Ann Lab Med.
2014 Jan;34(1):38-42. 10.3343/alm.2014.34.1.38.
Evaluation of a Novel Array-Based Toxoplasma, Rubella, Cytomegalovirus, and Herpes Simplex Virus IgG Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay and Its Comparison with Virion/Serion Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assays
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Suzhou Municipal Hospital, Suzhou Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Suzhou, China. zhongqiao1983@163.com
- KMID: 1781358
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2014.34.1.38
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
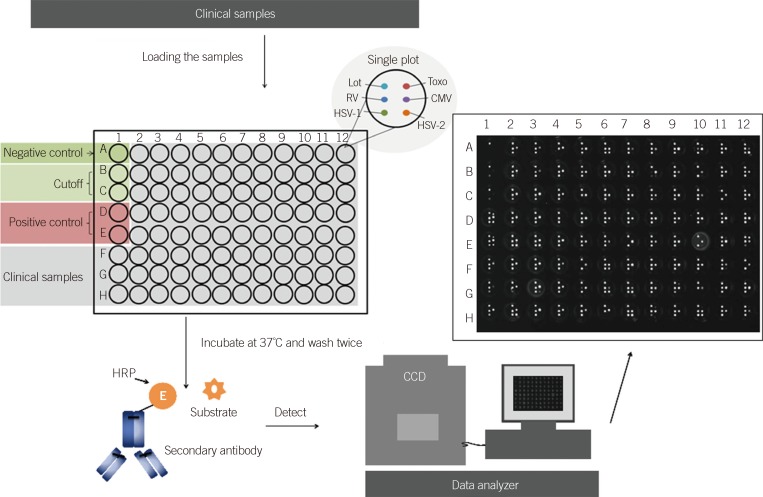
The dramatic increase in use of the IgG test for toxoplasma, rubella, cytomegalovirus (CMV), and herpes simplex virus (HSV) [TORCH] has led to the requirement for a high-efficiency method that can be used in the clinical laboratory. This study aimed to compare the results of BGI-Array ELISA TORCH IgG (BGI-GBI, China) screening method to those of Virion/Serion TORCH IgG ELISA (Virion/Serion, Germany).
METHODS
Serum specimens (n=400) submitted for routine IgG testing by Virion/Serion ELISA were also tested using the BGI-Array ELISA method. The agreements of these two kinds of method were analyzed by kappa-coefficients calculation.
RESULTS
Following repeat testing, the BGI-Array ELISA TORCH IgG assays demonstrated agreements of 99.5% (398/400 specimens), 98% (392/400 specimens), 99% (396/400 specimens), and 99.5% (398/400 specimens), respectively. The BGI-Array ELISA IgG assays provided results comparable to Virion/Serion ELISA results, with kappa-coefficients showing near-perfect agreement for the HSV (kappa=0.87), rubella (kappa=0.92) and CMV (kappa=0.93) and substantial agreement for the toxoplasma (kappa=0.80) IgG assays. The use of the BGI-Array ELISA TORCH IgG assays could reduce the turnaround time (1.5 hr vs. 5 hr by Virion/Serion ELISA for 100 specimens) and were easy to use.
CONCLUSIONS
BGI-Array ELISA TORCH IgG shows a good agreement with Virion/Serion ELISA methods and is suitable for clinical application.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Antibodies, Viral/blood
Cytomegalovirus/immunology/*metabolism
*Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Humans
Immunoglobulin G/*analysis/blood
Protozoan Infections/diagnosis
Reagent Kits, Diagnostic
Rubella virus/immunology/*metabolism
Sensitivity and Specificity
Simplexvirus/immunology/*metabolism
Toxoplasma/immunology/*metabolism
Virion/*immunology/metabolism
Virus Diseases/diagnosis
Antibodies, Viral
Immunoglobulin G
Reagent Kits, Diagnostic
Figure
Reference
-
1. TORCH syndrome and TORCH screening. Lancet. 1990; 335:1559–1561. PMID: 1972489.2. Newton ER. Diagnosis of perinatal TORCH infections. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1999; 42:59–70. quiz 174-5. PMID: 10073301.
Article3. Stegmann BJ, Carey JC. TORCH Infections. Toxoplasmosis, Other (syphilis, varicella-zoster, parvovirus B19), Rubella, Cytomegalovirus (CMV), and Herpes infections. Curr Womens Health Rep. 2002; 2:253–258. PMID: 12150751.4. Boutall A, Urban MF, Stewart C. Diagnosis, etiology, and outcome of fetal ascites in a South African hospital. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2011; 115:148–152. PMID: 21798534.
Article5. Binnicker MJ, Jespersen DJ, Harring JA. Multiplex detection of IgM and IgG class antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii, rubella virus, and cytomegalovirus using a novel multiplex flow immunoassay. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2010; 17:1734–1738. PMID: 20861325.6. Jiang L, Yu Z, Tang Z, Jiang T, Zhang C, Lu Z. Protein arrays based on biotin-streptavidin system for the simultaneous detection of TORCH infections. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2008; 8:2286–2292. PMID: 18572639.
Article7. Owen WE, Martins TB, Litwin CM, Roberts WL. Performance characteristics of six IMMULITE 2000 TORCH assays. Am J Clin Pathol. 2006; 126:900–905. PMID: 17074686.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Measurement of Rubella Antibodies among Korean Children by Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay
- Purification and use of herpes simplex virus(HSV) antigens form ELISA of anti-HSV igG and igM
- Evaluation of enzymum system@(ES-300) for enzyme linked immunosorbent assay: comparison with RIA and CLIA for T3, T4, fT4 and TSH
- Evaluation of enzymum system@(ES-300) for enzyme linked immunosorbent assay: comparison with RIA and CLIA for T3, T4, fT4 and TSH
- A Case of Herpes Simplex Virus Induced Focal Brainstem Encephalitis: A Case Report