Yonsei Med J.
2008 Dec;49(6):1023-1031. 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.6.1023.
Development of Monoclonal Antibodies Against Human IRF-5 and Their Use in Identifying the Binding of IRF-5 to Nuclear Import Proteins Karyopherin-alpha1 and -beta1
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jsshin6203@yuhs.ac
- 2Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Institute for Immunology and Immunological Diseases, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4NCRC for Nanomedical Technology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5ATGen Inc., Sungnam, Kyungkido, Korea.
- 6Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Borame Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1782953
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2008.49.6.1023
Abstract
- PURPOSE
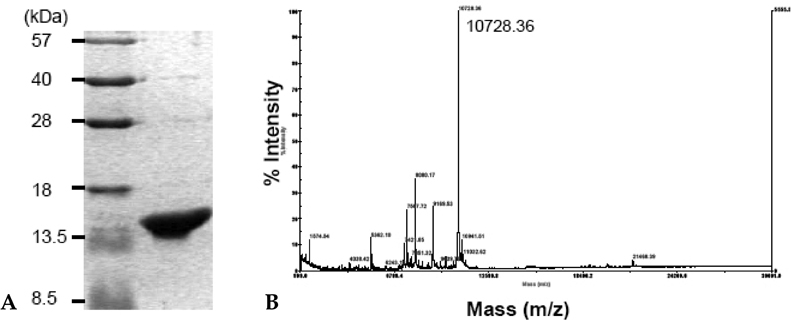
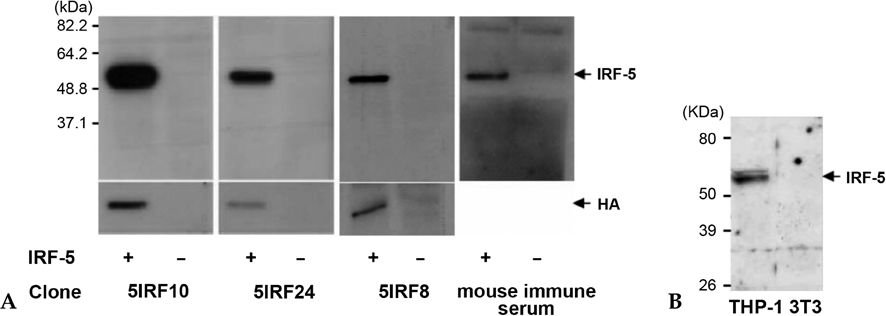
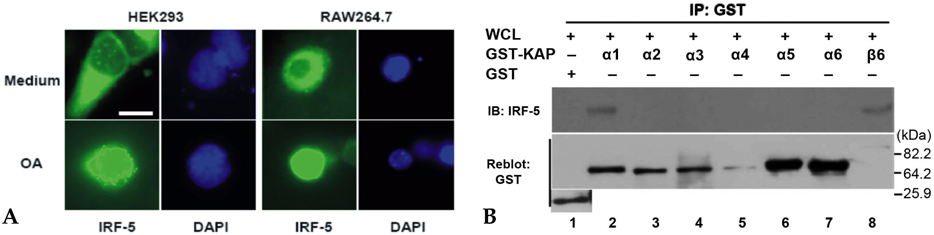
IRF-5 is a direct transducer of virus-mediated and TLR-mediated signaling pathways for the expression of cytokines and chemokines which form homodimers or heterodimers with IRF-7. However, direct IRF-5-specific monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are not available at present. These could be used to further evaluate the functions of IRF-5. In this study, we produced and characterized three mouse mAbs to human IRF-5. The binding of IRF-5 to nuclear import proteins was first identified using a mAb. MATERIALS AND METHODS: His-tagged human IRF-5 protein spanning amino acid residues 193- 257 was used as an antigen and three mAbs were produced. The mAbs were tested with ELISA, Western blot analysis (WB), immunofluorescent staining (IF), and immunoprecipitation (IP). In addition, the nuclear import protein which carried phosphorylated IRF-5 was identified using one of these mAbs. RESULTS: MAbs 5IRF8, 5IRF10 and 5IRF24 which reacted with the recombinant His-IRF-5(193-257) protein were produced. All mAbs bound to human IRF-5, but not to IRF-3 or IRF-7. They could be used for WB, IF, and IP studies. The binding of phosphorylated IRF-5 to karyopherin-alpha1 and -beta1 was also identified. CONCLUSION: Human IRF-5-specific mAbs are produced for studying the immunologic roles related to IRF-5. Phosphorylated IRF-5 is transported to the nucleus by binding to nuclear import proteins karyopherin-alpha1 and -beta1.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
*Antibodies, Monoclonal
Base Sequence
Cell Line
Cross Reactions
DNA Primers/genetics
Humans
Interferon Regulatory Factors/genetics/*immunology/*metabolism
Mice
Mice, Inbred BALB C
NIH 3T3 Cells
Protein Binding
Recombinant Proteins/genetics/immunology/metabolism
alpha Karyopherins/*metabolism
beta Karyopherins/*metabolism
Figure
Reference
-
