Korean J Gastroenterol.
2014 Jul;64(1):45-48. 10.4166/kjg.2014.64.1.45.
Colonic Abscess Induced by India Ink Tattooing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea. kimyeonsoo@hallym.or.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1791894
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2014.64.1.45
Abstract
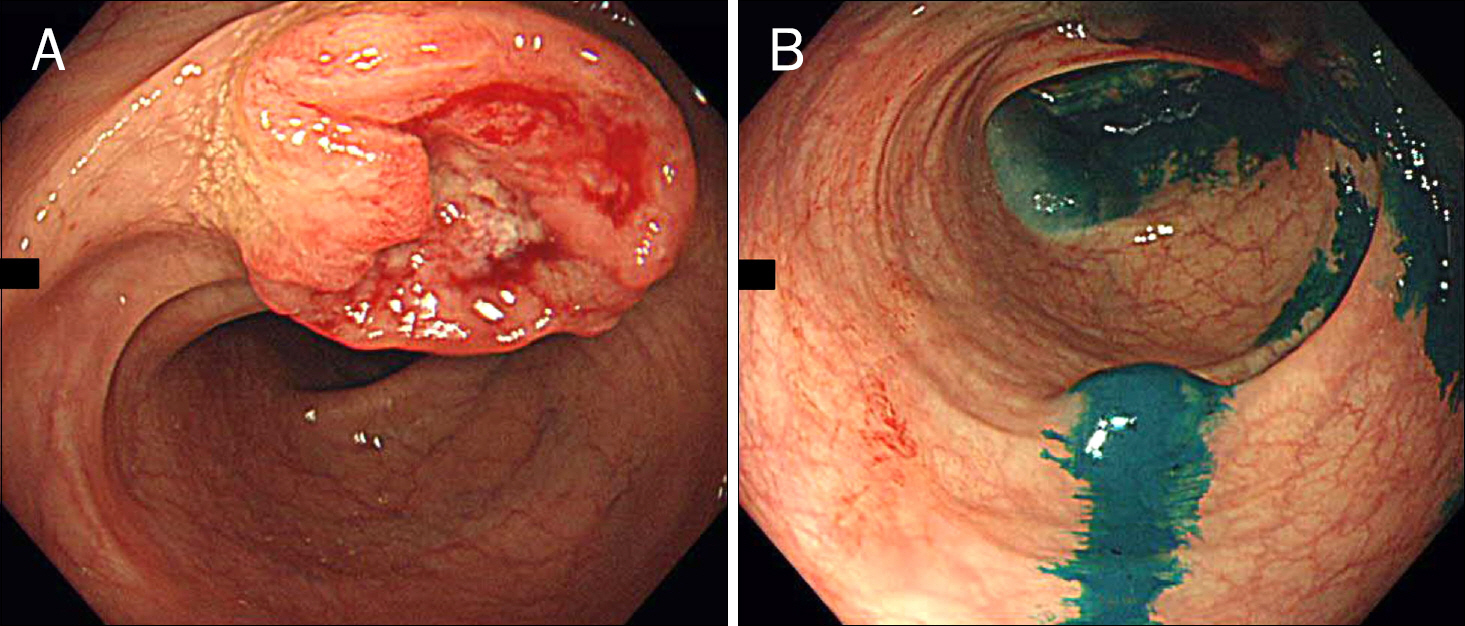
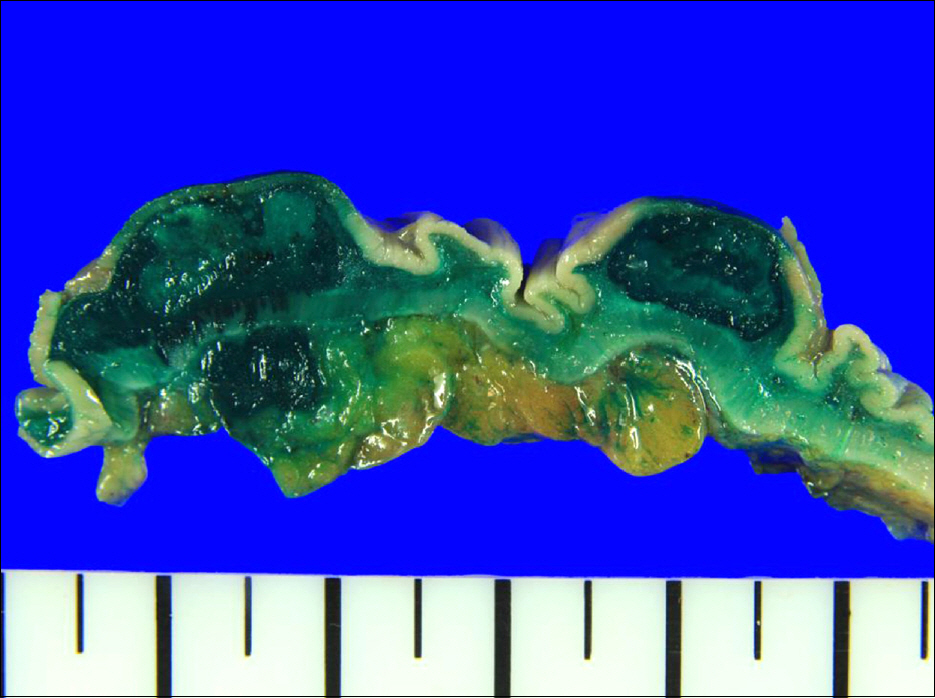
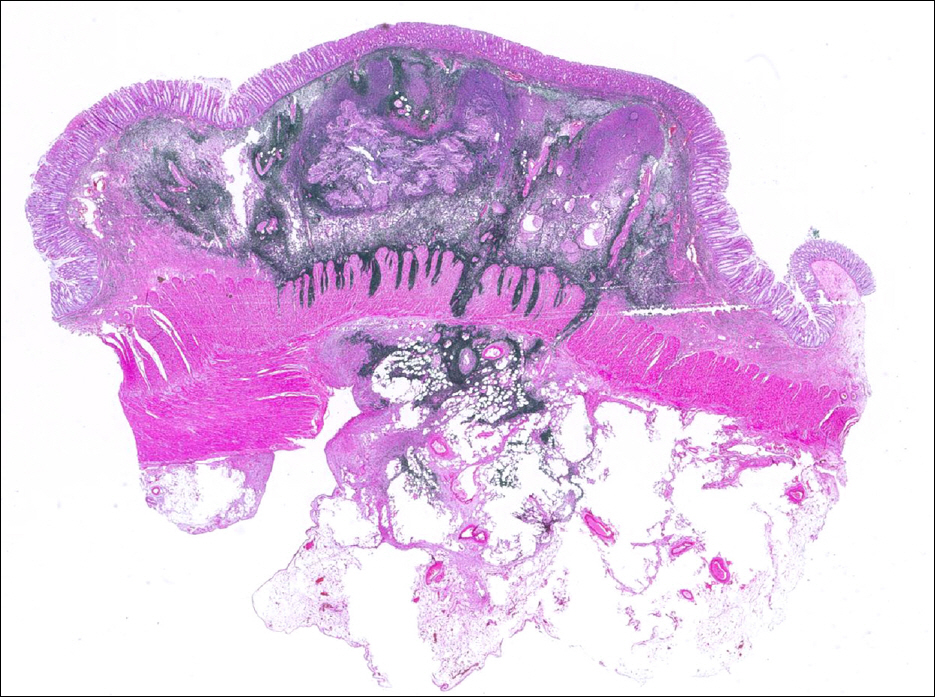
- Endoscopic tattooing with India ink is generally regarded as a safe procedure that enables ready identification of endoluminal cancer from the serosal surface. However, significant complications have been reported, including local inflammatory pseudotumor formation, peritonitis, rectus muscle abscess, small bowel infarction, and phlegmonous gastritis. Although the mechanism of complication is not completely understood, it may be related to the chemical compounds contained in the ink solution and enteric or extraenteric bacterial inoculation by injection needle or the ink itself. Authors encountered a case of a 60-year-old man with a resectable sigmoid colon cancer which was tattooed with India ink for subsequent localization in the intraoperative setting. During the laparoscopic operation, the proximal and distal margin of the lesion appeared edematous with bluish color. The distal resection margin was extended approximately 5 cm more than expected because of long extent of edematous mucosa. Histologic examination of the edematous tattooing area revealed an ink abscess spreading laterally above the muscularis propria. Although tattooing is widely used and relatively safe, the presented case indicates the risk of infection or inflammation by tattooing.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Yeung JM, Maxwell-Armstrong C, Acheson AG. Colonic tattooing in laparoscopic surgery – making the mark? Colorectal Dis. 2009; 11:527–530.
