Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) Syndrome Induced by Celecoxib and Anti-tuberculosis Drugs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. piolee2000@yahoo.co.kr
- 2Department of Neurology, Pusan National University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Pusan National University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1786894
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.3.521
Abstract
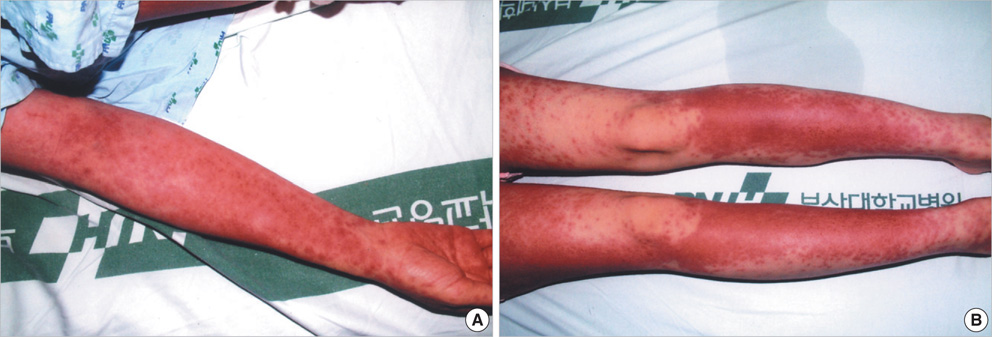
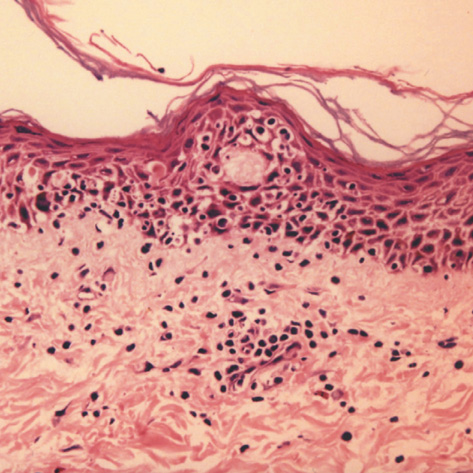
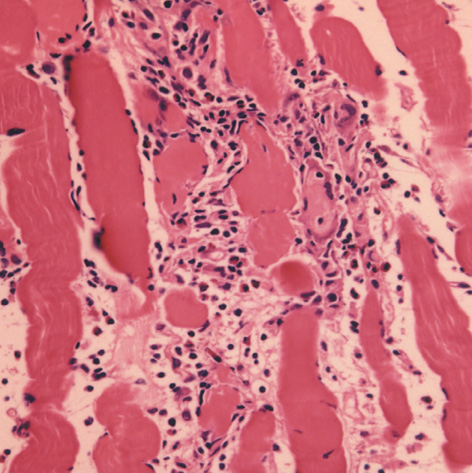
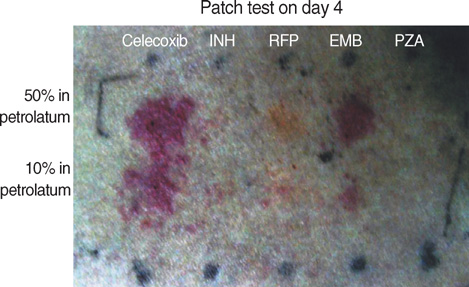
- Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) syndrome reflects a serious hypersensitivity reaction to drugs, characterized by skin rash, fever, lymph node enlargement, and internal organ involvement. So far, numerous drugs such as sulfonamides, phenobarbital, sulfasalazine, carbamazepine, and phenytoin have been reported to cause the DRESS syndrome. We report a case in a 29-yr-old female patient who had been on celecoxib and anti-tuberculosis drugs for one month to treat knee joint pain and pulmonary tuberculosis. Our patient's clinical manifestations included fever, lymphadenopathy, rash, hypereosinophilia, and visceral involvement (hepatitis and pneumonitis). During the corticosteroid administration for DRESS syndrome, swallowing difficulty with profound muscle weakness had developed. Our patient was diagnosed as DRESS syndrome with eosinophilic polymyositis by a histopathologic study. After complete resolution of all symptoms, patch tests were positive for both celecoxib and ethambutol. Although further investigations might be needed to confirm the causality, celecoxib and ethambutol can be added to the list of drugs as having the possibility of DRESS syndrome.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal/adverse effects
Antitubercular Agents/adverse effects
Arthritis/complications/*drug therapy
Drug Eruptions/*etiology/pathology
Eosinophilia/*chemically induced/pathology
Ethambutol/*adverse effects
Female
Humans
Myositis/chemically induced/pathology
Pyrazoles/*adverse effects
Sulfonamides/*adverse effects
Syndrome
Tuberculosis, Pulmonary/complications/*drug therapy
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) Syndrome Induced by Ethambutol and Rifampin
Eul Sik Jung, Byoungho Choi, Hyun Seok Choi, Byung Hoon Kim, Minsu Ha, Dongsu Shin, Jin Sun Park, Jong Rok Lee, Yiel-Hae Seo, Yoon Soo Park
Infect Chemother. 2012;44(3):197-200. doi: 10.3947/ic.2012.44.3.197.Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) Syndrome Induced by Ethambutol and Rifampin
Eul Sik Jung, Byoungho Choi, Hyun Seok Choi, Byung Hoon Kim, Minsu Ha, Dongsu Shin, Jin Sun Park, Jong Rok Lee, Yiel-Hae Seo, Yoon Soo Park
Infect Chemother. 2012;44(3):197-200. doi: 10.3947/ic.2012.44.3.197.Prevalence and Clinical Features of Drug Reactions With Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms Syndrome Caused by Antituberculosis Drugs: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Ho Yeon Jung, Sunmin Park, Beomsu Shin, Ji-Ho Lee, Seok Jeong Lee, Myoung Kyu Lee, Won-Yeon Lee, Suk Joong Yong, Sang-Ha Kim
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019;11(1):90-103. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.1.90.Concomitant Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptom Syndrome from Ethambutol and Autoimmune Hepatitis from Isoniazid
Joon Hyuk Choi, Nae-Yun Heo, Seung Ha Park, Chan Sun Park, Kyeong Min Jo, Woo Gyeong Kim, Kyung Han Nam
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2016;67(5):267-271. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2016.67.5.267.A Case of Fatal DRESS Syndrome Caused by Dapsone in a Patient with Behcet's Syndrome
Chang Hoon Lee, Sung Jo Jang, Seong Rheol Oh, Hyun Jung Kim, Myeung Su Lee
J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2009;16(3):253-257. doi: 10.4078/jkra.2009.16.3.253.
