J Korean Med Sci.
2011 Feb;26(2):308-311. 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.2.308.
Incontinentia Pigmenti in a Newborn with NEMO Mutation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. mychang@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1782125
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2011.26.2.308
Abstract
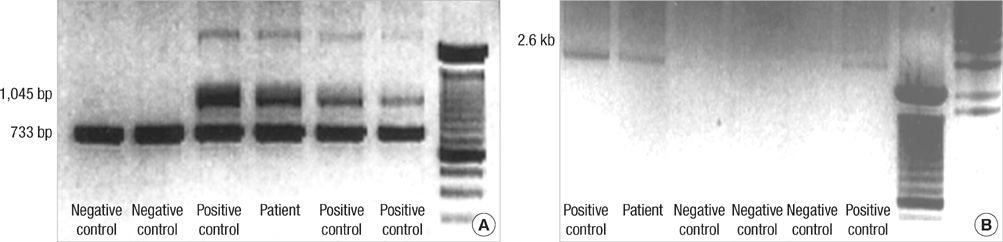
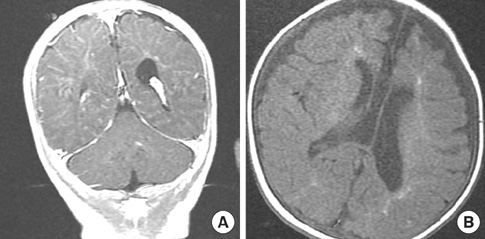
- Incontinentia pigmenti (IP) (OMIM #308300) is a rare X-linked dominant neuroectodermal multisystemic syndrome due to mutations in the gene for NF-kappaB essential modulator (NEMO). A term newborn girl who was born with erythematous vesicular eruptions developed recurrent seizures during the first and second weeks of her life. The serial MRIs demonstrated diffuse, progressive brain infarctions and subsequent encephalomalacia as well as brain atrophy. Skin biopsy found it was consistent with the vesicular stage of IP. Genetic analysis revealed a deletion exon 4-10 in NEMO gene associated with IP. We hereby report a Korean female baby with IP confirmed by mutation analysis of NEMO gene.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Steffann J, Raclin V, Smahi A, Woffendin H, Munnich A, Kenwrick SJ, Grebille AG, Benachi A, Dumez Y, Bonnefont JP, Hadj-Rabia S. A novel PCR approach for prenatal detection of the common NEMO rearrangement in incontinentia pigmenti. Prenat Diagn. 2004. 24:384–388.2. Bardaro T, Falco G, Sparago A, Mercadante V, Gean Molins E, Tarantino E, Ursini MV, D'Urso M. Two cases of misinterpretation of molecular results in incontinentia pigmenti, and a PCR-based method to discriminate NEMO/IKKgamma dene deletion. Hum Mutat. 2003. 21:8–11.3. Smahi A, Courtois G, Vabres P, Yamaoka S, Heuertz S, Munnich A, Israël A, Heiss NS, Klauck SM, Kioschis P, Wiemann S, Poustka A, Esposito T, Bardaro T, Gianfrancesco F, Ciccodicola A, D'Urso M, Woffendin H, Jakins T, Donnai D, Stewart H, Kenwrick SJ, Aradhya S, Yamagata T, Levy M, Lewis RA, Nelson DL. Genomic rearrangement in NEMO impairs NF-kappaB activation and is a cause of incontinentia pigmenti. The International Incontinentia Pigmenti (IP) Consortium. Nature. 2000. 405:466–472.4. Fusco F, Pescatore A, Bal E, Ghoul A, Paciolla M, Lioi MB, D'Urso M, Rabia SH, Bodemer C, Bonnefont JP, Munnich A, Miano MG, Smahi A, Ursini MV. Alterations of the IKBKG locus and diseases: an update and a report of 13 novel mutations. Hum Mutat. 2008. 29:595–604.5. Kim BJ, Shin HS, Won CH, Lee JH, Kim KH, Kim MN, Ro BI, Kwon OS. Incontinentia pigmenti: Clinical observation of 40 Korean cases. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. 21:474–477.6. Song MJ, Chae JH, Park EA, Ki CS. The common NF-κB essential modulator (NEMO) gene rearrangement in Korean patients with incontinentia pigmenti. J Korean Med Sci. 2010. 25:1513–1517.7. Hsiao PF, Lin SP, Chiang SS, Wu YH, Chen HC, Lin YC. NEMO gene mutations in Chinese patients with incontinentia pigmenti. J Formos Med Assoc. 2010. 109:192–200.8. Pacheco TR, Levy M, Collyer JC, de Parra NP, Parra CA, Garay M, Aprea G, Moreno S, Mancini AJ, Paller AS. Incontinentia pigmenti in male patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006. 55:251.9. Franco LM, Goldstein J, Prose NS, Selim MA, Tirado CA, Coale MM, McDonald MT. Incontinentia pigmenti in a boy with XXY mosaicism detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006. 55:136–138.10. Kenwrick S, Woffendin H, Jakins T, Shuttleworth SG, Mayer E, Greenhalgh L, Whittaker J, Rugolotto S, Bardaro T, Esposito T, D'Urso M, Soli F, Turco A, Smahi A, Hamel-Teillac D, Lyonnet S, Bonnefont JP, Munnich A, Aradhya S, Kashork CD, Shaffer LG, Nelson DL, Levy M, Lewis RA. International IP Consortium. Survival of male patients with incontinentia pigmenti carrying a lethal mutation can be explained by somatic mosaicism or Klinefelter syndrome. The International Incontinentia Pigmenti (IP) Consortium. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. 69:1210–1217.11. Maingay-de Groof F, Lequin MH, Roofthooft DW, Oranje AP, de Coo IF, Bok LA, van der Spek PJ, Mancini GM, Govaert PP. Extensive cerebral infarction in the newborn due to incontinentia pigmenti. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2008. 12:284–289.12. Shuper A, Bryan RN, Singer HS. Destructive encephalopathy in incontinentia pigmenti: a primary disorder? Pediatr Neurol. 1990. 6:137–140.13. Hennel SJ, Ekert PG, Volpe JJ, Inder TE. Insights into the pathogenesis of cerebral lesions in incontinentia pigmenti. Pediatr Neurol. 2003. 29:148–150.14. Goldberg MF, Custis PH. Retinal and other manifestations of incontinentia pigmenti (Bloch-Sulzberger Syndrome). Ophthalmology. 1993. 100:1645–1654.15. Lee AG, Goldberg MF, Gillard JH, Barker PB, Bryan RN. Intracranial assessment of incontinentia pigmenti using magnetic resonance imaging, angiography, and spectroscopic imaging. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1995. 149:573–580.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Incontinentia Pigmenti in a Boy with Klinefelter Syndrome
- The Common NF-kappaB Essential Modulator (NEMO) Gene Rearrangement in Korean Patients with Incontinentia Pigmenti
- A Case of Incontinentia Pigmenti with Multiple Brain Infarction
- A case of incontinentia pigmenti
- A Genetic Study in a Patient with Incontinentia Pigmenti