J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Apr;21(2):333-336. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.2.333.
Therapeutic Factors of Cognitive Behavioral Group Treatment for Social Phobia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Mettaa Institute of Cognitive Behavior Therapy, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Psychology, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea. psyclinic@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1781845
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.2.333
Abstract
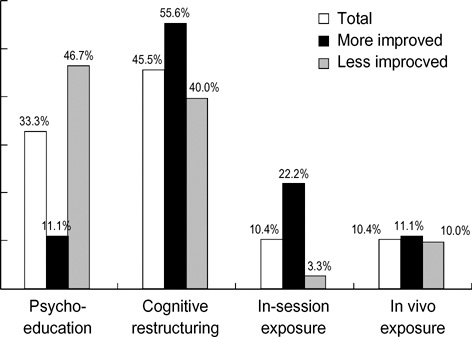
- This study investigated the therapeutic factors influencing the outcome of cognitive behavioral group treatment for social phobia and the most helpful therapeutic component. Fifty psychiatric outpatients who were diagnosed with social phobia according to the DSM-IV criteria were chosen as subjects. Patients were asked to complete the Yalom's Curative Factors Questionnaire and Therapeutic Components Evaluation Form at the end of their Cognitive Behavioral Group Treatment (CBGT). The patients who showed more improvement rated significantly higher in therapeutic factors such as "Interpersonal learning-output", "Guidance", "Universality", "Group cohesiveness" than the patients who showed less improvement. Among the four components of CBGT for social phobia, cognitive restructuring was rated as most helpful. These results suggest which therapeutic factors and components should be highlighted in CBGT for social phobia.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bloch S, Crouch E, Reibstein J. Therapeutic factors in group psychotherapy. A review. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1981. 38:519–526.2. Bloch S. Frances AJ, Hales RE, editors. Therapeutic factors in group psychotherapy. Annual Review. 1986. Vol 5. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Press;78–698.
Article3. Yalom ID. The Theory and Practice of Group Psychotherapy. 1995. 4th ed. New York: Basic Books;3–105.4. Heimberg RG, Becker RE, Goldfinger K, Vermilyea JA. Treatment of social phobia by exposure, cognitive restructuring, and homework assignments. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1985. 173:236–245.
Article5. Heimberg RG, Dodge CS, Hope DA, Kennedy CR, Zollo LJ, Becker RE. Cognitive-behavioral group treatment for social phobia: Comparison with a credible placebo control. Cog Ther Res. 1990. 14:1–23.6. Lucas RA, Telch MJ. Group versus Individual Treatment of social phobia. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the Association for the Advancement of Behavior Therapy. 1993. Atlanta, GA:7. Mattick RP, Peters L. Treatment of severe social phobia: Effects of guided exposure with and without cognitive restructuring. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1988. 56:251–260.
Article8. Mattick RP, Peters L, Clarke JC. Exposure and cognitive restructuring in social phobia: A controlled study. Behav Ther. 1989. 20:3–23.9. Huh YJ, Choi YH, Park KH. Therapeutic factors of group cognitive behavioral therapy for panic disorder. Cog Behav Ther in Korea. 2003. 3:57–67.10. Kim YS, Lim KY. A cognitive-behavioral group treatment of panic disorder: The effectiveness of the treatment and curative factors. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1995. 34:240–248.11. Lee HK, Cha JW, Ahn HJ, Kim SJ, Bong SY. Therapeutic factors in the outpatient group psychotherapy for the adolescents with conduct disorder. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2000. 39:309–322.12. Lee HK, Lee SY, Yoon SC, Ahn HJ. Therapeutic factors in the long-term outpatient group psychotherapy with the chronically mentally ill. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2000. 39:556–570.13. Yalom ID. The Theory and Practice of Group Psychotherapy. 1975. 2nd ed. New York: Basic Books.14. Di Nardo PA, Barlow DH. Anxiety Disorders Interview Schedule, Revised (ADIS-R). 1988. Albany, NY: Graywind Publications.15. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 1994. 4th ed. Washington DC: Author.16. Heimberg RG, Juster HR, Hope DA, Mattia JI. Stein MB, editor. Cognitive behavioral group treatment for social phobia: description, case presentation and empirical support. Social Phobia: Clinical and Research Perspectives. 1995. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Press;293–321.17. Marks IM, Mathews AM. Brief standard self-rating for phobic patients. Behav Res Ther. 1979. 17:263–267.
Article18. Brabender V, Albrecht E, Sillitti J, Cooper J, Kramer E. A study of curative factors in short-term group therapy. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1993. 34:643–644.19. Butler T, Fuhriman A. Patient perspective on the curative process: a comparison of day treatment and outpatient psychotherapy groups. Small Group Behav. 1980. 11:371–388.20. Butler T, Fuhriman A. Level of functioning and length of time in treatment: variables influencing patients' therapeutic experience in group psychotherapy. Int J Group Psychother. 1983. 33:489–505.
Article21. Colijn S, Hoencamp E, Snijders HJ, Van Der Spec MW, Duivenvoorden HJ. A comparison of curative factors in different types of group psychotherapy. Int J Group Psychother. 1991. 41:365–378.
Article22. Kapur R, Miller K, Mitchell G. Therapeutic factors within inpatient and outpatient psychotherapy groups. Br J Psychiatry. 1988. 152:229–233.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Social Work Intervention for Patients with Obesity
- Subtypes of Social Phobia and Clinical Implication of Offensive Subtype
- The Effects of Cognitive Behavioral Group Therapy Improving Social Cognition on the Self efficacy, Relationship Function and Social Skills for Chronic Schizophrenia
- Personality Factor and Defense Machanism in Social Phobia Patients
- Coping Strategies for Stress in Patients with Social Phobia-Comparison of Generalized and Nongeneralized Social Phobia