Yonsei Med J.
2007 Apr;48(2):218-224. 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.2.218.
Serum Amyloid A as a Useful Indicator of Disease Activity in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Institute for Immunology and Immunologic Diseases, Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sookonlee@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 1779523
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2007.48.2.218
Abstract
- PURPOSE
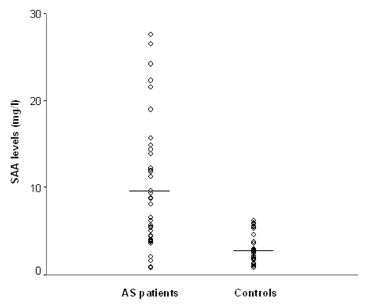
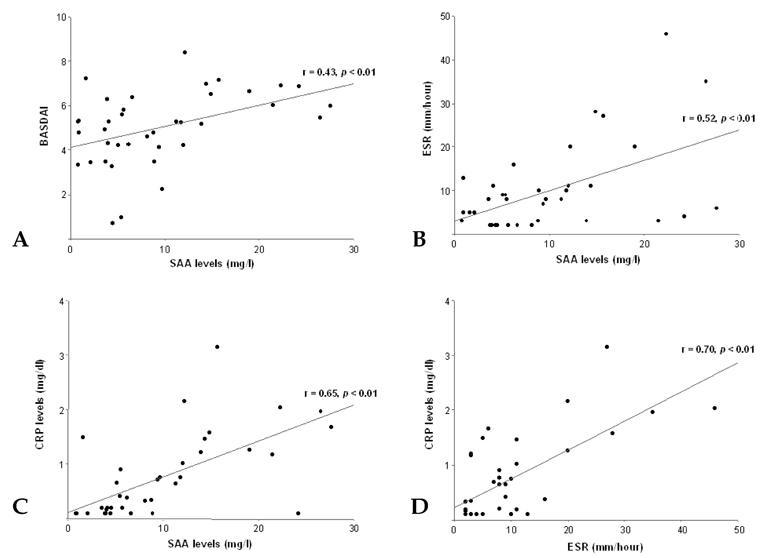
To investigate whether serum amyloid A (SAA) levels are increased in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and whether its levels correlate well with AS disease activity. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Thirty-eight patients with AS and 38 age- and sex-matched control subjects were enrolled in this cross-sectional study. Their SAA levels were quantitatively measured by immunonephelometry. An established, self-administered instrument for evaluating disease activity (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index, BASDAI) was used to measure and acute phase reactants, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP), in patients with AS. RESULTS: Patients with AS had a significantly higher mean SAA level than controls (9.52 +/- 7.49mg/L versus 2.73 +/- 1.57mg/L, p < 0.05), and the mean BASDAI score of patients with elevated SAA levels was significantly higher than that of patients with normal SAA levels (5.6 +/- 1.3 versus 4.4 +/- 1.5, p < 0.05). SAA levels showed significant correlations with BASDAI scores (r=0.431, p=0.007), ESR (r=0.521, p=0.001) and CRP levels (r=0.648, p < 0.001). Additionally, the correlation between ESR and CRP levels also appeared significant (r=0.703, p < 0.001). In those with normal ESR or CRP levels, SAA levels and BASDAI scores were elevated (p < 0.05) and showed a trend of positive correlation with one another. CONCLUSION: Our data showed that SAA levels were increased in patients with AS and correlated well with disease activity. These findings suggest that SAA can be used as a valuable indicator of disease activity in AS.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Serum Amyloid A Circulating Levels and Disease Activity in Patients with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Luca Cantarini, Teresa Giani, Antonella Fioravanti, Francesca Iacoponi, Gabriele Simonini, Ilaria Pagnini, Adriano Spreafico, Federico Chellini, Mauro Galeazzi, Rolando Cimaz
Yonsei Med J. 2012;53(5):1045-1048. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.5.1045.Coexistence of AA and AL Cardiac Amyloidosis in a Patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis Accompanying Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance
Woohyeon Kim, Seon A Kim, Kyung Jin Yun, Soo Jin Na, Ji In Hyun, Jung Im Jung, Seung-Ki Kwok, Sung-Hwan Park
J Rheum Dis. 2014;21(3):151-155. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2014.21.3.151.
