Korean J Radiol.
2011 Aug;12(4):499-503. 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.4.499.
Reversal in the Diameter of the Superior Ophthalmic Vein after an Epidural Blood Patch in a Case of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Shin Kong Wu Ho-Su Memorial Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan. yuhfeng.tsai@msa.hinet.net
- 2College of Medicine, Fu-Jen Catholic University, New Taipei City, Taiwan.
- 3Neuroimaging Center, Department of Health Management, Shin Kong Wu Ho-Su Memorial Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan.
- KMID: 1783217
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2011.12.4.499
Abstract
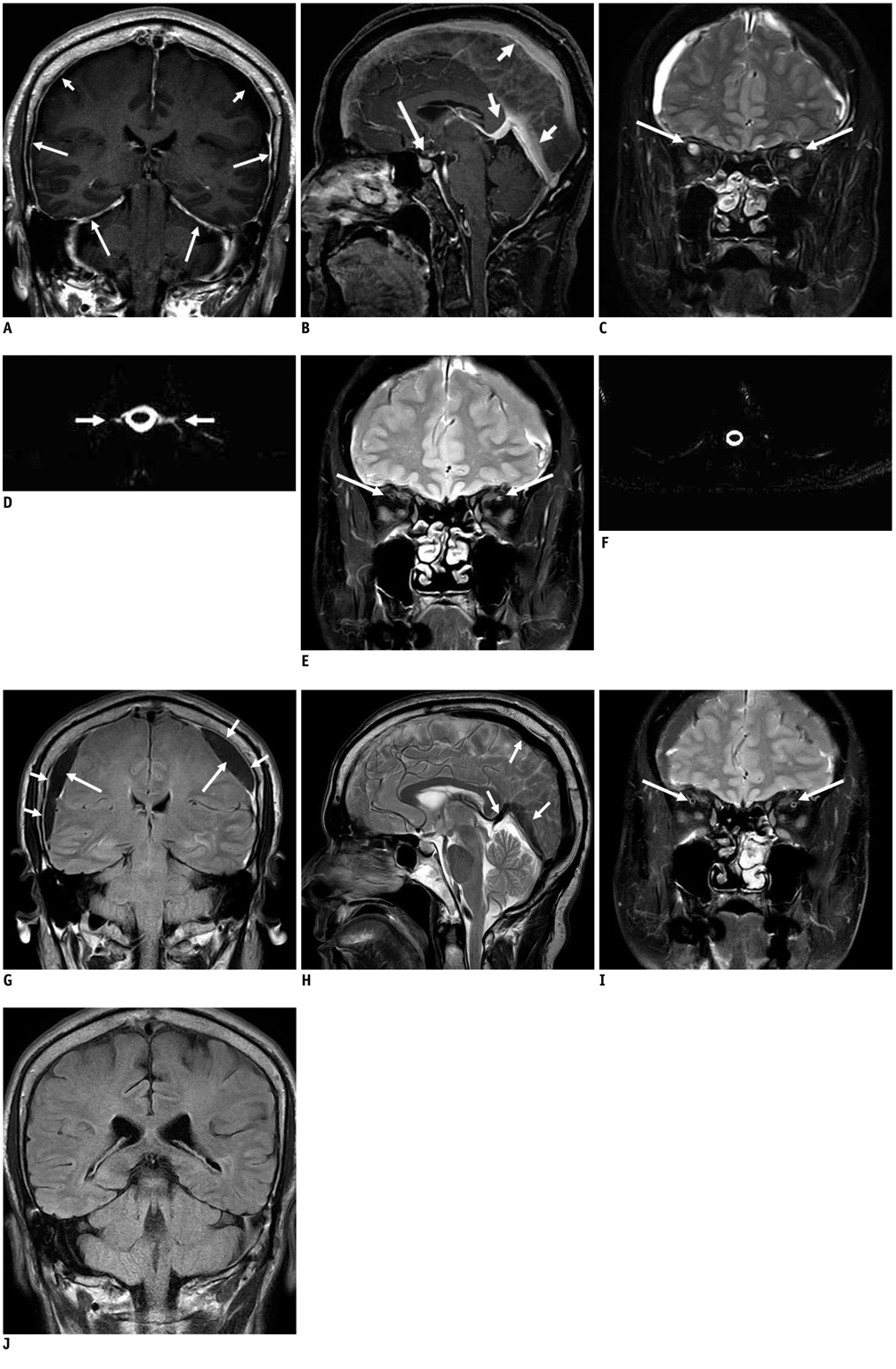
- Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is caused by single or multiple cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks in the spine with the prototypical symptom of postural headache. One of the characteristic MRI features in SIH is intracranial venous engorgement. This report presents a case of SIH with engorgement of the bilateral superior ophthalmic veins (SOVs) which resume their normal diameters by the third day of successful epidural blood patches (EBPs). We define this phenomenon as the "reversal of the SOV" sign.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schievink WI. Spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks and intracranial hypotension. JAMA. 2006. 295:2286–2296.2. Mokri B, Krueger BR, Miller GM, Piepgras DG. Meningeal gadolinium enhancement in low pressure headache. Ann Neurol. 1991. 30:294–295.3. Wang YF, Lirng JF, Fuh JL, Hseu SS, Wang SJ. Heavily T2-weighted MR myelography vs CT myelography in spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Neurology. 2009. 73:1892–1898.4. Tsai PH, Fuh JL, Lirng JF, Wang SJ. Heavily T2-weighted MR myelography in patients with spontaneous intracranial hypotension: a case-control study. Cephalalgia. 2007. 27:929–934.5. Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia. 2004. 24:Suppl 1. 9–160.6. Mokri B. Headaches caused by decreased intracranial pressure: diagnosis and management. Curr Opin Neurol. 2003. 16:319–326.7. Schievink WI, Morreale VM, Atkinson JL, Meyer FB, Piepgras DG, Ebersold MJ. Surgical treatment of spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks. J Neurosurg. 1998. 88:243–246.8. Schievink WI, Reimer R, Folger WN. Surgical treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension associated with a spinal arachnoid diverticulum. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1994. 