Evaluating the Degree of Conformity of Papillary Carcinoma and Follicular Carcinoma to the Reported Ultrasonographic Findings of Malignant Thyroid Tumor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, The Catholic Medial Center, Korea. sljung1@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, The Catholic Medical Center, Kangnam St. Mary's Hospital, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, The Catholic Medical Center, St. Mary's Hospital, Korea.
- KMID: 1779433
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2007.8.3.192
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
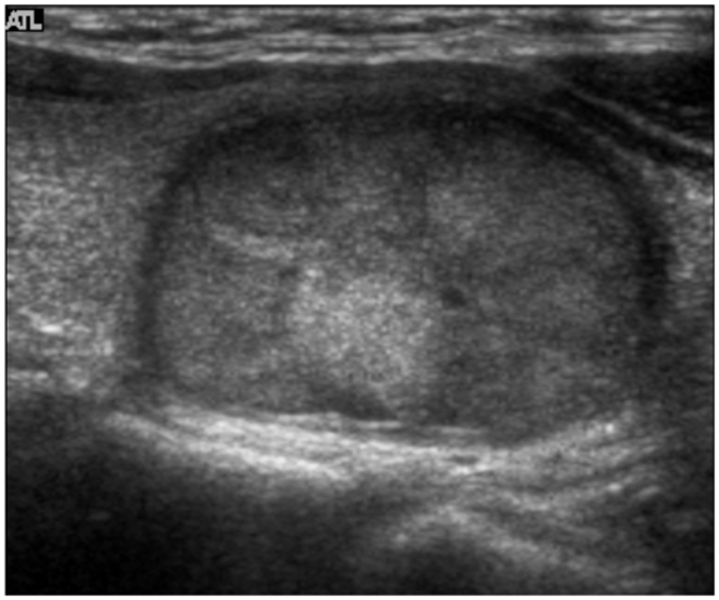
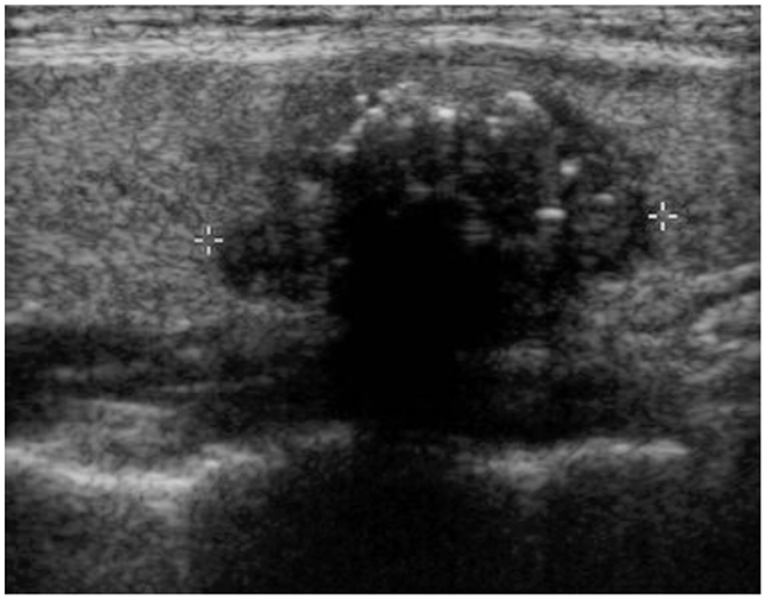
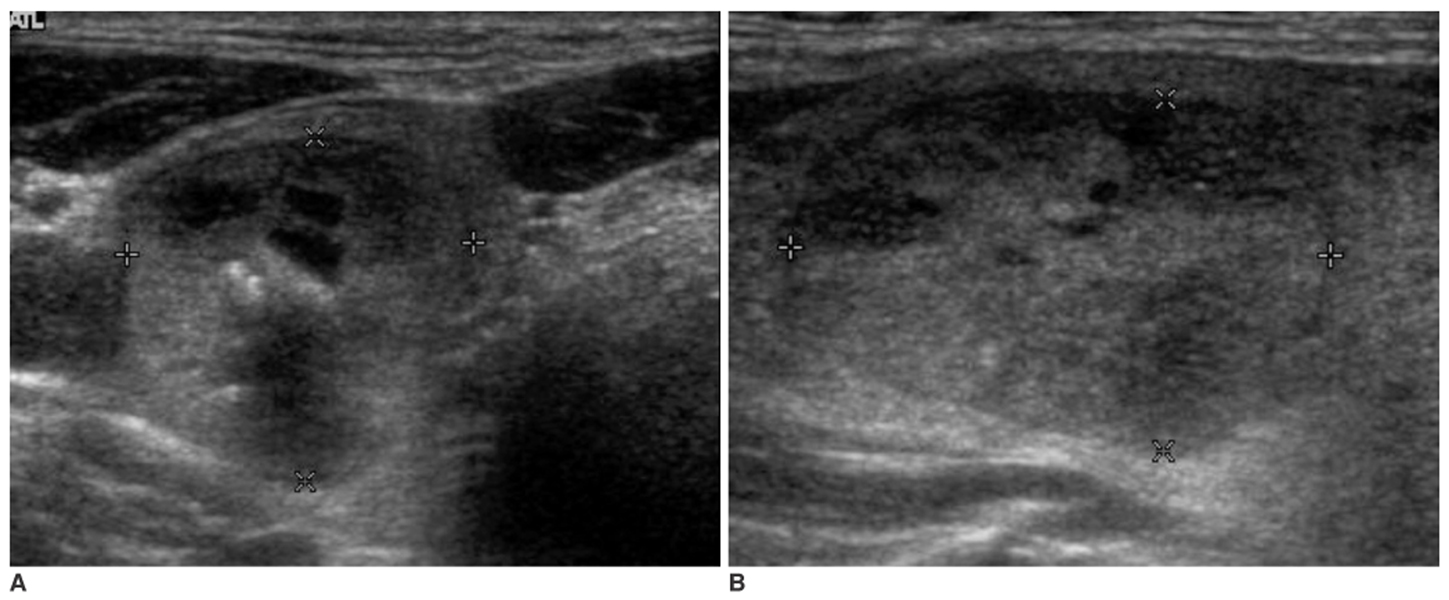
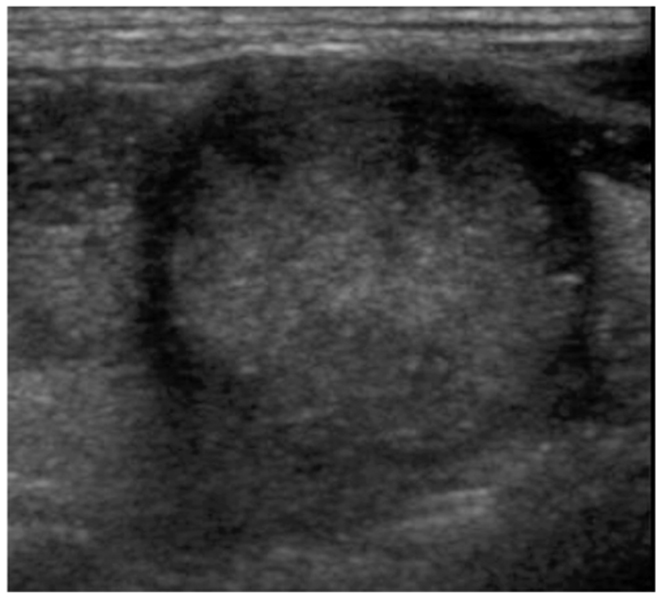
We wanted to evaluate the degree of conformity of papillary carcinoma and follicular carcinoma to the reported ultrasonographic findings of malignant thyroid tumor. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Between January 2003 and December 2004, fine needle aspiration biopsy was performed in 1,036 patients with palpable and non-palpable thyroid lesions. We retrospectively reviewed the ultrasonographic findings of patients with papillary carcinomas (n = 127) and follicular carcinomas (n = 23) that were proven by operation or fine needle aspiration biopsy. We analyzed the ultrasonographic findings of these nodules based on the reported ultrasonographic findings of malignant thyroid tumor: hypoechogenicity, a taller than wide orientation, a microlobulated or irregular margin, a thick hypoechoic rim (halo sign), microcalcification and cystic change. RESULTS: The echogenicity was hypoechoic in 72.4% (92/127) of the papillary