Reference
-
1. Uhlar CM, Whitehead AS. Serum amyloid A, the major vertebrate acute-phase reactant. Eur J Biochem. 1999. 265:501–523.2. Hoffman JS, Benditt EP. Changes in high density lipoprotein content following endotoxin administration in the mouse. Formation of serum amyloid protein-rich subfractions. J Biol Chem. 1982. 257:10510–10517.3. Marhaug G. Three assays for the characterization and quantitation of human serum amyloid A. Scand J Immunol. 1983. 18:329–338.4. Dowton SB, Peters CN, Jestus JJ. Regulation of serum amyloid A gene expression in Syrian hamsters by cytokines. Inflammation. 1991. 15:391–397.5. Strissel KJ, Girard MT, West-Mays JA, Rinehart WB, Cook JR, Brinckerhoff CE, et al. Role of serum amyloid A as an intermediate in the IL-1 and PMA-stimulated signaling pathways regulating expression of rabbit fibroblast collagenase. Exp Cell Res. 1997. 237:275–287.6. O'Hara R, Murphy EP, Whitehead AS, FitzGerald O, Bresnihan B. Acute-phase serum amyloid A production by rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue. Arthritis Res. 2000. 2:142–144.7. Vallon R, Freuler F, Desta-Tsedu N, Robeva A, Dawson J, Wenner P, et al. Serum amyloid A (apoSAA) expression is up-regulated in rheumatoid arthritis and induces transcription of matrix metalloproteinases. J Immunol. 2001. 166:2801–2807.8. Shimojima Y, Matsuda M, Gono T, Ishii W, Ikeda S. Serum amyloid A as a potent therapeutic marker in a refractory patient with polymyalgia rheumatica. Intern Med. 2005. 44:1009–1012.9. Salazar A, Pinto X, Mana J. Serum amyloid A and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol: serum markers of inflammation in sarcoidosis and other systemic disorders. Eur J Clin Invest. 2001. 31:1070–1077.10. van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984. 27:361–368.11. Garrett S, Jenkinson T, Kennedy LG, Whitelock H, Gaisford P, Calin A. A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index. J Rheumatol. 1994. 21:2286–2291.12. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. User demonstration of performance for precision and accuracy; proposed guideline EP15-P. 1998. Wayne, PA: NCCLS.13. Lance NJ, Curran JJ. Amyloidosis in a case of ankylosing spondylitis with a review of the literature. J Rheumatol. 1991. 18:100–103.14. van der Linden S, van der Heijde D. Clinical aspects, outcome assessment, and management of ankylosing spondylitis and postenteric reactive arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2000. 12:263–268.15. Kirwan J, Edwards A, Huitfeldt B, Thompson P, Currey H. The course of established ankylosing spondylitis and the effects of sulphasalazine over 3 years. Br J Rheumatol. 1993. 32:729–733.16. Scalapino KJ, Davis JC Jr. The treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Med. 2003. 2:159–165.17. Braun J, Brandt J, Listing J, Zink A, Alten R, Golder W, et al. Treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with infliximab: a randomised controlled multicentre trial. Lancet. 2002. 359:1187–1193.18. Rosenbaum JT. Effect of etanercept on iritis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. 50:3736–3737.19. Ortiz-Santamaria V, Valls-Roc M, Sanmarti M, Olive A. Anti-TNF treatment in secondary amyloidosis. Rheumatology. 2003. 42:1425–1426.20. Baraliakos X, Listing J, Rudwaleit M, Brandt J, Sieper J, Braun J. Radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis after two years of treatment with the tumour necrosis factor-α antibody infliximab. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. 64:1462–1466.21. Lange U, Boss B, Teichmann J, Klor HU, Neeck G. Serum amyloid A- an indicator of inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int. 2000. 19:119–122.22. Cunnane G, Grehan S, Geoghegan S, McCormack C, Shields D, Whitehead AS, et al. Serum amyloid A in the assessment of early inflammatory arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2000. 27:58–63.23. Marhaug G, Dowton SB. Serum amyloid A: an acute phase apolipoprotein and precursor of AA amyloid. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1994. 8:553–573.24. Hachulla E, Saile R, Parra HJ, Hatron PY, Gosset D, Fruchart JC, et al. Serum amyloid A concentrations in giant-cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica: a useful test in the management of the disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1991. 9:157–163.25. Yamane T, Yamauchi H, Abe N, Torio N, Shimada R, Senba T, et al. Serum amyloid A as a useful index of disease activity in polymyalgia rheumatica. Ryumachi. 2003. 43:544–548.26. Vinje O, Moller P, Mellbye J. Immunological variables and acute-phase reactants in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew's syndrome) and their relatives. Clin Rheumatol. 1984. 3:501–513.27. Ostensen M, Marhaug G, Husby G. Amyloid-related serum protein (SAA) during and after pregnancy in healthy women and women with rheumatic disease. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand[c]. 1985. 93:1–5.28. Hagihara K, Nishikawa T, Isobe T, Song J, Sugamata Y, Yoshizaki K. IL-6 plays a critical role in the synergistic induction of human serum amyloid A (SAA) gene when stimulated with proinflammatory cytokines as analyzed with an SAA isoform real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. 314:363–369.29. Thorn CF, Lu ZY, Whitehead AS. Regulation of the human acute phase serum amyloid A genes by tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6 and glucocorticoids in hepatic and epithelial cell lines. Scand J Immunol. 2004. 59:152–158.30. Gabay C, Kushner I. Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med. 1999. 340:448–454.31. Malle E, Steinmetz A, Raynes JG. Serum amyloid A (SAA): an acute phase protein and apolipoprotein. Atherosclerosis. 1993. 102:131–146.32. Kisilevsky R, Tam SP. Acute phase serum amyloid A, cholesterol metabolism, and cardiovascular disease. Pediatr Pathol Mol Med. 2002. 21:291–305.33. Cunnane G. Amyloid precursors and amyloidosis in inflammatory arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001. 13:67–73.34. Kluve-Beckerman B, Liepnieks JJ, Wang L, Benson MD. A cell culture system for the study of amyloid pathogenesis. Amyloid formation by peritoneal macrophages cultured with recombinant serum amyloid A. Am J Pathol. 1999. 155:123–133.35. Ray A, Zhang DH, Siegel MD, Ray P. Regulation of interleukin-6 gene expression by steroids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995. 762:79–87.36. Knudsen PJ, Dinarello CA, Strom TB. Glucocorticoids inhibit transcriptional and post-transcriptional expression of interleukin 1 in U937 cells. J Immunol. 1987. 139:4129–4134.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Study of ankylosing Spondylitis
- Clinieal Values of Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography ( SPECT ) in Ankylosing Spondylitis
- TNF-alpha Inhibitor Treatment in an Ankylosing Spondylitis Patient with Secondary Amyloidosis that Manifest with Diarrhea: A Case Report
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: Prevention And Surgical Correction Of Deformity
- Development of osteoporosis and the imbalance of RANKL/OPG in ankylosing spondylitis