Clin Orthop Surg.
2014 Jun;6(2):153-158. 10.4055/cios.2014.6.2.153.
Accurate Leg Length Measurement in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Comparison of Computer Navigation and a Simple Manual Measurement Device
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kanazawa University Graduate School of Medical Science, Kanazawa, Japan. kogawawagao@yahoo.co.jp
- KMID: 1784660
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.2.153
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Several studies have shown that better placement of the acetabular cup and femoral stem can be achieved in total hip arthroplasty (THA) by using the computer navigation system rather than the free-hand alignment methods. However, there have been no comparisons of the relevant clinical advantages in using the computer navigation as opposed to the manual intraoperative measurement devices. The purpose of this study is to determine whether the use of computer navigation can improve postoperative leg length discrepancy (LLD) compared to the use of the measurement device.
METHODS
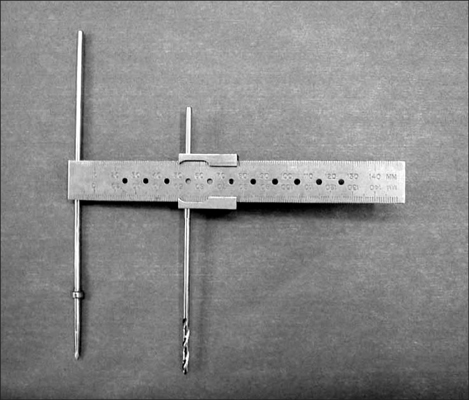
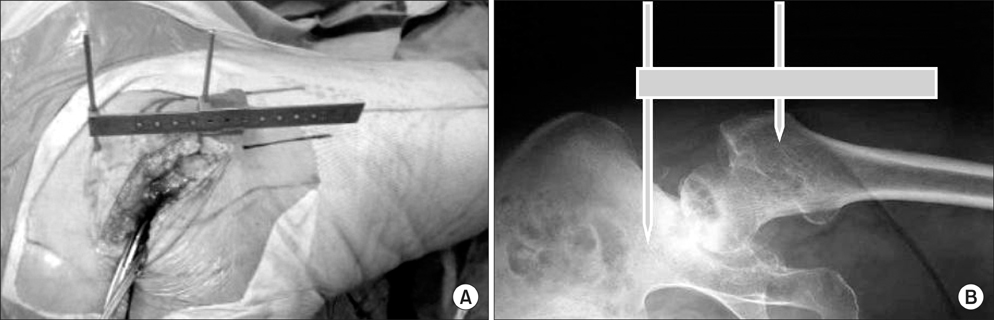
We performed a retrospective study comparing 30 computer-assisted THAs with 40 THAs performed using a simple manual measurement device.
RESULTS
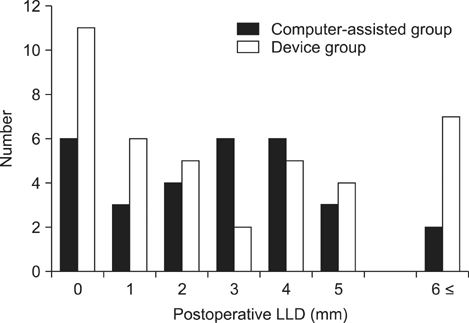
The postoperative LLD was 3.0 mm (range, 0 to 8 mm) in the computer-assisted group and 2.9 mm (range, 0 to 10 mm) in the device group. Statistically significant difference was not seen between the two groups.
CONCLUSIONS
The results showed good equalization of the leg lengths using both computed tomography-based navigation and the simple manual measurement device.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. McGee HM, Scott JH. A simple method of obtaining equal leg length in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985; (194):269–270.2. Woolson ST, Harris WH. A method of intraoperative limb length measurement in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985; (194):207–210.3. Ranawat CS, Rao RR, Rodriguez JA, Bhende HS. Correction of limb-length inequality during total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2001; 16(6):715–720.4. Shiramizu K, Naito M, Shitama T, Nakamura Y, Shitama H. L-shaped caliper for limb length measurement during total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86(7):966–969.5. Maeda T, Kabata T, Ebara H. A gauge for limb length measurement during total hip arthroplasty. J Joint Surg. 2006; 25:452–455.6. Hofmann AA, Bolognesi M, Lahav A, Kurtin S. Minimizing leg-length inequality in total hip arthroplasty: use of preoperative templating and an intraoperative x-ray. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2008; 37(1):18–23.7. White TO, Dougall TW. Arthroplasty of the hip: leg length is not important. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84(3):335–338.8. Konyves A, Bannister GC. The importance of leg length discrepancy after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87(2):155–157.9. Jasty M, Webster W, Harris W. Management of limb length inequality during total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996; (333):165–171.10. Sugano N, Nishii T, Miki H, Yoshikawa H, Sato Y, Tamura S. Mid-term results of cementless total hip replacement using a ceramic-on-ceramic bearing with and without computer navigation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007; 89(4):455–460.11. Ybinger T, Kumpan W, Hoffart HE, Muschalik B, Bullmann W, Zweymuller K. Accuracy of navigation-assisted acetabular component positioning studied by computed tomography measurements: methods and results. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22(6):812–817.12. Langlotz U, Grutzner PA, Bernsmann K, et al. Accuracy considerations in navigated cup placement for total hip arthroplasty. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2007; 221(7):739–753.13. Manzotti A, Cerveri P, De Momi E, Pullen C, Confalonieri N. Does computer-assisted surgery benefit leg length restoration in total hip replacement? Navigation versus conventional freehand. Int Orthop. 2011; 35(1):19–24.14. Schmerwitz U. Total hip arthroplasty: first experiences with pinless THA software to determine leg length and offset. Orthopedics. 2007; 30:10 Suppl. S124–S126.15. Murphy SB, Ecker TM. Evaluation of a new leg length measurement algorithm in hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 463:85–89.16. Edeen J, Sharkey PF, Alexander AH. Clinical significance of leg-length inequality after total hip arthroplasty. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 1995; 24(4):347–351.17. Bose WJ. Accurate limb-length equalization during total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2000; 23(5):433–436.18. Sarin VK, Pratt WR, Bradley GW. Accurate femur repositioning is critical during intraoperative total hip arthroplasty length and offset assessment. J Arthroplasty. 2005; 20(7):887–891.19. Haaker RG, Tiedjen K, Ottersbach A, Rubenthaler F, Stockheim M, Stiehl JB. Comparison of conventional versus computer-navigated acetabular component insertion. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22(2):151–159.20. Kalteis T, Handel M, Bathis H, Perlick L, Tingart M, Grifka J. Imageless navigation for insertion of the acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty: is it as accurate as CT-based navigation? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006; 88(2):163–167.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Computer-Assisted Total Hip Arthroplasty
- Fixing Leg Length Discrepancies after Total Hip Arthroplasty
- Leg Length Discrepancy after Total Hip Arthroplasty
- Reliability and Validity of the Femorotibial Mechanical Axis Angle in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: Navigation versus Weight Bearing or Supine Whole Leg Radiographs
- The Effect of Sagittal Knee Deformity on Preoperative Measurement of Coronal Mechanical Alignment during Total Knee Arthroplasty