J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Jun;23(3):540-543. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.3.540.
Brunnera's Gland Hyperplasia: Treatment of Severe Diffuse Nodular Hyperplasia Mimicking a Malignancy on Pancreatic-Duodenal Area
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. 20040544@eulji.ac.kr
- KMID: 1786899
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.3.540
Abstract
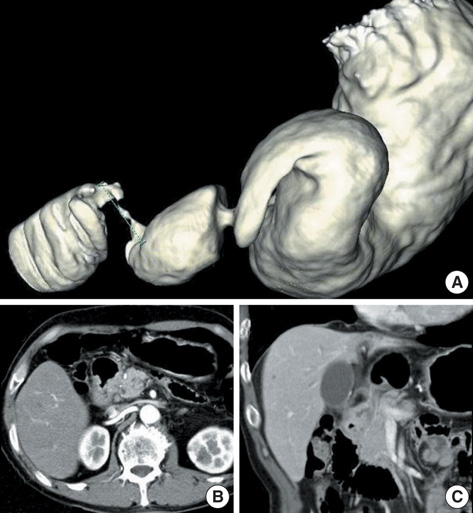
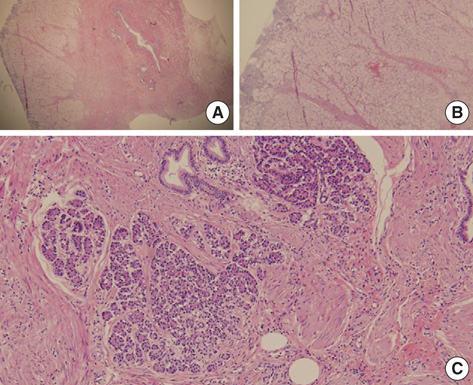
- Brunnera's gland hyperplasia is a benign tumor of the duodenum and it is rarely associated with clinical symptoms. We report on a 64-yr-old man with Brunnera's gland hyperplasia who had undergone a duodenocephalo-pancreatectomy. The reason is that he presented upper gastrointestinal obstructive symptoms and the esophagogastroduodenoscopic finding revealed the lesion to be an infiltrating type mass on the second portion of the duodenum with luminal narrowing. An abdominal computed tomography showed a 2.5 cm-sized mass in the duodenal second portion with a suspicious pancreatic invasion and 7 mm-sized lymph node around the duodenum. Duodenocephalopancreatectomy was successfully performed. Histological examination revealed a Brunnera's gland hyperplasia. The final diagnosis was the coexistence of Brunnera's gland hyperplasia and pancreatic heterotopia with a pancreatic head invasion. The literature on Brunnera's gland hyperplasia is reviewed.
MeSH Terms
-
Brunner Glands/*pathology/radiography
*Choristoma
Diagnosis, Differential
Duodenal Neoplasms/*pathology/radiography/surgery
Duodenum/pathology/radiography
Endoscopy, Gastrointestinal
Humans
Hyperplasia
Male
Middle Aged
Pancreatic Diseases/*pathology/radiography
Pancreaticoduodenectomy
Severity of Illness Index
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tan YM, Wong WK. Giant Brunneroma as an unusual cause of upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage: report of a case. Surg Today. 2002. 32:910–912.
Article2. Peetz ME, Moseley HS. Brunner's gland hyperplasia. Am Surg. 1989. 55:474–477.3. de Silva S, Chandrasoma P. Giant duodenal hamartoma consisting mainly of Brunner's glands. Am J Surg. 1977. 133:240–243.
Article4. Bastlein C, Decking R, Voeth C, Ottenjann R. Giant Brunneroma of the duodenum. Endoscopy. 1988. 20:154–155.
Article5. Franzin G, Musola R, Ghidini O, Manfrini C, Fratton A. Nodular hyperplasia of Brunner's glands. Gastrointest Endosc. 1985. 31:374–378.
