J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Oct;24(5):867-873. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.5.867.
Marked Individual Variation in Isoflavone Metabolism After a Soy Challenge Can Modulate the Skeletal Effect of Isoflavones in Premenopausal Women
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology, Department of Internal Medicine, Cheil General Hospital and Women's Healthcare Center, Kwandong University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kiok.han@cgh.co.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Marynoll General Hospital, Inje University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1782008
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.5.867
Abstract
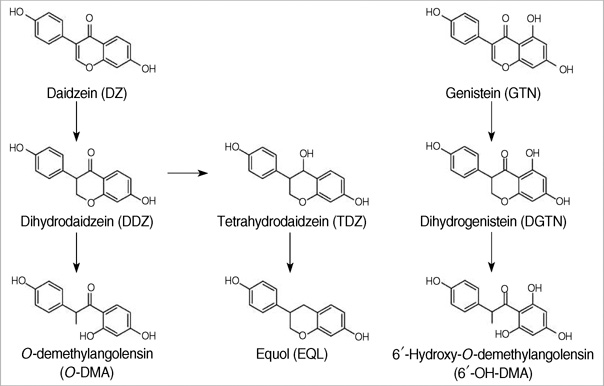
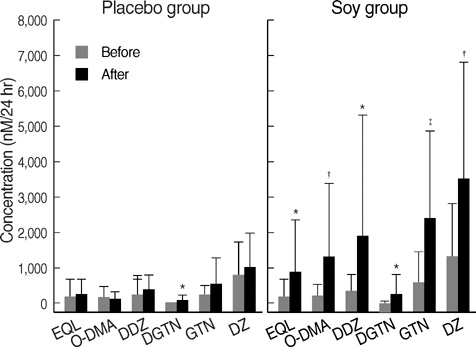
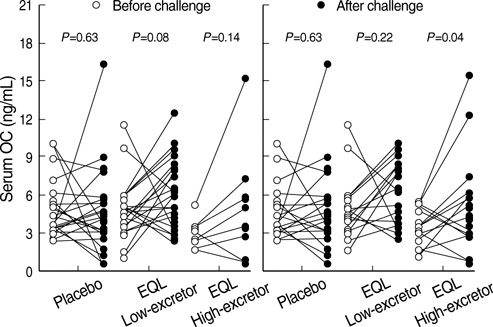
- Soy-isoflavones may act as estrogenic agonists or antagonists depending on the endogenous hormone status. These clinical effects can be exerted variably in individuals by the metabolic ability to produce a more potent metabolite than precursors. The objective of this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was to investigate the skeletal effect of isoflavones according to their metabolic variability in premenopausal women. Volunteers were randomly assigned to receive either soy-extract isoflavones (n=32) or lactose (n=21) once a day for three menstrual cycles. After intervention, the urinary excretions of isoflavones and their metabolites were significantly higher in the soy group than in the placebo group and showed a large inter-individual variation. Women in the soy group were divided into subgroups according to their ability to excrete more potent metabolites. Serum osteocalcin and urine deoxypyridinoline showed a tendency to increase after a challenge in equol high-excretors. Serum osteocalcin concentration in the genistein high-excretors increased significantly after a challenge (P=0.04) but did not increase in either the placebo or genistein low-excretors. An estrogenic antagonistic effect of isoflavones on bone turnover was observed in premenopausal women who are able to produce more potent metabolites.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Combined effects of soy isoflavone and lecithin on bone loss in ovariectomized mice
Sang Baek Kim, Freshet Assefa, Su Jeong Lee, Eui Kyun Park, Sung Soo Kim
Nutr Res Pract. 2021;15(5):541-554. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2021.15.5.541.
Reference
-
1. Ososki AL, Kennelly EJ. Phytoestrogens: a review of the present state of research. Phytother Res. 2003. 17:845–869.
Article2. Murkies AL, Wilcox G, Davis SR. Clinical review 92: phytoestrogens. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998. 83:297–303.3. Harris DM, Besselink E, Henning SM, Go VLW, Heber D. Phytoestrogens induce differential estrogen receptor alpha- or beta-mediated responses in transfected breast cancer cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2005. 230:558–568.
Article4. Hwang CS, Kwak HS, Lim HJ, Lee SH, Kang YS, Choe TB, Hur HG, Han KO. Isoflavone metabolites and their in vitro dual functions: they can act as an estrogenic agonist or antagonist depending on the estrogen concentration. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2006. 101:246–253.
Article5. Potter SM, Baum JA, Teng H, Stillman RJ, Shay NF, Erdman JW Jr. Soy protein and isoflavones: their effects on blood lipids and bone density in postmenopausal women. Am J Clin Nutr. 1988. 68(6):Suppl. 1375S–1379S.
Article6. Alekel DL, Germain AS, Peterson CT, Hanson KB, Stewart JW, Toda T. Isoflavone-rich soy protein isolate attenuates bone loss in the lumbar spine of perimenopausal women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000. 72:844–852.
Article7. Marini H, Minutoli L, Polito F, Bitto A, Altavilla D, Atteritano M, Gaudio A, Mazzaferro S, Frisina A, Frisina N, Lubrano C, Bonaiuto M, D'Anna R, Cannata ML, Corrado F, Adamo EB, Wilson S, Squadrito F. Effects of the phytoestrogen genistein on bone metabolism in osteopenic postmenopausal women: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2007. 146:839–847.8. Morabito N, Crisafulli A, Vergara C, Gaudio A, Lasco A, Frisina N, D'Anna R, Corrado F, Pizzoleo MA, Cincotta M, Altavilla D, Ientile R, Squadrito F. Effects of genistein and hormone-replacement therapy on bone loss in early postmenopausal women: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. J Bone Miner Res. 2002. 17:1904–1912.
