New Insights in the Clinical Understanding of Behcet's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology and Cutaneous Biology Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dbang@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1779684
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.1.35
Abstract
- Behcet's disease is a chronic relapsing multisystemic inflammatory disorder characterized by four major symptoms (oral aphthous ulcers, genital ulcers, skin lesions, and ocular lesions) and occasionally by five minor symptoms (arthritis, gastrointestinal ulcers, epididymitis, vascular lesions, and central nervous system symptoms). Although the etiology of Behcet's disease is still unknown, there have been recent advances in immunopathogenic studies, genome-wide association studies, animal models, diagnostic markers, and new biological agents. These advances have improved the clinical understanding of Behcet's disease and have enabled us to develop new treatment strategies for this intractable disease, which remains one of the leading causes of blindness.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibodies and Joint Involvement in Behçet's Disease
Sung Bin Cho, Ju Hee Lee, Keun Jae Ahn, Byung Gi Bae, Taegyun Kim, Yong-Beom Park, Soo-Kon Lee, Kwang Hoon Lee, Dongsik Bang
Yonsei Med J. 2012;53(4):759-764. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.4.759.Epidemiologic and Etiological Features of Korean Patients With Behçet’s Disease
Soo Hyun Choi, BA, Do-Young Kim
J Rheum Dis. 2021;28(4):183-191. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2021.28.4.183.Carpal Tunnel Syndrome in Behçet's Disease
Jungsoo Lee, Suhyun Cho, Do Young Kim, Zhenlong Zheng, Hoon Park, Dongsik Bang
Yonsei Med J. 2015;56(4):1015-1020. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.4.1015.Behçet's Disease with Deep Vaginal Ulcer Diagnosed for the First Time during Pregnancy
Eun Hye Lee, Tae Kyung Lee, JoonHo Lee
Perinatology. 2019;30(2):110-115. doi: 10.14734/PN.2019.30.2.110.Recurrent focal myofasciitis of Behçet syndrome mimics infectious myofasciitis: a case report
Sang Wan Chung, Joo Ho Lee, You-Jung Ha, Eun Ha Kang, Yun Jong Lee
J Rheum Dis. 2023;30(4):268-271. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2023.0020.
Reference
-
1. Feigenbaum A. Description of Behçet's syndrome in the Hippocratic third book of endemic diseases. Br J Ophthalmol. 1956. 40:355–357.
Article2. Behçet H. Über rezidivierende, aphthöse, durch ein Virus verursachte Geschwüre am Auge, und an den Genitalien. Dermatol Wochenschr. 1937. 105:1152–1157.3. Behçet H. Some observations on the clinical picture of the so-called triple symptom complex. Dermatologica. 1940. 81:73–83.
Article4. Jensen T. Sur les ulcerations aphteuses de la muqueues de la bouche et de la peau genitale combiness avec les sumptomes oculaires (syndrome Behçet). Acta Derm Venereol. 1941. 22:64–79.5. Sezer FN. The isolation of a virus as the cause of Behcet's diseases. Am J Ophthalmol. 1953. 36:301–315.6. Bouzas A. The Adamantiades-Behçet's syndrome. Bull Soc Hellen Ophthalmol. 1956. 24:41.7. Strachan RW, Wigzell FW. Polyarthritis in Behcet's multiple symptom complex. Ann Rheum Dis. 1963. 22:26–35.
Article8. Robinson HMJ, McCrumb FRJ. Comparative analysis of the mucocutaneous ocular syndromes: report of eleven cases and review of the literature. Arch Dermatol Syphil. 1950. 61:539.9. Firestein GS, Gruber HE, Weisman MH, Zvaifler NJ, Barber J, O'Duffy JD. Mouth and genital ulcers with inflamed cartilage: MAGIC syndrome. Five patients with features of relapsing polychondritis and Behçet's disease. Am J Med. 1985. 79:65–72.
