Yonsei Med J.
2011 Mar;52(2):333-338. 10.3349/ymj.2011.52.2.333.
The Effects of a Single Bolus of Remifentanil on Corrected QT Interval Change during Sevoflurane Induction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. haewon7@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1779672
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2011.52.2.333
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Opioids may affect changes in the corrected QT interval (QTc) during anesthetic induction. This study examine whether a single bolus of remifentanil would prolong QTc after laryngeal mask airway (LMA) insertion during sevoflurane induction.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Forty women of American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status 1 (ASA PS1) undergoing gynecological surgery were studied. All patients were induced using three vital capacity inhalation inductions with 5% sevoflurane. Two minutes after induction, the inspiratory concentration of sevoflurane was reduced to 2%. Using double-blinded randomization, patients were allocated into one of two groups, receiving either saline (placebo group, n = 20) or 0.25 microg.kg-1 remifentanil (remifentanil group, n = 20) over a period of thirty seconds. Sixty seconds later, LMA insertion was performed. Recordings were taken with a 12-lead electrocardiogram at baseline, 2 min after induction and 1 and 3 min after LMA insertion. QTc was calculated by Bazett's formula. The mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR) were also measured at each time point.
RESULTS
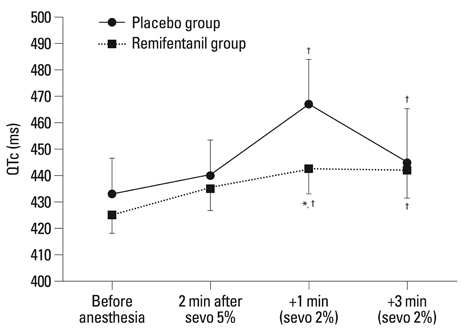
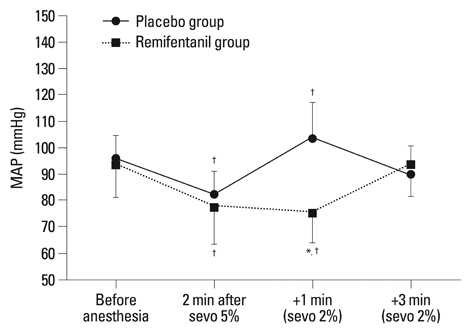
The QTc interval was significantly prolonged in the placebo group as compared to the remifentanil group at 1 min after LMA insertion (467.8 +/- 16.5 vs. 442.7 +/- 21.3 ms, p < 0.001). However, there was no significant difference in QTc at 3 min after LMA insertion between the two groups. MAP and HR were significantly higher in the placebo group (p < 0.001).
CONCLUSION
A single bolus of remifentanil is safe method to attenuate prolonged QTc associated with insertion of LMA.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Anesthetics, Inhalation/adverse effects/*pharmacology
Anesthetics, Intravenous/administration & dosage/*pharmacology
Electrocardiography/drug effects
Female
Gynecologic Surgical Procedures/adverse effects
Heart Rate/*drug effects
Humans
Methyl Ethers/adverse effects/*pharmacology
Middle Aged
Piperidines/*pharmacology
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Kidney Function in Living Donors Undergoing Nephrectomy by Sevoflurane or Desflurane Anesthesia
Min-Soo Kim, Jeong-Rim Lee, Myoung-Soo Kim, Sung-Yeon Ham, Seung-Ho Choi
Yonsei Med J. 2013;54(5):1266-1272. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.5.1266.
Reference
-
1. Booker PD, Whyte SD, Ladusans EJ. Long QT syndrome and anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 2003. 90:349–366.
Article2. Aypar E, Karagoz AH, Ozer S, Celiker A, Ocal T. The effects of sevoflurane and desflurane anesthesia on QTc interval and cardiac rhythm in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2007. 17:563–567.
Article3. Gupta A, Lawrence AT, Krishnan K, Kavinsky CJ, Trohman RG. Current concepts in the mechanisms and management of drug-induced QT prolongation and torsade de pointes. Am Heart J. 2007. 153:891–899.
Article4. Katchman AN, McGroary KA, Kilborn MJ, Kornick CA, Manfredi PL, Woosley RL, et al. Influence of opioid agonists on cardiac human ether-a-go-go-related gene K(+) currents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002. 303:688–694.