Article6. Perez A, Saltzman JR, Carr-Locke DL, Brooks DC, Osteen RT, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW, Whang EE. Benign nonampullary duodenal neoplasms. J Gastrointest Surg. 2003. 7:536–541.7. Iusco D, Roncoroni L, Violi V, Donadei E, Sarli L. Brunner's gland hamartoma: 'over-treatment' of a voluminous mass simulating a malignancy of the pancreatic-duodenal area. JOP. 2005. 6:348–353.8. Walden DT, Marcon NE. Endoscopic injection and polypectomy for bleeding Brunner's gland hamartoma: case report and expanded literature review. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998. 47:403–407.
Article9. Nakanishi T, Takeuchi T, Hara K, Sugimoto A. A great Brunner's gland adenoma of the duodenal bulb. Dig Dis Sci. 1984. 29:81–85.
Article10. Deren MD, Henry PD. Adenoma of Brunner's glands. Ann Intern Med. 1956. 44:180–187.
Article11. Buchanan EB. Nodular hyperplasia of Brunner's glands of the duodenum. Am J Surg. 1961. 101:253–257.
Article12. Grossman ML. The glands of Brunner. Physiol Rev. 1958. 38:675–690.
Article13. Gourtsoyiannis NC, Bays D, Papaioannou N, Theotokas J, Barouxis G, Karabelas T. Benign tumors of the small intestine: preoperative evaluation with a barium infusion technique. Eur J Radiol. 1993. 16:115–125.
Article14. Cwikiel W, Andren-Sandberg A. Diagnostic difficulties with duodenal malignancies revisited: a new strategy. Gastrointest Radiol. 1991. 16:301–304.
Article15. Adell-Carceller R, Salvador-Sanchis JL, Navarro-Navarro J, Segarra-Soria M, Garcia-Calvo R, Gibert-Gerez J, Colom-Costa J. Laparoscopically treated duodenal hamartoma of Brunner's glands. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1997. 7:298–300.16. Bae SW, Lee DK, Baik SG, Kwon SO, Cho MY. A Brunner's Gland Adenoma Removed by Endoscopic Polypectomy. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 1993. 13:83–86.17. De Castella H. Brunner's gland adenoma. An unusual cause of intestinal bleeding. Br J Surg. 1966. 53:153–156.18. Akino K, Kondo Y, Ueno A, Yamazaki K, Hosokawa M, Shimoji H, Adachi T, Honda S, Ichiyanagi S, Akahonai Y, Fujisawa Y, Takahashi H, Arimura Y, Endo T, Imai K. Carcinoma of duodenum arising from Brunner's gland. J Gastroenterol. 2002. 37:293–296.
Article19. Skellenger ME, Kinner BM, Jordan PH Jr. Brunner's gland hamartomas can mimic carcinoma of the head of the pancreas. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1983. 156:774–776.20. Lightwood R, Reber HA, Way LW. The risk and accuracy of pancreatic biopsy. Am J Surg. 1976. 132:189–194.
Article21. Ingram DM, Sheiner HJ, Shilkin KB. Operative biopsy of the pancreas using the Trucut needle. Aust N Z J Surg. 1978. 48:203–206.
Article22. Tweedle DE. Peroperative transduodenal biopsy of the pancreas. Gut. 1979. 20:992–996.
Article23. Spjut HJ, Ramos AJ. An evaluation of biopsy-frozen section of the ampullary region and pancreas: a report of 68 consecutive patients. Ann Surg. 1957. 146:923–930.24. Isaacson R, Weiland LH, McIlrath DC. Biopsy of the pancreas. Arch Surg. 1974. 109:227–230.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sporadic Non-ampullary Duodenal Adenoma Overriding the Cystic Dilatation of Brunner's Gland Hyperplasia
- A Case of Brunner's Gland Hyperplasia of the Duodenal Second Portion with Annular Stricture Causing an Induced Obstruction
- Focal Nodular Hyperplasia
- Malignant Transformation of Nodular Hyperplasia in the Thyroid: A Case Report
- Focal Nodular Hyperplasia of the Liver