Article10. Levine JA, O'Duffy JD. Godeau P, Wechsler B, editors. Pseudo-Behçet's syndrome-a description of twenty-three cases. Behçet's disease: Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Behçet's disease. 1993. June 30 to July 1, 1993; Paries, France. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers;295–298.11. Lee S, Bang D, Lee ES, Sohn S. Behçet's disease: a guide to its clinical understanding. 2001. 1st ed. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer Verlag.12. Lee S. Bang D, Lee ES, Lee S, editors. Behçet's disease or Behçet's syndrome-considerations for the unified diagnosis related terminology. Behçet's disease: Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Behçet's disease. 2000. May 27-29, 2000; Seoul, Korea. Seoul: Design Mecca;40–42.13. Barnes CG. Yazici Y, Yazici H, editors. History and diagnosis. Behçet's syndrome. 2010. 1st ed. New York: Springer;7–33.
Article14. Verity DH, Marr JE, Ohno S, Wallace GR, Stanford MR. Behçet's disease, the Silk Road and HLA-B51: historical and geographical perspectives. Tissue Antigens. 1999. 54:213–220.
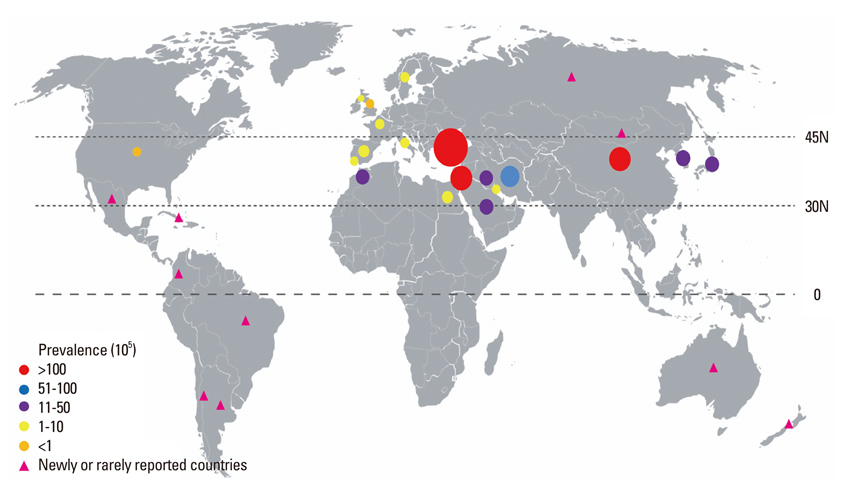
Article15. Davatchi F, Shahram F, Chams-Davatchi C, Shams H, Nadji A, Akhlaghi M, et al. Behcet's disease: from East to West. Clin Rheumatol. 2010. 29:823–833.
Article16. Bang D, Lee ES, Lee S. Eun HC, Kim SC, Lee WS, editors. Behçet's disease. Asian Skin and Skin Diseases: special book of the 22nd World Congress of Dermatology. 2011. May 24-29, 2011; Seoul, Korea. Seoul: MEDrang Inc;313–325.17. Chung YL, Bang DS, Lee ES, Lee SN, Mok JW, Park KS. Behçet's disease: the first Mongolian case in literature showing HLA B51, MICA gene type *5/*6. Yonsei Med J. 2003. 44:935–938.
Article18. Liozon E, Roussin C, Puéchal X, Garou A, Valadier P, Périnet I, et al. Behçet's disease in East African patients may not be unusual and is an HLA-B51 negative condition: a case series from Mayotte (Comoros). Joint Bone Spine. 2011. 78:166–170.
Article19. Davatchi F, Shahram F, Chams-Davatchi C, Shams H, Nadji A, Akhlaghi M, et al. Behéet's disease in Iran: analysis of 6500 cases. Int J Rheum Dis. 2010. 13:367–373.20. Yurdakul S, Yazici Y. Yazici Y, Yazici H, editors. Epidemiology of Behçet's syndrome and regional differences in disease expression. Behçet's syndrome. 2010. 1st ed. New York: Springer;35–52.21. Tugal-Tutkun I. Behçet disease in the developing world. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 2010. 50:87–98.
Article22. Yazici Y, Yurdakul S, Yazici H. Behçet's syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2010. 12:429–435.
Article23. Yurdakul S, Günaydin I, Tüzün Y, Tankurt N, Pazarli H, Ozyazgan Y, et al. The prevalence of Behçet's syndrome in a rural area in northern Turkey. J Rheumatol. 1988. 15:820–822.24. Yesudian PD, Edirisinghe DN, O'Mahony C. Behçet's disease. Int J STD AIDS. 2007. 18:221–227.
Article25. Sakane T, Takeno M, Suzuki N, Inaba G. Behçet's disease. N Engl J Med. 1999. 341:1284–1291.