Reference
-
1. Bocquet H, Bagot M, Roujeau JC. Drug-induced pseudolymphoma and drug hypersensitivity syndrome (Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms: DRESS). Semin Cutan Med Surg. 1996. 15:250–257.
Article2. Sullivan JR, Shear NH. The drug hypersensitivity syndrome: what is the pathogenesis. Arch Dermatol. 2001. 137:357–364.3. Marques S, Milpied B, Foulc P, Barbarot S, Cassagnau E, Stalder JF. Severe cutaneous drug reactions to celecoxib (Celebrex). Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2003. 130:1051–1055.4. La Grenade L, Lee L, Weaver J, Bonnel R, Karwoski C, Governale L, Brinker A. Comparison of reporting of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in association with selective COX-2 inhibitors. Drug Saf. 2005. 28:917–924.
Article5. Knowles S, Shapiro L, Shear NH. Should celecoxib be contraindicated in patients who are allergic to sulfonamides? Revisiting the meaning of sulfa allergy. Drug Saf. 2001. 24:239–247.6. Strauss RM, Green ST, Gawkrodger DJ. Rifampicin allergy confirmed by an intradermal test, but with a negative patch test. Contact Dermatitis. 2001. 45:108.
Article7. Pitt FW. Hook EW, Mandell GL, Gwaltney JM, editors. Tuberculosis, prevention and therapy. Current concepts of infectious disease. 1977. New York: John Wiley & Sons;181–194.8. Holdiness MR. Adverse cutaneous reactions to antituberculosis drugs. Int J Dermatol. 1985. 24:280–285.
Article9. Pegram PS Jr, Mountz JD, O'Bar PR. Ethambutol-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis. Arch Intern Med. 1981. 141:1677–1678.
Article10. Kaufman LD, Kephart GM, Seidman RJ, Buhner D, Qvarfordt I, Nassberger L, Gleich GJ. The spectrum of eosinophilic myositis. Clinical and immunopathogenic studies of three patients, and review of the literature. Arthritis Rheum. 1993. 36:1014–1024.11. Meng Q, Ying S, Corrigan CJ, Wakelin M, Assoufi B, Mogbel R, Kay AB. Effects of rapamycin, cyclosporine A, and dexamethasone on interleukin 5-induced eosinophil degranulation and prolonged survival. Allergy. 1997. 52:1095–1101.12. Ahn CM, Moon JH, Moon JG, Lee KM, Lee JH, Hong CS, Park JW. A case of cephalosporin-induced DRESS (Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms) syndrome with acute renal failure. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005. 25:69–72.13. Valencak J, Ortiz-Urda S, Heere-Ress E, Kunstfeld R, Base W. Carbamazepine induced DRESS syndrome with recurrent fever and exanthema. Int J Dermatol. 2004. 43:51–54.14. Kano Y, Inaoka M, Sakuma K, Shiohara T. Virus reactivation and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) therapy of drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Toxicology. 2005. 209:165–167.
Article15. Tas S, Simonart T. Management of drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS syndrome): an update. Dermatology. 2003. 206:353–356.
Article16. Kim CW, Choi GS, Yun CH, Kim DI. Drug hypersensitivity to previously tolerated phenytoin by carbamazepine-induced DRESS syndrome. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. 21:768–772.
Article17. Lachapelle JM, Maibach HI. Patch testing. Prick testing. A practical guide. 2003. Berlin: Springer.18. Arellano F, Sacristan JA. Allopurinol hypersensitivity syndrome: a review. Ann Pharmacother. 1993. 27:337–343.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rasagiline Induced Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms Syndrome: A Case Report
- Drug Rash With Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms Syndrome Induced by Chloral Hydrate in Early Childhood
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) Syndrome Induced by Ethambutol and Rifampin
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptom Syndrome Due to Everolimus: A Case Report
- A Case of the Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptom (DRESS) Following Isoniazid Treatment