Ann Lab Med.
2014 Jan;34(1):76-79. 10.3343/alm.2014.34.1.76.
Fatal Pulmonary Mucormycosis Caused by Rhizopus microsporus in a Patient with Diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. seoyh@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 1781367
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2014.34.1.76
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
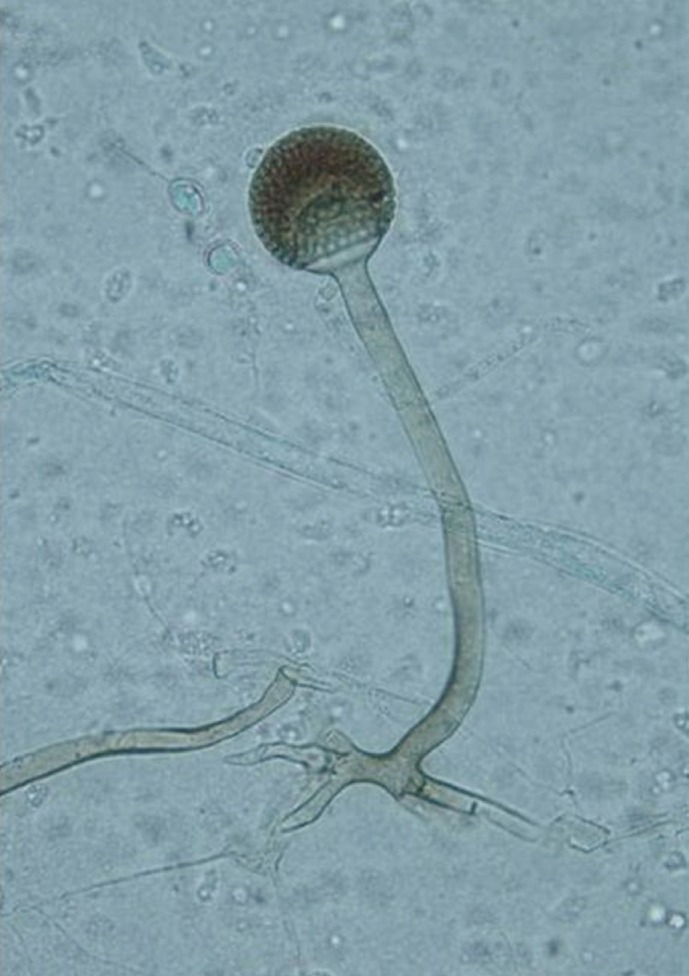
Figure
Reference
-
1. Garcia-Hermoso D, Dannaoui E, Lortholary O, Dromer F. Agents of systemic and subcutaneous mucormycosis and entomophthoromycosis. In : Versalovic J, Carroll KC, Funke G, Jorgensen JH, Landry ML, Warnock DW, editors. Manual of clinical microbiology. 10th ed. Washington, DC: ASM press;2011. p. 1880–1901.2. Ibrahim AS, Spellberg B, Walsh TJ, Kontoyiannis DP. Pathogenesis of mucormycosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2012; 54(Suppl 1):S16–S22. PMID: 22247441.
Article3. Hamilos G, Samonis G, Kontoyiannis DP. Pulmonary mucormycosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2011; 32:693–702. PMID: 22167397.
Article4. Ribes JA, Vanover-Sams CL, Baker DJ. Zygomycetes in human disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2000; 13:236–301. PMID: 10756000.
Article5. Schwarz P, Bretagne S, Gantier JC, Garcia-Hermoso D, Lortholary O, Dromer F, et al. Molecular identification of zygomycetes from culture and experimentally infected tissues. J Clin Microbiol. 2006; 44:340–349. PMID: 16455881.
Article6. Park Y. Sequence analysis of the internal transcribed spacer of ribosomal DNA in the genus Rhizopus. Mycobiology. 2005; 33:109–112. PMID: 24049483.7. Kontoyiannis DP, Lionakis MS, Lewis RE, Chamilos G, Healy M, Perego C, et al. Zygomycosis in a tertiary-care cancer center in the era of Aspergillus-active antifungal therapy: a case-control observational study of 27 recent cases. J Infect Dis. 2005; 191:1350–1360. PMID: 15776383.8. Roden MM, Zaoutis TE, Buchanan WL, Knudsen TA, Sarkisova TA, Schaufele RL, et al. Epidemiology and outcome of zygomycosis: a review of 929 reported cases. Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 41:634–653. PMID: 16080086.
Article9. Garg J, Sujatha S, Garg A, Parija SC. Nosocomial cutaneous zygomycosis in a patient with diabetic ketoacidosis. Int J Infect Dis. 2009; 13:e508–e510. PMID: 19428282.
Article10. de Mol P, Meis JF. Disseminated Rhizopus microsporus infection in a patient on oral corticosteroid treatment: a case report. Neth J Med. 2009; 67:25–28. PMID: 19155544.11. Vigouroux S, Morin O, Moreau P, Méchinaud F, Morineau N, Mahé B, et al. Zygomycosis after prolonged use of voriconazole in immunocompromised patients with hematologic disease: attention required. Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 40:e35–e37. PMID: 15712069.
Article12. Balajee SA, Borman AM, Brandt ME, Cano J, Cuenca-Estrella M, Dannaoui E, et al. Sequence-based identification of aspergillus, fusarium, and mucorales species in the clinical mycology laboratory: where are we and where should we go from here? J Clin Microbiol. 2009; 47:877–884. PMID: 19073865.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Rhinocerebral Mucormycosis Misdiagnosed as Herpes Zoster
- Chronic Recurrent Cutaneous Mucormycosis due to Rhizopus arrhizus
- Pulmonary mucormycosis with an appearance of consolidation
- A Case of Cutaneous Mucormycosis Occurring after Systemic Steroid Therapy
- A Case of Rhinocerebral Mucormycosis in a Diabetic Woman