Article26. Azizlerli G, Köse AA, Sarica R, Gül A, Tutkun IT, Kulaç M, et al. Prevalence of Behçet's disease in Istanbul, Turkey. Int J Dermatol. 2003. 42:803–806.
Article27. Kim DK, Chang SN, Bang D, Lee ES, Lee S. Clinical analysis of 40 cases of childhood-onset Behçet's disease. Pediatr Dermatol. 1994. 11:95–101.
Article28. Sungur G, Hazirolan D, Hekimoglu E, Kasim R, Duman S. Late-onset Behçet's disease: demographic, clinical, and ocular features. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010. 248:1325–1330.
Article29. Fietta P. Behçet's disease: familial clustering and immunogenetics. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005. 23:S96–S105.30. Bang DS, Oh SH, Lee KH, Lee ES, Lee SN. Influence of sex on patients with Behçet's disease in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2003. 18:231–235.
Article31. Bang D, Chun YS, Haam IB, Lee ES, Lee S. The influence of pregnancy on Behçet's disease. Yonsei Med J. 1997. 38:437–443.
Article32. Ohno S, Ohguchi M, Hirose S, Matsuda H, Wakisaka A, Aizawa M. Close association of HLA-Bw51 with Behçet's disease. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982. 100:1455–1458.33. Kaneko F, Oyama N, Yanagihori H, Isogai E, Yokota K, Oguma K. The role of streptococcal hypersensitivity in the pathogenesis of Behçet's Disease. Eur J Dermatol. 2008. 18:489–498.34. Wallace GR, Niemczyk E. Genetics in ocular inflammation--basic principles. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2011. 19:10–18.
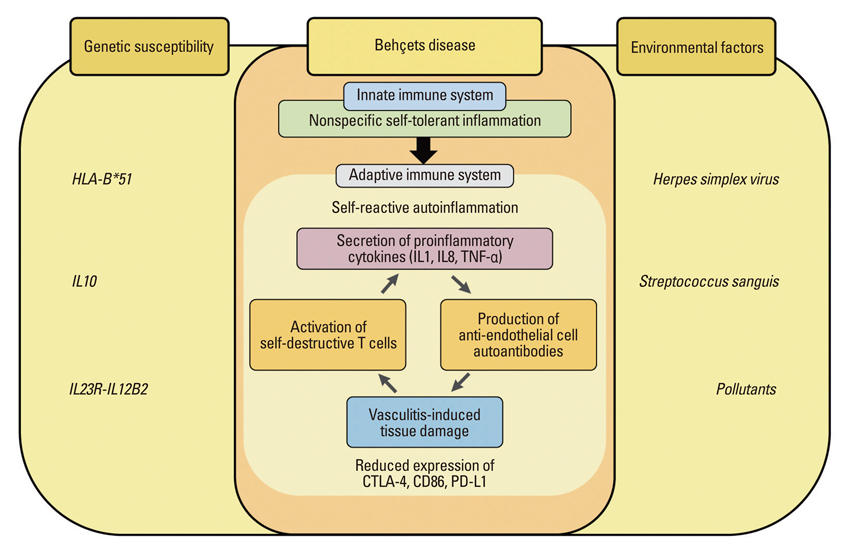
Article35. Remmers EF, Cosan F, Kirino Y, Ombrello MJ, Abaci N, Satorius C, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants in the MHC class I, IL10, and IL23R-IL12RB2 regions associated with Behçet's disease. Nat Genet. 2010. 42:698–702.
Article36. Mizuki N, Meguro A, Ota M, Ohno S, Shiota T, Kawagoe T, et al. Genome-wide association studies identify IL23R-IL12RB2 and IL10 as Behçet's disease susceptibility loci. Nat Genet. 2010. 42:703–706.
Article37. Lew W, Chang JY, Jung JY, Bang D. Increased expression of interleukin-23 p19 mRNA in erythema nodosum-like lesions of Behçet's disease. Br J Dermatol. 2008. 158:505–511.
Article38. Shim J, Lee ES, Park S, Bang D, Sohn S. CD4(+) CD25(+) regulatory T cells ameliorate Behçet's disease-like symptoms in a mouse model. Cytotherapy. 2011. 13:835–847.
