Korean J Lab Med.
2007 Apr;27(2):133-138. 10.3343/kjlm.2007.27.2.133.
Hematologic and Clinical Features of 3q21q26 Syndrome: Extremely Poor Prognosis and Association with Central Diabetes Insipidus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. ejseo@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1781473
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2007.27.2.133
Abstract
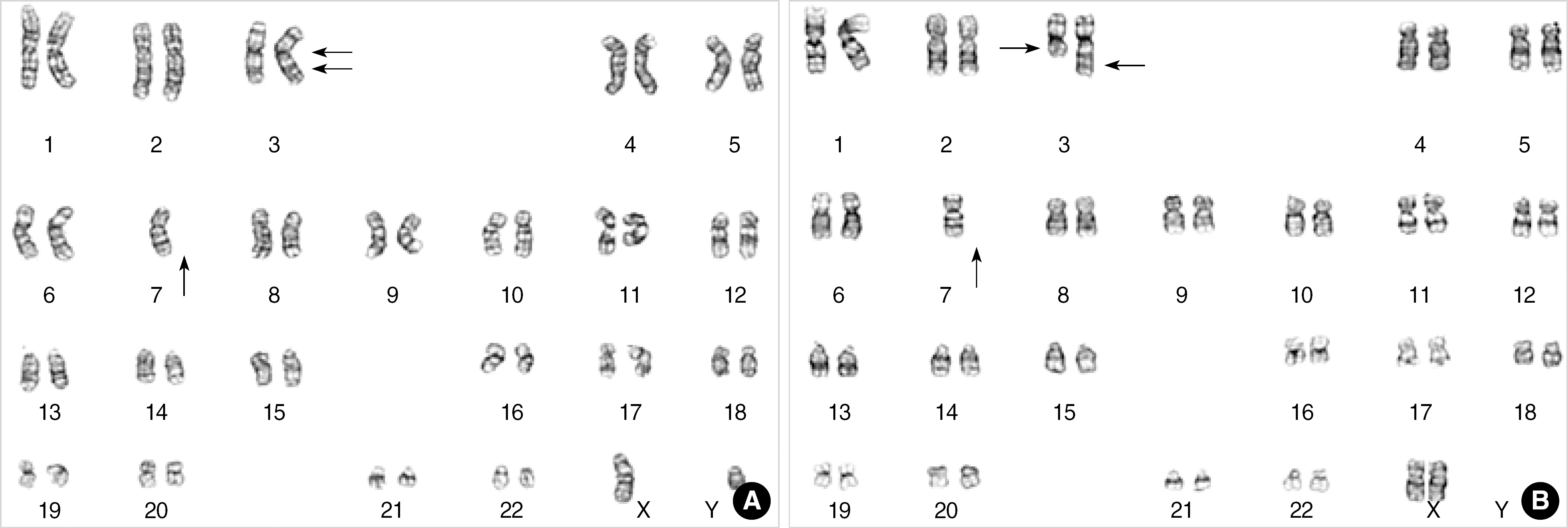
- BACKGROUND: 3q21q26 syndrome includes chromosomal abnormalities of inv(3)(q21q26), t(3;3) (q21;q26), and ins(3;3)(q26;q21q26). It causes hematological diseases by the leukemogenic mechanism that the enhancer of ribophorin I gene in 3q21 induces the transcription of ecotropic viral integration site-1 gene in 3q26. Recently, it has been proposed that the 3q21q26 syndrome may be preceded by diabetes insipidus (DI), particularly when combined with monosomy 7, and is a unique disease entity. METHODS: From May 2001 to June 2006, a total of 5 patients with hematologic malignancy were found to have 3q21q26 syndrome and monosomy 7. Laboratory findings, clinical data, and association with DI were investigated. RESULTS: The rearrangement type of 3q21q26 was inv(3)(q21q26) in four patients and t(3;3)(q21; q26) in one. These patients' French American British types were AML M1, M2, M4 and M7, showing evident dysmegakaryopoiesis. Aberrant antigenic expressions of CD7 and CD56 were observed. The platelet count was relatively high as AML. All the five patients were refractory or in early relapse. Patient 5 was diagnosed with AML M7 20 days after being diagnosed with DI. While DI was well controlled with oral desmopressin, leukemia was refractory to chemotherapy. CONCLUSIONS: This study supports the recent opinion that 3q21q26 syndrome with monosomy 7 combined with DI is a disease of unique characteristics. In the relation between DI and monosomy 7 or 3q21q26 syndrome, there has been no explanation about how acquired abnormality of hematopoietic cells affects production of DDAVP by neurohormonal cells in hypothalamus. The mechanism needs further study, and this research should contribute to the understanding of genetic roles in leukemia appearing in different forms.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Concomitant Inv(3)(q21q26) and Cryptic BCR/ABL1 Rearrangement in the Blast Crisis of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Hyejin Lee, Chihyun Cho, Min-Jung Kwon, Myung-Hyun Nam, Chang Kyu Lee, Young Kee Kim
Lab Med Online. 2011;1(3):163-167. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2011.1.3.7.