1. Miyamoto M, Fujita T, Kimura Y, Maruyama M, Harada H, Sudo Y, et al. Regulated expression of a gene encoding a nuclear factor, IRF-1, that specifically binds to IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. Cell. 1988. 54:903–913.
Article2. Lohoff M, Mak TW. Roles of interferon-regulatory factors in T-helper-cell differentiation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005. 5:125–135.
Article3. Taniguchi T, Ogasawara K, Takaoka A, Tanaka N. IRF family of transcription factors as regulators of host defense. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001. 19:623–655.
Article4. Negishi H, Ohba Y, Yanai H, Takaoka A, Honma K, Yui K, et al. Negative regulation of Toll-like-receptor signaling by IRF-4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. 102:15989–15994.
Article5. Sato M, Suemori H, Hata N, Asagiri M, Ogasawara K, Nakao K, et al. Distinct and essential roles of transcription factors IRF-3 and IRF-7 in response to viruses for IFN-alpha/beta gene induction. Immunity. 2000. 13:539–548.
Article6. Yeow WS, Au WC, Juang YT, Fields CD, Dent CL, Gewert DR, et al. Reconstitution of virus-mediated expression of interferon alpha genes in human fibroblast cells by ectopic interferon regulatory factor-7. J Biol Chem. 2000. 275:6313–6320.
Article7. Au WC, Yeow WS, Pitha PM. Analysis of functional domains of interferon regulatory factor 7 and its association with IRF-3. Virology. 2001. 280:273–282.
Article8. Iwamura T, Yoneyama M, Yamaguchi K, Suhara W, Mori W, Shiota K, et al. Induction of IRF-3/-7 kinase and NF-kappaB in response to double-stranded RNA and virus infection: common and unique pathways. Genes Cells. 2001. 6:375–388.
Article9. Doyle S, Vaidya S, O'Connell R, Dadgostar H, Dempsey P, Wu T, et al. IRF3 mediates a TLR3/TLR4-specific antiviral gene program. Immunity. 2002. 17:251–263.
Article10. Barnes BJ, Moore PA, Pitha PM. Virus-specific activation of a novel interferon regulatory factor, IRF-5, results in the induction of distinct interferon alpha genes. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:23382–23390.
Article11. Takaoka A, Yanai H, Kondo S, Duncan G, Negishi H, Mizutani T, et al. Integral role of IRF-5 in the gene induction programme activated by Toll-like receptors. Nature. 2005. 434:243–249.
Article12. Barnes BJ, Kellum MJ, Field AE, Pitha PM. Multiple regulatory domains of IRF-5 control activation, cellular localization, and induction of chemokines that mediate recruitment of T lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. 22:5721–5740.
Article13. Barnes BJ, Field AE, Pitha-Rowe PM. Virus-induced heterodimer formation between IRF-5 and IRF-7 modulates assembly of the IFNA enhanceosome in vivo and transcriptional activity of IFNA genes. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278:16630–16641.
