Infect Chemother.
2011 Apr;43(2):203-205. 10.3947/ic.2011.43.2.203.
Primary psoas abscess caused by Streptococcus agalactiae
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Gil Hospital, Incheon, Korea. karmacho@gmail.com
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Gil Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1782362
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2011.43.2.203
Abstract
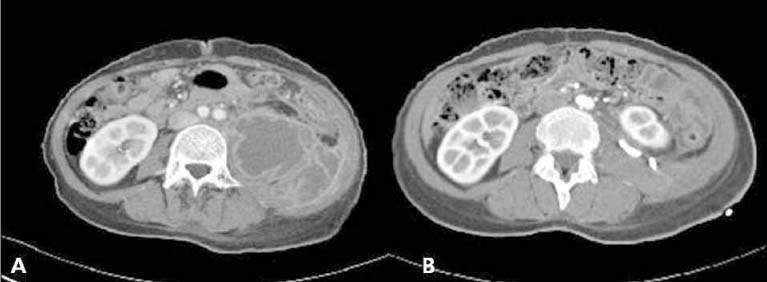
- Group B streptococcus (Streptococcus agalactiae, GBS), a primary pathogen in postpartum infection, has rarely been reported in psoas abscess. Primary proas abscess occurs less frequently than secondary abscess, which originates from infections of adjacent organs, such as intraabdominal infection, osteomyelitis, perirenal abscess, and retroperitoneal hematomas. We describe a case of primary psoas abscess caused by GBS. A 44-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus presented with left flank pain, intermittent fever, dysuria, and discomfort during walking. Abdominal CT showed multiseptated cystic mass in wide areas of the retroperitoneal space. Pus culture showed Streptococcus agalactiae. The patient responded to penicillin G treatment for 3 weeks.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim ES, Park BK, Lee SJ, Rue JI, Ahn HJ, Han SH, Lee YW. A case of bilateral psoas abscesses in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Korean J Med. 2001. 61:567–571.2. Agrawal SN, Dwivedi AJ, Khan M. Primary psoas abscess. Dig Dis Sci. 2002. 47:2103–2105.3. Park CB, Kim KS, Shin JH, Suh GJ, Youn YK. Clinical presentations, diagnosis, and treatments of a psoas abscess. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 2005. 16:346–351.4. Jang KJ, Park KW, Yoon JH, Yeon JB. Primary psoas abscess: a case report. Korean J Urol. 1983. 24:326–328.5. Choi JH, Kim MC, Im SG, Cho SK, Shin SS, Oh YJ, Choi YH, Park KJ, Hwang SC. Psoas abscess: analysis of 24 cases. Korean J Med. 2003. 65:343–349.6. Kuo CM, Wu CK, Lien WC. Bilateral psoas abscess formation after acupuncture. J Emerg Med. 2011. 40:215–216.
Article7. Kim JH, Choi KH, Choi SM, Oh YM, Seo JS, Lee WJ. Bilateral primary psoas abscess in heat-stroke patient: a case report. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 2006. 17:199–202.8. Park HJ, Jeon YC, Lee K, Byun TJ, Kim TY, Eun CS, Han DS, Sohn JH. Psoas abscess with hip contracture in a patient with Crohn\'s disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008. 52:188–191.9. Seong SS, Lee JW, Wang JK, Lee YY, Kim IS, Choi IY, Ahn MJ. A case of bilateral psoas abscess in multiple myeloma patient. Korean J Med. 2004. 67:Suppl 3. S862–S866.10. Lee MH, Choi SM, Ji JS, Kim SI, Kim YR, Kang MW. A case of primary Salmonella psoas abscess complicated with iliac artery aneurysm and deep vein thrombosis. Infect Chemother. 2003. 35:118–122.11. Jeon CH, Jeoung US, Chung GY, Kim S. The recurrent psoas abscess caused by two different pathogens: a case report. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2007. 42:553–555.
Article12. Kern L, Rassbach C, Ottolini M. Streptococcal pyomyositis of the psoas: case reports and review. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2006. 22:250–253.13. Lin MF, Lau YJ, Hu BS, Shi ZY, Lin YH. Pyogenic psoas abscess: analysis of 27 cases. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 1999. 32:261–268.14. Christin L, Sarosi GA. Pyomyositis in North America: case reports and review. Clin Infect Dis. 1992. 15:668–677.
Article15. Huang JJ, Ruaan MK, Lan RR, Wang MC. Acute pyogenic iliopsoas abscess in Taiwan: clinical features, diagnosis, treatments and outcome. J Infect. 2000. 40:248–255.
Article16. Ricci MA, Rose FB, Meyer KK. Pyogenic psoas abscess: worldwide variations in etiology. World J Surg. 1986. 10:834–843.
Article17. Wu TL, Huang CH, Hwang DY, Lai JH, Su RY. Primary pyogenic abscess of the psoas muscle. Int Orthop. 1998. 22:41–43.
Article18. Phares CR, Lynfield R, Farley MM, Mohle-Boetani J, Harrison LH, Petit S, Craig AS, Schaffner W, Zansky SM, Gershman K, Stefonek KR, Albanese BA, Zell ER, Schuchat A, Schrag SJ. Active Bacterial Core surveillance/Emerging Infections Program Network. Epidemiology of invasive group B streptococcal disease in the United States, 1999-2005. JAMA. 2008. 299:2056–2065.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Primary Pyogenic Psoas Abscess in Child
- A perinephric abscess caused by Streptococcus agalactiae
- Pyogenic Sacroiliitis with Psoas Abscess: A case report
- Primary Psoas Abscess: A Case Report
- Two Cases of Streptococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome Caused by Streptococcus agalactiae and Streptococcus dysagalactiae