carcinomas, but it was isoechoic in 65.2% (15/23) of the follicular carcinomas (p < 0.001). The nodule shape was tall or round in 74.1% of the papillary carcinomas, but it was flat in 72.7% of the follicular carcinomas (p < 0.001). The tumor margin was microlobulated or irregular in 92.9% of the papillary carcinomas and in 60.9% of the follicular carcinomas (p < 0.001). A hypoechoic rim was seen in 26% of the papillary carcinomas (thin rim: 13.4%, thick rim: 12.6%) and in 86.6% of the follicular carcinomas (thin rim: 39.1%, thick rim: 47.8%, p < 0.001). Microcalcifications were demonstrated in 33.9% of the papillary carcinomas and in none of the cases of follicular carcinoma (p < 0.001). A solid mass without cystic change were seen in 98.4% of the papillary carcinomas and in 82.6% of the follicular carcinomas (p < 0.001). CONCLUSION: The previously reported ultrasonography findings of malignant thyroid tumor are in conformity with most of the papillary carcinomas, but not with follicular carcinomas. The current ultrasonographic features for thyroid malignancy should be cautiously applied as the indication for needle aspiration biopsy so that follicular carcinomas are not missed by too narrow and strict biopsy criteria.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Impact of Nodule Size on Malignancy Risk Differs according to the Ultrasonography Pattern of Thyroid Nodules
Min Ji Hong, Dong Gyu Na, Jung Hwan Baek, Jin Yong Sung, Ji-Hoon Kim
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(3):534-541. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.3.534.Ultrasound-Guided Core Needle Biopsy Techniques for Intermediate or Low Suspicion Thyroid Nodules: Which Method is Effective for Diagnosis?