Article39. Lee KH, Chung HS, Kim HS, Oh SH, Ha MK, Baik JH, et al. Human alpha-enolase from endothelial cells as a target antigen of anti-endothelial cell antibody in Behçet's disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:2025–2035.
Article40. Lee J, Wu W, Lee H, Chang J, Bang D, Lee K. The cross-reactivity of anti human α-enolase antibody in the sera of Behçet's disease patients to Streptococcus sanguis antigen. Korean J Invest Dermatol. 2005. 12:83–92.41. Lee S, Bang D, Cho YH, Lee ES, Sohn S. Polymerase chain reaction reveals herpes simplex virus DNA in saliva of patients with Behçet's disease. Arch Dermatol Res. 1996. 288:179–183.
Article42. Sohn S, Lee ES, Bang D, Lee S. Behçet's disease-like symptoms induced by the Herpes simplex virus in ICR mice. Eur J Dermatol. 1998. 8:21–23.43. Sohn S, Bang D, Lee ES, Kwon HJ, Lee SI, Lee S. Experimental studies on the antiviral agent famciclovir in Behçet's disease symptoms in ICR mice. Br J Dermatol. 2001. 145:799–804.
Article44. Sim JH, Park MJ, Park S, Lee ES. Altered expression of costimulatory molecules in Behçet's disease according to clinical activity. Br J Dermatol. 2011. 164:1285–1291.
Article45. Direskeneli H. Autoimmunity vs autoinflammation in Behcet's disease: do we oversimplify a complex disorder? Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006. 45:1461–1465.
Article46. Stojanov S, Kastner DL. Familial autoinflammatory diseases: genetics, pathogenesis and treatment. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2005. 17:586–599.
Article47. Criteria for diagnosis of Behçet's disease. International Study Group for Behçet's Disease. Lancet. 1990. 335:1078–1080.48. Kurokawa MS, Yoshikawa H, Suzuki N. Behçet's disease. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2004. 25:557–568.
Article49. Oh SH, Han EC, Lee JH, Bang D. Comparison of the clinical features of recurrent aphthous stomatitis and Behçet's disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009. 34:e208–e212.
Article50. Cheon JH, Kim ES, Shin SJ, Kim TI, Lee KM, Kim SW, et al. Development and validation of novel diagnostic criteria for intestinal Behçet's disease in Korean patients with ileocolonic ulcers. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009. 104:2492–2499.
Article51. Denecke T, Staeck O, Amthauer H, Hänninen EL. PET/CT visualises inflammatory activity of pulmonary artery aneurysms in Behçet disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2007. 34:970.
Article52. Cho SB, Yun M, Lee JH, Kim J, Shim WH, Bang D. Detection of cardiovascular system involvement in Behçet's disease using fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011. 40:461–466.
Article53. Coskun B, Saral Y, Gödekmerdan A, Erden I, Coskun N. Activation markers in Behçet's disease. Skinmed. 2005. 4:282–286.
Article54. Han EC, Cho SB, Ahn KJ, Oh SH, Kim J, Kim DS, et al. Expression of Pro-inflammatory Protein S100A12 (EN-RAGE) in Behçet's Disease and Its Association with Disease Activity: a Pilot Study. Ann Dermatol. 2011. 23:313–320.
Article55. Oh SH, Lee KY, Lee JH, Bang D. Clinical manifestations associated with high titer of anti-streptolysin O in Behcet's disease. Clin Rheumatol. 2008. 27:999–1003.
Article56. Bang D. Clinical spectrum of Behçet's disease. J Dermatol. 2001. 28:610–613.