Article9. Cheong JM, Martin BR, Jackson GS, Elmore D, McCabe GP, Nolan JR, Barnes S, Peacock M, Weaver CM. Soy isoflavones do not affect bone resorption in postmenopausal women: a dose-response study using a novel approach with 41Ca. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007. 92:577–582.
Article10. Reinwald S, Weaver CM. Soy isoflavones and bone health: a double-edged sword? J Nat Prod. 2006. 69:450–459.
Article11. Ho SC, Chan SG, Yi Q, Wong E, Leung PC. Soy intake and the maintenance of peak bone mass in Hong Kong Chinese women. J Bone Miner Res. 2001. 16:1363–1369.
Article12. Anderson JJ, Chen X, Boass A, Symons M, Kohlmeier M, Renner JB, Garner SC. Soy isoflavones: no effects on bone mineral content and bone mineral density in healthy, menstruating young adult women after one year. J Am Coll Nutr. 2002. 21:388–393.
Article13. Mei J, Yeung SS, Kung AW. High dietary phytoestrogen intake is associated with higher bone mineral density in postmenopausal but not premenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 86:5217–5221.
Article14. Setchell KD, Brown NM, Lydeking-Olsen E. The clinical importance of the metabolite equol-a clue to the effectiveness of soy and its isoflavones. J Nutr. 2002. 132:3577–3584.
Article15. Joannou GE, Kelly GE, Reeder AY, Waring M, Nelson C. A urinary profile study of dietary phytoestrogens. The identification and mode of metabolism of new isoflavonoids. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1995. 54:167–184.
Article16. Chang YC, Nair MG. Metabolites of daidzein and genistein by intestinal bacteria. J Nat Prod. 1995. 58:1892–1896.17. Rowland I, Wiseman H, Sanders T, Adlercreutz H, Bowey E. Metabolism of oestrogens and phytoestrogens: role of the gut microflora. Biochem Soc Trans. 1999. 27:304–308.
Article18. Axelson M, Setchell KD. The excretion of lignans in rats-evidence for an intestinal bacterial source for this new group of compounds. FEBS Lett. 1981. 123:337–342.19. Setchell KD, Zimmer-Nechemias L, Cai J, Heubi JE. Exposure of infants to phyto-oestrogens from soy-based infant formula. Lancet. 1997. 350:23–27.
Article20. Setchell KD, Zimmer-Nechemias L, Cai J, Heubi JE. Isoflavone content of infant formulas and the metabolic fate of these phytoestrogens in early life. Am J Clin Nutr. 1998. 68(6):Suppl. 1453S–1461S.
Article21. Setchell KD, Brown NM, Desai PB, Desai PB, Zimmer-Nechimias L, Wolfe B, Jakate AS, Creutzinger V, Heubi JE. Bioavailability, disposition, and dose-response effects of soy isoflavones when consumed by healthy women at physiologically typical dietary intakes. J Nutr. 2003. 133:1027–1035.
Article22. Wangen KE, Duncan AM, Merz-Demlow BE, Xu X, Marcus R, Phipps WR, Kurzer MS. Effects of soy isoflavones on markers of bone turnover in premenopausal and postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000. 85:3043–3048.
Article23. Zittermann A, Geppert J, Baier S, Zehn N, Gouni-Berthold I, Berthold HK, Reinsberg J, Stehle P. Short-term effects of high soy supplementation on sex hormones, bone markers, and lipid parameters in young female adults. Eur J Nutr. 2004. 43:100–108.
Article24. Cassidy A, Bingham S, Setchell KD. Biological effects of a diet of soy protein rich in isoflavones on the menstrual cycle of premenopausal women. Am J Clin Nutr. 1994. 60:333–340.
Article25. Lu LJ, Anderson KE, Grady JJ, Nagamani M. Effects of soya consumption for one month on steroid hormones in premenopausal women: implication for breast cancer risk reduction. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1996. 5:63–70.26. Wu AH, Stanczyk FZ, Hendrich S, Murphy PA, Zhang C, Wan P, Pike MC. Effects of soy foods on ovarian function in premenopausal women. Br J Cancer. 2000. 82:1879–1886.
Article27. Maskarinec G, Franke AA, Williams AE, Hebshi S, Oshiro C, Murphy S, Stanczyk FZ. Effects of a 2-year randomized soy intervention on sex hormone levels in premenopausal women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004. 13:1736–1744.28. Duncan AM, Merz-Demlow BE, Xu X, Phipps WR, Kurzer MS. Premenopausal equol excretors show plasma hormone profiles associated with lowered risk of breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2000. 9:581–586.29. Kuiper GG, Lemmen JG, Carlsson B, Corton C, Safe SH, van der Saag PT, van der Burg B, Gustafsson JÅ. Interaction of estrogenic chemicals and phytoestrogens with estrogen receptor beta. Endocrinology. 1998. 139:4252–4263.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study on Dietary Isoflavone Intake from Soy Food and Urinary Isoflavone Excretion and, Menopausal Symptoms in Korean Women in Rural Areas
- Validation of soy isoflavone intake and its health effects: a review of the development of exposure biomarkers
- Survey on the Consumption of the Phytoestrogen Isoflavone in Postmenopausal Korean Women
- Effect of Soy Isoflavone Intake on Water Maze Performance and Brain Acetylcholinesterase Activity in Rats
- Effect of Genistein and Soy Protein on Lipids Metabolism in Ovariectomized Rats