Article2. Frager DH, Frager JD, Wolf EL, Beneventano TC. Problems in the colonoscopic localization of tumors: continued value of the barium enema. Gastrointest Radiol. 1987; 12:343–346.
Article3. Montorsi M, Opocher E, Santambrogio R, et al. Original technique for small colorectal tumor localization during laparoscopic surgery. Dis Colon Rectum. 1999; 42:819–822.
Article4. Ohdaira T, Konishi F, Nagai H, et al. Intraoperative localization of colorectal tumors in the early stages using a marking clip de-tector system. Dis Colon Rectum. 1999; 42:1353–1355.
Article5. Sauntry JP, Knudtson KP. A technique for marking the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract after polypectomy. Cancer. 1958; 11:607–610.
Article6. Ponskyx JL, King JF. Endoscopic marking of colonic lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 1975; 22:42–43.7. Fu KI, Fujii T, Kato S, et al. A new endoscopic tattooing technique for identifying the location of colonic lesions during laparoscopic surgery: a comparison with the conventional technique. Endoscopy. 2001; 33:687–691.
Article8. Miyoshi N, Ohue M, Noura S, et al. Surgical usefulness of in-docyanine green as an alternative to India ink for endoscopic marking. Surg Endosc. 2009; 23:347–351.
Article9. Alba LM, Pandya PK, Clarkston WK. Rectus muscle abscess associated with endoscopic tattooing of the colon with India ink. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 52:557–558.
Article10. Park SI, Genta RS, Romeo DP, Weesner RE. Colonic abscess and focal peritonitis secondary to India ink tattooing of the colon. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991; 37:68–71.
Article11. Singh S, Arif A, Fox C, Basnyat P. Complication after preoperative India ink tattooing in a colonic lesion. Dig Surg. 2006; 23:303.
Article12. Coman E, Brandt LJ, Brenner S, Frank M, Sablay B, Bennett B. Fat necrosis and inflammatory pseudotumor due to endoscopic tattooing of the colon with India ink. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991; 37:65–68.
Article13. Nizam R, Siddiqi N, Landas SK, Kaplan DS, Holtzapple PG. Colonic tattooing with India ink: benefits, risks, and alternatives. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996; 91:1804–1808.14. Lightdale CJ. India ink colonic tattoo: blots on the record. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991; 37:99–100.
Article15. Kang HJ, Lee BI, Kim BW, et al. Potential cancer cell inoculation of tattoo site through use of a contaminated needle. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:884–886.
Article16. Sawaki A, Nakamura T, Suzuki T, et al. A two-step method for marking polypectomy sites in the colon and rectum. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 57:735–737.
Article17. Park JW, Sohn DK, Hong CW, et al. The usefulness of preoperative colonoscopic tattooing using a saline test injection method with prepackaged sterile India ink for localization in laparoscopic colorectal surgery. Surg Endosc. 2008; 22:501–505.
Article18. Yamada A, Nobusawa E, Cao MS, et al. Epitope changes on the haemagglutinin molecule of recently isolated H1N1 influenza viruses. J Gen Virol. 1991; 72:97–102.
Article19. Shatz BA, Weinstock LB, Swanson PE, Thyssen EP. Longterm safety of India ink tattoos in the colon. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997; 45:153–156.
Article20. Fennerty MB, Sampliner RE, Hixson LJ, Garewal HS. Effectiveness of India ink as a long-term colonic mucosal marker. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992; 87:79–81.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Corneal Tattooing to Mask the Opacification after Amniotic Membrane Grafting for Corneal Ulcer
- Small Efforts Can Prevent Big Mistakes: Preoperative Colonoscopic Tattooing Using Indocyanine Green
- Preoperative Localization of Early Colorectal Cancer or a Malignant Polyp by Using the Patient's Own Blood
- Preoperative Colonoscopic Tattooing Using a Direct Injection Method with Indocyanine Green for Localization of Colorectal Tumors: An Efficacy and Safety Comparison Study
- Endoscopic India Ink Marking of the Colonic Mucosa