80:736–739.9. Franzini A, Messina G, Nazzi V, Mea E, Leone M, Chiapparini L, et al. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome: a novel speculative physiopathological hypothesis and a novel patch method in a series of 28 consecutive patients. J Neurosurg. 2010. 112:300–306.10. Lai TH, Fuh JL, Lirng JF, Tsai PH, Wang SJ. Subdural haematoma in patients with spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Cephalalgia. 2007. 27:133–138.11. Schievink WI, Maya MM, Moser FG, Tourje J. Spectrum of subdural fluid collections in spontaneous intracranial hypotension. J Neurosurg. 2005. 103:608–613.12. Tosaka M, Sato N, Fujimaki H, Tanaka Y, Kagoshima K, Takahashi A, et al. Diffuse pachymeningeal hyperintensity and subdural effusion/hematoma detected by fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR imaging in patients with spontaneous intracranial hypotension. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008. 29:1164–1170.13. Mokri B. The Monro-Kellie hypothesis: applications in CSF volume depletion. Neurology. 2001. 56:1746–1748.14. Silverberg GD, Heit G, Huhn S, Jaffe RA, Chang SD, Bronte-Stewart H, et al. The cerebrospinal fluid production rate is reduced in dementia of the Alzheimer's type. Neurology. 2001. 57:1763–1766.15. Farb RI, Forghani R, Lee SK, Mikulis DJ, Agid R. The venous distension sign: a diagnostic sign of intracranial hypotension at MR imaging of the brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007. 28:1489–1493.16. Spektor S, Piontek E, Umansky F. Orbital venous drainage into the anterior cavernous sinus space: microanatomic relationships. Neurosurgery. 1997. 40:532–539. discussion 539-540.17. Chen WT, Fuh JL, Lirng JF, Lu SR, Wu ZA, Wang SJ. Collapsed superior ophthalmic veins in patients with spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Neurology. 2003. 61:1265–1267.18. Chen CC, Luo CL, Wang SJ, Chern CM, Fuh JL, Lin SH, et al. Colour doppler imaging for diagnosis of intracranial hypotension. Lancet. 1999. 354:826–829.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intracranial Hypertension Following Epidural Blood Patch in a Patient With Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
- Epidural Blood Patch in Patient with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: A case report
- Epidural Blood Patch to Treat Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
- Three Cases of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension ( SIH ) Treated with Epidural Blood Patch
- Epidural Blood Patch for the Treatment of Abducens Nerve Palsy due to Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: A Case Report