID: 18162979.
Article8. Won DI, Kim BC. Optimized flow cytometry to measure anti-ABO immunoglobulin G. Lab Medicine. 2012; 43:281–290.
Article9. Roback JD, editor. Technical Manual. 17th ed. Bethesda: American Association of Blood Banks;2011. p. 907.10. Berneman ZN, van Bockstaele DR, Uyttenbroeck WM, Van Zaelen C, Cole-Dergent J, Muylle L, et al. Flow-cytometric analysis of erythrocytic blood group A antigen density profile. Vox Sang. 1991; 61:265–274. PMID: 1776244.
Article11. Won DI. Comparison method of reactivity of anti-human immunoglobulin reagents for flow cytometry. Korean J Lab Med. 2003; 23:214–219.12. Cho CH, Kim HN, Yun SG, Choi GR, Choi JY, Kim JS, et al. Evaluation of ABO antibody titration using tube and column agglutination techniques. Lab Med Online. 2011; 1:57–63.
Article13. Shirey RS, Cai W, Montgomery RA, Chhibber V, Ness PM, King KE. Streamlining ABO antibody titrations for monitoring ABO-incompatible kidney transplants. Transfusion. 2010; 50:631–634. PMID: 19906036.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Column Agglutination Technique and Tube Test for ABO Antibody Titration and Crossmatching
- Comparison of Total and IgG ABO Antibody Titers in Healthy Individuals by Using Tube and Column Agglutination Techniques
- Evaluation of the Automated QWALYS-3 System for ABO and RhD Grouping and Unexpected Antibody Screening
- Evaluation of the Automated Blood Bank Systems Galileo NEO and QWALYS-3 for ABO-RhD Typing and Antibody Screening
- Changes in SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers 6 months after the booster dose of BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine among health care workers