Yonsei Med J.
2011 Mar;52(2):288-292. 10.3349/ymj.2011.52.2.288.
Splenic Abscess: A Single Institution Study and Review of the Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Gil Hospital, Incheon, Korea. kimkk@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 1779665
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2011.52.2.288
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to review our experience with splenic abscesses, with respect to the relevant aspects of splenic abscesses and treatment outcomes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed the cases of 18 patients who had splenic abscesses and who were treated at our hospital from November 1993 to December 2008.
RESULTS
The most common symptom at presentation was abdominal pain in 12 patients (66.7%). The median duration from symptom onset until establishment of a diagnosis was 22 days. Streptococcus viridians was the most common pathogen (27.8%), follow by Klebsiella pneumoniae (22.2%). The mortality rate during the inpatient period and the previous 90 days was 16.6%. Three of four patients with Klebsiella pneumoniae showed a single abscess pocket. Four patients (22.2%) underwent percutaneous drainage, eight (44.5%) recieved antibiotic treatment only and six (33.3%) underwent splenectomy.
CONCLUSION
There is no gold standard for treating splenic abscesses. Treatment should be customized for each patient.
MeSH Terms
-
Abscess/diagnosis/drug therapy/microbiology/surgery/*therapy
Adult
Aged
Anti-Bacterial Agents/therapeutic use
Drainage
Female
Humans
Klebsiella Infections/diagnosis/drug therapy/microbiology/surgery
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Male
Middle Aged
Splenectomy
Splenic Diseases/diagnosis/drug therapy/*microbiology/surgery
Streptococcal Infections/diagnosis/drug therapy/microbiology/surgery
Treatment Outcome
Viridans Streptococci
Young Adult
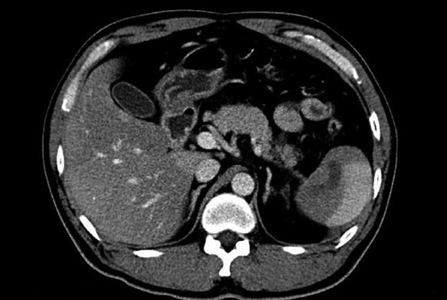
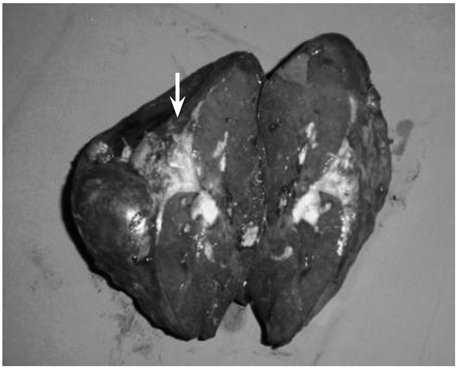
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Asymptomatic Splenic Cysts in an Immunocompromised Patient: Should They Be Investigated
Hyunjung Hwang, Myong Ki Baeg, Pumsoo Kim, Yu Jin Kim, Seok Hyung Kang
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2018;72(4):209-212. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2018.72.4.209.
Reference
-
1. Chun CH, Raff MJ, Contreras L, Varghese R, Waterman N, Daffner R, et al. Splenic abscess. Medicine (Baltimore). 1980. 59:50–65.
Article2. Nelken N, Ignatius J, Skinner M, Christensen N. Changing clinical spectrum of splenic abscess. A multicenter study and review of the literature. Am J Surg. 1987. 154:27–34.3. Ng KK, Lee TY, Wan YL, Tan CF, Lui KW, Cheung YC, et al. Splenic abscess: diagnosis and management. Hepatogastroenterology. 2002. 49:567–571.4. Chang KC, Chuah SK, Changchien CS, Tsai TL, Lu SN, Chiu YC, et al. Clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of splenic abscess: a review of 67 cases in a single medical center of Taiwan. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. 12:460–464.
