J Korean Med Sci.
2004 Feb;19(1):130-133. 10.3346/jkms.2004.19.1.130.
A Case of Hodgkin's Lymphoma Associated with Sensory Neuropathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. kkkim@www.amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Diagnostic Pathology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1785707
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2004.19.1.130
Abstract
- Peripheral neuropathies occur in lymphoma patients. Causes of neuropathy include chemotherapy, opportunistic infections, and the lymphoma itself. We report a patient with lymphoma whose chief complaint was a sensory loss in the hands and feet. Electrophysiologic studies and sural nerve biopsy showed sensory polyneuropathies. We hypothesize that this neuropathy is associated with lymphoma-related ganglionopathy, and among the possible causes, we suspect that a systemic cause such as a paraneoplastic syndrome is the most likely pathogenic etiology. However, further follow-up will be necessary to see whether sensory symptoms change with lymphoma treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
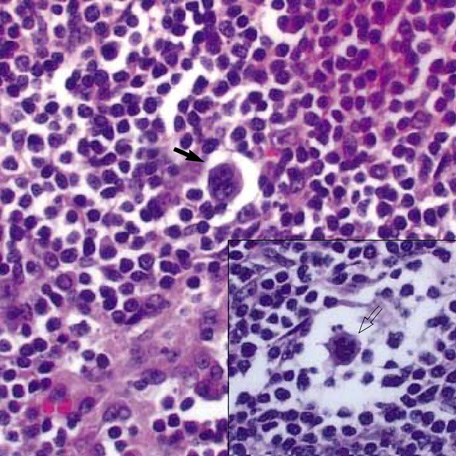
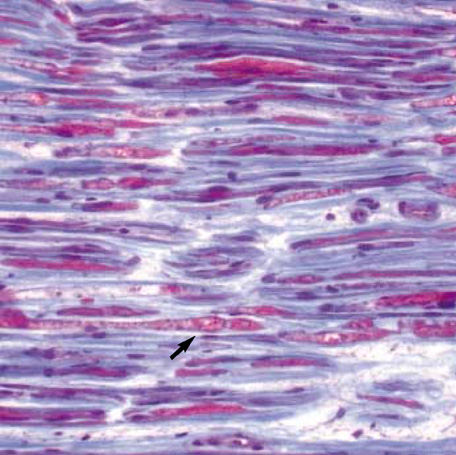
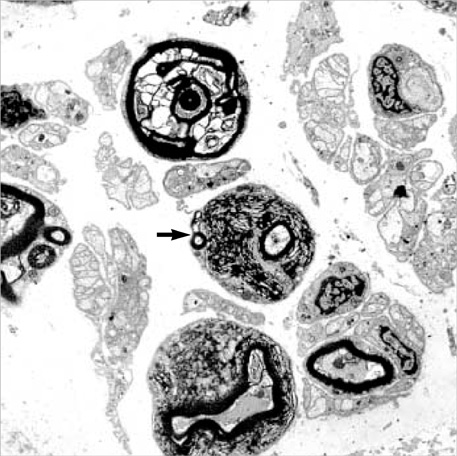
Figure
Reference
-
1. Vital C, Vital A, Julien J, Rivel J, deMascarel A, Vergier B, Henry P, Barat M, Reiffer J, Broustet A. Peripheral neuropathies and lymphoma without monoclonal gammopathy: A new classification. J Neurol. 1990. 237:177–185.
Article2. Sterman AB, Schaumburg HH, Asbury AK. The acute sensory neuronopathy syndrome: a distinct clinical entity. Ann Neurol. 1980. 7:354–358.
Article3. Dumitru D, Amato AA, Zawarts MJ. Electrodiagnostic medicine. 2002. 2nd. Philadelphia: Hanley & Belfus;992–993.4. Gherardi RK, Chretien F, Delfau-Larue MH, Authier FJ, Moulignier A, Roulland-Dussoix D, Belec L. Neuropathy in diffuse infiltrative lymphocytosis syndrome. An HIV neuropathy, not a lymphoma. Neurology. 1998. 50:1041–1044.
Article5. Chen YT, Godwin TA, Mouradian JA. Immunohistochemistry and gene rearrangement studies in the diagnosis of malignant lymphomas: A comparison of 152 cases. Hum Pathol. 1991. 22:1249–1257.
Article6. McLeod JG. Dyck PJ, Thomas PK, Griffin JW, editors. Peripheral neuropathy associated with lymphomas, leukemias, and polycythemia vera. Peripheral neuropathy. 1993. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders;1591–1598.7. Walsh JC. Neuropathy associated with lymphoma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971. 34:42–50.
Article8. Kim HW, Park SY. A case of angiocentric T cell lymphoma accompanied with multiple erythematous nodules, subcutaneous mass on the right face and peripheral polyneuropathy. Korean J Hematol. 1997. 32:140–145.9. Kim CH, Paik KW. A case report of infiltrative polyneuropathy associated with lymphoma. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2001. 25:724–728.10. Schold SC, Cho ES, Somasundaram M, Posner JB. Subacute motor neuronopathy: A remote effect of lymphoma. Ann Neurol. 1979. 5:271–287.
Article11. Thomas FP, Vallejos U, Foitl DR, Miller JR, Barrett R, Fetell MR, Knowles DM, Latov N, Hays AP. B cell small lymphocytic lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia with peripheral neuropathy: two cases with neuropathological findings and lymphocyte marker analysis. Acta Neuropathol. 1990. 80:198–203.
Article12. Plante-Bordeneuve V, Baudrimont M, Gorin NC, Gherardi RK. Subacute sensory neuropathy associated with Hodgkin's disease. J Neurol Sci. 1994. 121:155–158.
Article13. Lee SM, Harper P, Luthert P, Hughes RAC. Primary CNS lymphoma in association with IgM kappa paraproteinaemia and peripheral polyneuropathy: A case report. Eur Neurol. 1995. 35:237–239.
Article14. Gemignani F, Marchesi G, Di Giovanni G, Salih S, Quaini F, Nobile-Orazio E. Low-grade non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma presenting as sensory neuropathy. Eur Neurol. 1996. 36:138–141.15. McLeod JG. Dyck PJ, Thomas PK, Griffin JW, editors. Paraneoplastic neuropathies. Peripheral neuropathy. 1993. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders;1583–1590.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Autoantibody-Mediated Sensory Polyneuropathy Associated with Indolent B-Cell Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma: A Report of Two Cases
- Hereditary Sensory Neuropathy Type 2 (Congenital sensory neuropathy): A case report
- Composite follicular lymphoma and classic Hodgkin lymphoma
- Pathologic Characteristics and Differential Diagnosis of Hodgkin Lymphoma
- A Case of Primary Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma of the Ovary