Article5. Wilton NC, Hantler CB. Congenital long QT syndrome: changes in QT interval during anesthesia with thiopental, vecuronium, fentanyl, and isoflurane. Anesth Analg. 1987. 66:357–360.6. Chang DJ, Kweon TD, Nam SB, Lee JS, Shin CS, Park CH, et al. Effects of fentanyl pretreatment on the QTc interval during propofol induction. Anaesthesia. 2008. 63:1056–1060.
Article7. Komatsu R, Turan AM, Orhan-Sungur M, McGuire J, Radke OC, Apfel CC. Remifentanil for general anaesthesia: a systematic review. Anaesthesia. 2007. 62:1266–1280.
Article8. Kweon TD, Nam SB, Chang CH, Kim MS, Lee JS, Shin CS, et al. The effect of bolus administration of remifentanil on QTc interval during induction of sevoflurane anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 2008. 63:347–351.
Article9. Johnston AJ, Hall JM, Levy DM. Anaesthesia with remifentanil and rocuronium for caesarean section in a patient with long-QT syndrome and an automatic implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2000. 9:133–136.
Article10. E14: The clinical evaluation of QT/QTc interval prolongation and proarrhytmhic potential for nonantiarrhythmic drugs. International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. (http://www.ich.org).11. Fujii Y, Tanaka H, Toyooka H. Circulatory responses to laryngeal mask airway insertion or tracheal intubation in normotensive and hypertensive patients. Can J Anaesth. 1995. 42:32–36.
Article12. Zaballos M, Jimeno C, Almendral J, Atienza F, Patiño D, Valdes E, et al. Cardiac electrophysiological effects of remifentanil: study in a closed-chest porcine model. Br J Anaesth. 2009. 103:191–198.
Article13. Lee MP, Kua JS, Chiu WK. The use of remifentanil to facilitate the insertion of the laryngeal mask airway. Anesth Analg. 2001. 93:359–362.
Article14. Grewal K, Samsoon G. Facilitation of laryngeal mask airway insertion: effects of remifentanil administered before induction with target-controlled propofol infusion. Anaesthesia. 2001. 56:897–901.15. Suzuki KS, Oohata M, Mori N. Multiple-deep-breath inhalation induction with 5% sevoflurane and 67% nitrous oxide: comparison with intravenous injection of propofol. J Anesth. 2002. 16:97–101.
Article16. Epstein RH, Stein AL, Marr AT, Lessin JB. High concentration versus incremental induction of anesthesia with sevoflurane in children: a comparison of induction times, vital signs, and complications. J Clin Anesth. 1998. 10:41–45.
Article17. Korpinen R, Saarnivaara L, Siren K. QT interval of the ECG, heart rate and arterial pressure during anaesthetic induction: comparative effects of alfentanil and esmolol. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1995. 39:809–813.
Article18. Sivalingam P, Kandasamy R, Madhavan G, Dhakshinamoorthi P. Conditions for laryngeal mask insertion. A comparison of propofol versus sevoflurane with or without alfentanil. Anaesthesia. 1999. 54:271–276.
Article19. Hall AP, Thompson JP, Leslie NA, Fox AJ, Kumar N, Rowbotham DJ. Comparison of different doses of remifentanil on the cardiovascular response to laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation. Br J Anaesth. 2000. 84:100–102.
Article20. Ma D, Sapsed-Byrne SM, Chakrabarti MK, Whitwam JG. Synergistic antinociceptive interaction between sevoflurane and intrathecal fentanyl in dogs. Br J Anaesth. 1998. 80:800–806.
Article21. Lischke V, Wilke HJ, Probst S, Behne M, Kessler P. Prolongation of the QT-interval during induction of anesthesia in patients with coronary artery disease. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1994. 38:144–148.
Article22. Weber G, Stark G, Stark U. Direct cardiac electrophysiologic effects of sufentanil and vecuronium in isolated guinea-pig hearts. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1995. 39:1071–1074.23. Moss AJ. Measurement of the QT interval and the risk associated with QTC interval prolongation: a review. Am J Cardiol. 1993. 72:23B–25B.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effect of remifentanil and lidocaine on time interval acquired for successful tracheal intubation in inhalational induction using sevoflurane
- Effects of Glycopyrrolate or Atropine on Hemodynamic Responses during Anesthetic Induction with Remifentanil and Sevoflurane in Elderly Patients
- Effects of intraoperative single bolus fentanyl administration and remifentanil infusion on postoperative nausea and vomiting
- Adequate sevoflurane concentrations in inhalation induction of sevoflurane following administration of remifentanil
- Effect of Low-dose Rocuronium on Tracheal Intubating Conditions during Induction of 8 vol% Sevoflurane with Remifentanil