Article5. de Bree E, Tsiftsis D, Christodoulakis M, Harocopos G, Schoretsanitis G, Melissas J. Splenic abscess: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Acta Chir Belg. 1998. 98:199–202.
Article6. Ooi LL, Nambiar R, Rauff A, Mack PO, Yap TL. Splenic abscess. Aust N Z J Surg. 1992. 62:780–784.
Article7. Smyrniotis V, Kehagias D, Voros D, Fotopoulos A, Lambrou A, Kostopanagiotou G, et al. Splenic abscess. An old disease with new interest. Dig Surg. 2000. 17:354–357.8. Chou YH, Hsu CC, Tiu CM, Chang T. Splenic abscess: sonographic diagnosis and percutaneous drainage or aspiration. Gastrointest Radiol. 1992. 17:262–266.
Article9. Green SL, Scott LK. Cryptogenic splenic abscess. Va Med. 1986. 113:164–166.10. Ralls PW, Quinn MF, Colletti P, Lapin SA, Halls J. Sonography of pyogenic splenic abscess. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1982. 138:523–525.
Article11. Carbonell AM, Kercher KW, Matthews BD, Joels CS, Sing RF, Heniford BT. Laparoscopic splenectomy for splenic abscess. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2004. 14:289–291.
Article12. Kang M, Saxena AK, Gulati M, Suri S. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous catheter drainage of splenic abscess. Pediatr Radiol. 2004. 34:271–273.
Article13. Thanos L, Dailiana T, Papaioannou G, Nikita A, Koutrouvelis H, Kelekis DA. Percutaneous CT-guided drainage of splenic abscess. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002. 179:629–632.
Article14. Tung CC, Chen FC, Lo CJ. Splenic abscess: an easily overlooked disease? Am Surg. 2006. 72:322–325.
Article15. Paris S, Weiss SM, Ayers WH Jr, Clarke LE. Splenic abscess. Am Surg. 1994. 60:358–361.16. Teich S, Oliver GC, Canter JW. The early diagnosis of splenic abscess. Am Surg. 1986. 52:303–307.17. Ooi LL, Leong SS. Splenic abscesses from 1987 to 1995. Am J Surg. 1997. 174:87–93.
Article18. Llenas-García J, Fernández-Ruiz M, Caurcel L, Enguita-Valls A, Vila-Santos J, Guerra-Vales JM. Splenic abscess: a review of 22 cases in a single institution. Eur J Intern Med. 2009. 20:537–539.
Article19. Allal R, Kastler B, Gangi A, Bensaid AH, Bouali O, Cherrak C, et al. Splenic abscesses in typhoid fever: US and CT studies. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1993. 17:90–93.20. Torres JR, Gotuzzo E, Istúriz R, Elster C, Wolff M, Northland R, et al. Salmonellal splenic abscess in the antibiotic era: a Latin American perspective. Clin Infect Dis. 1994. 19:871–875.
Article21. Sarr MG, Zuidema GD. Splenic abscess--presentation, diagnosis, and treatment. Surgery. 1982. 92:480–485.22. Gleich S, Wolin DA, Herbsman H. A review of percutaneous drainage in splenic abscess. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1988. 167:211–216.23. Ferraioli G, Brunetti E, Gulizia R, Mariani G, Marone P, Filice C. Management of splenic abscess: report on 16 cases from a single center. Int J Infect Dis. 2009. 13:524–530.
Article24. Westh H, Reines E, Skibsted L. Splenic abscesses: a review of 20 cases. Scand J Infect Dis. 1990. 22:569–573.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ruptured Splenic Abscess with Pneumoperitoneum: A Rare Presentation
- Splenic Abscess Associated with Endocarditis in a Patient on Hemodialysis: A Case Report
- A Case of Splenic Abscess with Multiple Fistulas Caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae
- A case Report of Splenic Abscess
- Combined Hepatic and Splenic Abscesses in a Patient with Ulcerative Colitis