Reference
-
References
1. Testoni N, Borsaru G, Martinelli G, Carboni C, Ruggeri D, Ottaviani E, et al. 3q21 and 3q26 cytogenetic abnormalities in acute myeloblastic leukemia: biological and clinical features. Haematologica. 1999; 84:690–4.2. Ogawa S, Kurokawa M, Tanaka T, Mitani K, Inazawa J, Hangaishi A, et al. Structurally altered Evi-1 protein generated in the 3q21q26 syndrome. Oncogene. 1996; 13:183–91.3. Breccia M, Petti MC, Ottaviani E, Mancini M, D'Elia GM, Mecarocci S, et al. Diabetes insipidus as first manifestation of acute myeloid leukaemia with EVI-1-positive, 3q21q26 syndrome and T cell-line antigen expression: what is the EVI-1 gene role? Br J Haematol. 2002; 118:438–41.
Article4. Keung YK, Buss D, Powell BL, Pettenati M. Central diabetes insipidus and inv(3)(q21q26) and monosomy 7 in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2002; 136:78–81.
Article5. Lavabre-Bertrand T, Bourquard P, Chiesa J, Bertheas MF, Lefort G, Taib J, et al. Diabetes insipidus revealing acute myelogenous leukaemia with a high platelet count, monosomy 7 and abnormalities of chromosome 3: a new entity? Eur J Haematol. 2001; 66:66–9.
Article6. Fujisawa S, Tanabe J, Harano H, Kanamori H, Motomura S, Mohri H, et al. Acute minimally differentiated myeloid leukemia (M0) with inv(3)(q21q26). Leuk Lymphoma. 1999; 35:627–30.
Article7. Muller CI, Engelhardt M, Laubenberger J, Kunzmann R, Engelhardt R, Lubbert M. Myelodysplastic syndrome in transformation to acute myeloid leukemia presenting with diabetes insipidus: due to pituitary infiltration association with abnormalities of chromosomes 3 and 7. Eur J Haematol. 2002; 69:115–9.8. Lahortiga I, Vazquez I, Agirre X, Larrayoz MJ, Vizmanos JL, Gozzetti A, et al. Molecular heterogeneity in AML/MDS patients with 3q21q26 rearrangements. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2004; 40:179–89.
Article9. Schmidt HH, Pirc-Danoewinata H, Linkesch W, Strunk D, Wieser R. inv(3)(q21q26) in AML/MDS: monitoring of the malignant clone with interphase FISH. Haematologica. 2003; 88:ECR38.10. Secker-Walker LM, Mehta A, Bain B. Abnormalities of 3q21 and 3q26 in myeloid malignancy: a United Kingdom Cancer Cytogenetic Group study. Br J Haematol. 1995; 91:490–501.
