J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Oct;24(5):844-848. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.5.844.
Risk Factors for Serious Bacterial Infection in Febrile Young Infants in a Community Referral Hospital
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. choicw@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 1782004
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.5.844
Abstract
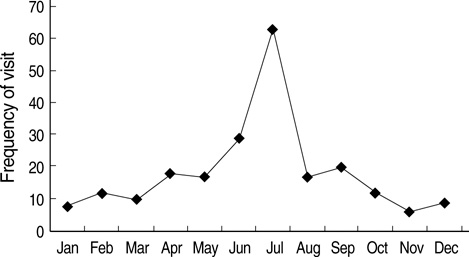
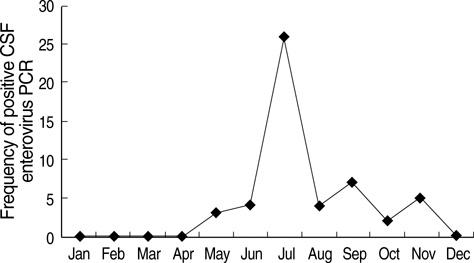
- Differentiation of serious bacterial infection (SBI) from self-limiting viral illness in febrile infants younger than three months is a significant challenge for clinicians. We aimed to assess the risk factors for SBI in febrile infants. Data were obtained from 221 infants younger than three months who visited a single community referral hospital for fever and underwent a complete sepsis workup between August 2003 and July 2006. The causes of fever were febrile illness without a documented cause (FISDC, 65%), urinary tract infection (UTI, 12%), aseptic meningitis (12%), bacteremia (4%), bacterial meningitis (2%). Cerebrospinal fluid enterovirus polymerase chain reaction was positive in 28% of FISDC and 48% of aseptic meningitis cases. When UTI was excluded, the risk factors for SBI were 1) C-reactive protein (CRP) level of > or =1.87 mg/dL and 2) fevers of > or =38.9degrees C. The specificity and negative predictive values of risk factors 1) and 2) for the diagnosis of SBI were 94% and 95%, respectively. We concluded that enteroviral infection may be a major cause of febrile episodes in infants younger than three months. If UTI could be excluded, the presence of CRP levels > or =1.87 mg/dL and fevers of > or =38.9degrees C can be used as criteria to rule out SBI in these infants.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Etiology and Clinical Manifestations of Fever in Infants Younger than 3 Months Old: A Single Institution Study, 2008-2010
Joon Young Seok, Ji Eun Kang, Eun Young Cho, Eun Hwa Choi, Hoan Jong Lee
Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2012;19(3):121-130. doi: 10.14776/kjpid.2012.19.3.121.Clinical Characteristics of Fever without Localizing Sign in Infants Younger than 100 Days of Age in a Single Center
Hyun Suk Lee, Kye Hyang Lee
Pediatr Infect Vaccine. 2016;23(2):128-136. doi: 10.14776/piv.2016.23.2.128.
Reference
-
1. Nelson DS, Walsh K, Fleisher GR. Spectrum and frequency of pediatric illness presenting to a general community hospital emergency department. Pediatrics. 1992. 90:5–10.2. Baraff LJ, Bass JW, Fleisher GR, Klein JO, McCracken GH Jr, Powell KR, Schriger DL. Practice guideline for the management of infants and children 0 to 36 months of age with fever without source. Ann Emerg Med. 1993. 22:1198–1210.
Article3. Luszczak M. Evaluation and management of infants and young children with fever. Am Fam Physician. 2001. 64:1219–1226.4. Levine DA, Platt SL, Dayan PS, Macias CG, Zorc JJ, Krief W, Schor J, Bank D, Fefferman N, Shaw KN, Kuppermann N. Risk of serious bacterial infection in young febrile infants with respiratory syncytial virus infections. Pediatrics. 2004. 113:1728–1734.
Article5. Pantell RH, Newman TB, Bernzweig J, Bergman DA, Takayama JI, Segal M, Finch SA, Wasserman RC. Management and outcomes of care of fever in early infancy. JAMA. 2004. 291:1203–1212.
Article6. Bachur RG, Harper MB. Predictive model for serious bacterial infections among infants younger than 3 months of age. Pediatrics. 2001. 108:311–316.
Article7. Trautner BW, Caviness AC, Gerlacher GR, Demmler G, Macias CG. Prospective evaluation of the risk of serious bacterial infection in children who present to the emergency department with hyperpyrexia (temperature of 106°F or higher). Pediatrics. 2006. 118:34–40.
Article8. McCarthy PL, Sharpe MR, Spiesel SZ, Dolan TF, Forsyth BW, De-Witt TG, Fink HD, Baron MA, Cicchetti DV. Observation scales to identify serious illness in febrile children. Pediatrics. 1982. 70:802–809.9. Dagan R, Sofer S, Phillip M, Shachak E. Ambulatory care of febrile infants younger than 2 months of age classified as being at low risk for having serious bacterial infections. J Pediatr. 1988. 112:335–360.
Article10. Baskin MN, O'Rourke EJ, Fleisher GR. Outpatient treatment of febrile infants 28 to 89 days of age with intramuscular administration of ceftriaxone. J Pediatr. 1992. 120:22–27.
Article11. Baker MD, Bell LM, Avner JR. Outpatient management without antibiotics of fever in selected infants. N Engl J Med. 1993. 329:1437–1441.
Article12. Melnick JL. Evans AS, editor. Enterovirus. Viral infections of humans-epidemiology and control. 1989. 3rd edn. New York: Plenum;191–203.13. Morens DM. Enteroviral disease in early infancy. J Pediatr. 1978. 92:374–377.
Article14. Cherry JD. Remington JS, Klein JO, editors. Enteroviruses. Infectious diseases of the fetus and newborn infant. 2001. 5th edn. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company;477–518.15. Furione M, Zavattoni M, Gatti M, Percivalle E, Fioroni N, Gerna G. Rapid detection of enteroviral RNA in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from patients with aseptic meningitis by reverse transcription-nested polymerase chain reaction. New Microbiol. 1998. 21:343–351.16. Palacios Poggio G, Cisterna D, Freire MC, Cello J. RT-nested PCR for the detection of enterovirus in biological samples from patients with suspected enteroviral infections. Rev Argent Microbiol. 2000. 32:165–172.17. Glimaker M, Johansson B, Olcen P, Ehrnst A, Forsgren M. Detection of enteroviral RNA by polymerase chain reaction in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with aseptic meningitis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1993. 25:547–557.18. Thoren A, Widell A. PCR for the diagnosis of enteroviral meningitis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1994. 26:249–254.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Usefulness of Low-Risk Criteria for Serious Bacterial Infections in Febrile Infants Younger than 90 Days of Age
- Usefulness of Low Risk Criteria for Serious Bacterial Infection Among Febrile Infants Younger than Three Months of Age
- Study of Serious Bacterial Infections in Febrile Infants Younger than Three Months of Age
- Differentiation between Viral and Urinary Tract Infections Using the Modified Rochester Criteria In Febrile Infants Younger than three Months
- A Necessity for Lumbar Puncture and VCUG in Febrile UTI Infants less than 3 Months of Age