Article14. Mori T, Anazawa Y, Iiizumi M, Fukuda S, Nakamura Y, Arakawa H. Identification of the interferon regulatory factor 5 gene (IRF-5) as a direct target for p53. Oncogene. 2002. 21:2914–2918.
Article15. Yanai H, Chen HM, Inuzuka T, Kondo S, Mak TW, Takaoka A, et al. Role of IFN regulatory factor 5 transcription factor in antiviral immunity and tumor suppression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. 104:3402–3407.
Article16. Hu G, Mancl ME, Barnes BJ. Signaling through IFN regulatory factor-5 sensitizes p53-deficient tumors to DNA damage-induced apoptosis and cell death. Cancer Res. 2005. 65:7403–7412.
Article17. Graham RR, Kozyrev SV, Baechler EC, Reddy MV, Plenge RM, Bauer JW, et al. A common haplotype of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) regulates splicing and expression and is associated with increased risk of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet. 2006. 38:550–555.
Article18. Sigurdsson S, Nordmark G, Göring HH, Lindroos K, Wiman AC, Sturfelt G, et al. Polymorphisms in the tyrosine kinase 2 and interferon regulatory factor 5 genes are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Hum Genet. 2005. 76:528–537.19. Barnes BJ, Richards J, Mancl M, Hanash S, Beretta L, Pitha PM. Global and distinct targets of IRF-5 and IRF-7 during innate response to viral infection. J Biol Chem. 2004. 279:45194–45207.
Article20. Macara IG. Transport into and out of the nucleus. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2001. 65:570–594.21. Lin R, Yang L, Arguello M, Penafuerte C, Hiscott J. A CRM1-dependent nuclear export pathway is involved in the regulation of IRF-5 subcellular localization. J Biol Chem. 2005. 280:3088–3095.22. Youn JH, Shin JS. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of HMGB1 is regulated by phosphorylation that redirects it toward secretion. J Immunol. 2006. 177:7889–7897.23. Mancl ME, Hu G, Sangster-Guity N, Olshalsky SL, Hoops K, Fitzgerald-Bocarsly P, et al. Two discrete promoters regulate the alternatively spliced human interferon regulatory factor-5 isoforms. Multiple isoforms with distinct cell type-specific expression, localization, regulation, and function. J Biol Chem. 2005. 280:21078–21090.24. Bialojan C, Takai A. Inhibitory effect of a marine-sponge toxin, okadaic acid, on protein phosphatases. Specificity and kinetics. Biochem J. 1988. 256:283–290.
Article25. Cobb J, Cargile B, Handel MA. Acquisition of competence to condense metaphase I chromosomes during spermatogenesis. Dev Biol. 1999. 205:49–64.
Article26. Kim KJ, Kanellopoulos-Langevin C, Merwin RM, Sachs DH, Asofsky R. Establishment and characterization of BALB/c lymphoma lines with B cell properties. J Immunol. 1979. 122:549–554.27. Kumar KP, McBride KM, Weaver BK, Dingwall C, Reich NC. Regulated nuclear-cytoplasmic localization of interferon regulatory factor 3, a subunit of double-stranded RNA-activated factor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. 20:4159–4168.
Article28. Dieguez-Gonzalez R, Calaza M, Perez-Pampin E, de la Serna AR, Fernandez-Gutierrez B, Castaneda S, et al. Association of interferon regulatory factor 5 haplotypes, similar to that found in systemic lupus erythematosus, in a large subgroup of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. 58:1264–1274.
Article29. Couzinet A, Tamura K, Chen HM, Nishimura K, Wang Z, Morishita Y, et al. A cell-type-specific requirement for IFN regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) in Fas-induced apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. 105:2556–2561.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Human fibroblasts in idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis express HLA-DR antigens
- Human Papillomavirus Infection
- Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis presented as an abdominal mass and nephrotic syndrome
- IL-4 inhibits proliferation of renal carcinoma cells by increasing the expression of p21WAF1 and IRF-1
- Expression of Interferon Regulatory Factors in Breast Cancer Tissue