Article11. Shi G, Weh HJ, Duhrsen U, Zeller W, Hossfeld DK. Chromosomal abnormality inv(3)(q21q26) associated with multilineage hematopoietic progenitor cells in hematopoietic malignancies. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1997; 96:58–63.
Article12. Shaffer LG, Tommerup N, editors. An International System for Human Cytogenetics Nomenclature (ISCN). Basel: Karger;2005.13. Lee CL. Double inversion (3)(q21q26) and monosomy 7 in a case of acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1999; 111:99–101.14. Schnittger S, Schoch C, Streubel B, Hinrichs HF, Otremba B, Parwaresch R, et al. A case of atypical myelodysplastic syndrome with micromegakaryocytes, normal platelet count, and t(3;12)(q21;p13) with inv(3)(q21q26). Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1997; 20:292–8.
Article15. Bouscary D, Fontenay-Roupie M, Chretien S, Hardy AC, Viguie F, Picard F, et al. Thrombopoietin is not responsible for the thrombocytosis observed in patients with acute myeloid leukemias and the 3q21q26 syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1995; 91:425–7.
Article16. Schnittger S, de Sauvage FJ, Le Paslier D, Fonatsch C. Refined chromosomal localization of the human thrombopoietin gene to 3q27-q28 and exclusion as the responsible gene for thrombocytosis in patients with rearrangements of 3q21 and 3q26. Leukemia. 1996; 10:1891–6.17. Lee YH, Lee KA, Kim SH. 3q chromosomal abnormalities associated with dysmegakaryopoiesis in acute leukemias. Korean J Clin Pathol. 2001; 21:18–23.18. Reiter E, Greinix H, Rabitsch W, Keil F, Schwarzinger I, Jaeger U, et al. Low curative potential of bone marrow transplantation for highly aggressive acute myelogenous leukemia with inversioin inv (3)(q21-q26) or homologous translocation t(3;3) (q21;q26). Ann Hematol. 2000; 79:374–7.19. Jolkowska J, Witt M. The EVI-1 gene–its role in pathogenesis of human leukemias. Leuk Res. 2000; 24:553–8.20. Buonamici S, Chakraborty S, Senyuk V, Nucifora G. The role of EVI1 in normal and leukemic cells. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2003; 31:206–12.
Article21. Nucifora G, Laricchia-Robbio L, Senyuk V. EVI1 and hematopoietic disorders: history and perspectives. Gene. 2006; 368:1–11.
Article22. Nieboer P, Vellenga E, Adriaanse R, van de Loosdrecht AA. Central diabetes insipidus preceding acute myeloid leukemia with t(3;12) (q26;p12). Neth J Med. 2000; 56:45–7.23. Kollen WJ, Ball LM, Snijder P, van Zelderen-Bhola SL, Egeler RM. Diabetes insipidus in a child with a monosomy-7 associated myelodysplastic syndrome and neurofibromatosis I. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2003; 40:257–9.
Article24. Hoyt PR, Bartholomew C, Davis AJ, Yutzey K, Gamer LW, Potter SS, et al. The Evi1 proto-oncogene is required at midgestation for neural, heart, and paraxial mesenchyme development. Mech Dev. 1997; 65:55–70.25. Mannucci PM. Desmopressin (DDAVP) in the treatment of bleeding disorders: the first 20 years. Blood. 1997; 90:2515–21.
Article26. Luckner G, Dunser MW, Jochberger S, Mayr VD, Wenzel V, Ulmer H, et al. Arginine vasopressin in 316 patients with advanced vasodilatory shock. Crit Care Med. 2005; 33:2659–66.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome in a Patient with Central Diabetes Insipidus and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Central Diabetes Insipidus Associated with Symptomatic Cytomegalovirus Infection in an Extremely Low Birth Weight Infant
- A Case of Central Diabetes Insipidus Associated with Brachycephaly
- Morphea and Verruca Plana Complicated in Central Diabetes Insipidus
- A case of Sheehan's syndrome with central diabetes insipidus showing hemorrhagic pituitary apoplexy