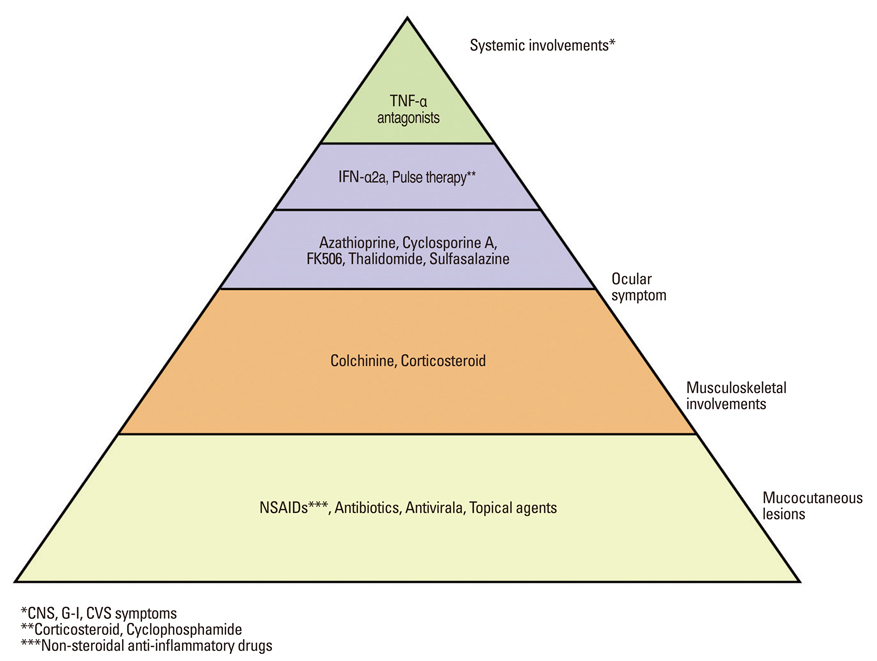
Article57. Bang D. Treatment of Behçet's disease. Yonsei Med J. 1997. 38:401–410.
Article58. Arayssi T, Hamdan A. New insights into the pathogenesis and therapy of Behçet's disease. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2004. 4:183–188.
Article59. Hatemi G, Silman A, Bang D, Bodaghi B, Chamberlain AM, Gul A, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of Behçet disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. 67:1656–1662.60. Hamuryudan V, Kötter I. Yazici Y, Yazici H, editors. Medical management of Behçet's syndrome. Behçet's syndrome. 2010. 1st ed. New York: Springer;317–338.61. Evereklioglu C. Current concepts in the etiology and treatment of Behçet disease. Surv Ophthalmol. 2005. 50:297–350.
Article62. Pato E, Muñoz-Fernández S, Francisco F, Abad MA, Maese J, Ortiz A, et al. Systematic review on the effectiveness of immunosuppressants and biological therapies in the treatment of autoimmune posterior uveitis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011. 40:314–323.
Article63. Al-Otaibi LM, Porter SR, Poate TW. Behçet's disease: a review. J Dent Res. 2005. 84:209–222.
Article64. Alexoudi I, Kapsimali V, Vaiopoulos A, Kanakis M, Vaiopoulos G. Evaluation of current therapeutic strategies in Behçet's disease. Clin Rheumatol. 2011. 30:157–163.
Article65. Alpsoy E, Akman A. Behçet's disease: an algorithmic approach to its treatment. Arch Dermatol Res. 2009. 301:693–702.
Article66. Gul A. Standard and novel therapeutic approaches to Behçet's disease. Drugs. 2007. 67:2013–2022.
Article67. Arida A, Fragiadaki K, Giavri E, Sfikakis PP. Anti-TNF agents for Behçet's disease: analysis of published data on 369 patients. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011. 41:61–70.
Article68. Cobo-Ibáñez T, del Carmen Ordóñez M, Muñoz-Fernández S, Madero-Prado R, Martín-Mola E. Do TNF-blockers reduce or induce uveitis? Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008. 47:731–732.
Article69. Wendling D, Paccou J, Berthelot JM, Flipo RM, Guillaume-Czitrom S, Prati C, et al. New Onset of Uveitis During Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Treatment for Rheumatic Diseases. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011. [Epub ahead of print].
Article70. Kaneko F, Togashi A, Saito S, Sakuma H, Oyama N, Nakamura K, et al. Behçet's disease (Adamantiades-Behçet's disease). Clin Dev Immunol. 2011. 2011:681956.
Article71. Ideguchi H, Suda A, Takeno M, Ueda A, Ohno S, Ishigatsubo Y. Behçet disease: evolution of clinical manifestations. Medicine (Baltimore). 2011. 90:125–132.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Behcet's Disease Associated with Pyoderma Gangrenosum
- Diagnostic criteria of Behcet's disease: problems and suggestions
- A Case of Pyoderma Gangrenosum Occurring in Behcet's Disease
- Update on the Treatment of Intestinal Behcet's Disease
- A Case of Pheochromocytoma Misdiagnosed as Activation of Behcet's Disease