Soo Yeon Hahn, Jung Hee Shin, Young Lyun Oh, Ko Woon Park
Korean J Radiol. 2019;20(10):1454-1461. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.0841.Sonographic Analysis of Malignant Thyroid Nodules by Surgeon
Gun Go M.D., Jin Chul Koh M.D., Sang Yong Choi M.D., Shin Hee Park M.D., Kwang Chan Lee M.D., Chin Seung Kim M.D.
Korean J Endocr Surg. 2010;10(4):224-228. doi: 10.16956/kjes.2010.10.4.224.Comparison of Korean vs. American Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System in Malignancy Risk Assessment of Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules
Sunyoung Kang, Seul Ki Kwon, Hoon Sung Choi, Min Joo Kim, Young Joo Park, Do Joon Park, Sun Wook Cho
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1111-1120. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2021.1208.
Reference
-
1. Frates MC, Benson CB, Charbouneau JW, Cibas ES, Clark OH, Coleman BG, et al. Management of thyroid nodules detected at US: Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound consensus conference statement. Radiology. 2005. 237:794–800.2. Kim EK, Park CS, Chung WY, Oh KK, Kim DI, Lee JT, et al. New sonographic criteria for recommending fine-needle aspiration biopsy of nonpalpable solid nodules of the thyroid. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002. 178:687–691.3. Frates MC, Benson CB, Doubilet PM, Cibas ES, Marqusee E. Can color Doppler sonography aid in prediction of malignancy of thyroid nodules? J Ultrasound Med. 2003. 22:127–131.4. Papini E, Guglielmi R, Bianchini A, Crescenzi A, Taccogna S, Nardi F, et al. Risk of malignancy in nonpalpable thyroid nodules: predictive value of ultrasound and color-Doppler features. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 87:1941–1946.5. Chan BK, Desser TS, McDougall IR, Weigel RJ, Jeffrey RB Jr. Common and uncommon sonographic features of papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Ultrasound Med. 2003. 22:1083–1090.6. Nam-Goong IS, Kim HY, Gong G, Lee HK, Hong SJ, Kim WB, et al. Ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration of thyroid incidentaloma: correlation with pathologic findings. Clin Endocrinol. 2004. 60:21–28.7. Rumack CM, Wilson SR, Charboneau JW. Diagnostic Ultrasound. 2005. 3rd ed. St. Louis: Mosby;735–770.8. Fukunari N, Nagahama M, Sugino K, Mimura T, Ito K. Clinical evaluation of color Doppler imaging for the differential diagnosis of thyroid follicular lesions. World J Surg. 2004. 28:1261–1265.9. Iannuccilli JD, Cronan JJ, Monchik JM. Risk for malignancy of thyroid nodules as assessed by sonographic criteria: the need for biopsy. J Ultrasound Med. 2004. 23:1455–1464.10. Wienke JR, Chong WK, Fielding JR, Zou KH, Mittelstaedt CA. Sonographic features of benign thyroid nodules: interobserver reliability and overlap with malignancy. J Ultrasound Med. 2003. 22:1027–1031.11. Pellitteri PK, McCaffrey TV. Tumor and tumor-like lesion in thyroid endocrine surgery of the head and neck. 2002. 1st ed. Pennsylvania: Singular publishing group;21–47.12. Miyakawa M, Onoda N, Etoh M, Fukuda I, Takano K, Okamoto T, et al. Diagnosis of thyroid follicular carcinoma by the vascular pattern and velocimeteric parameters using high resolution pulsed and power Doppler ultrasonography. Endocr J. 2005. 52:207–212.13. Shimura H, Haraguchi K, Hiejima Y, Fukunari N, Fujimoto Y, Katagiri M, et al. Distinct diagnositic criteria for ultrasonographic examination of papillary thyroid carcinoma: a multicenter study. Thyroid. 2005. 15:251–258.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Mixed Follicular-Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Ultrasonographic Findings of Papillary Thyroid Cancer with or without Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- Differential Diagnosis of a Follicular Carcinoma and Papillary Carcinoma of the Thyroid Gland Based on Sonographic Findings
- Oxyphilic Papillary Carcinoma of the Thyroid in Fine Needle Aspiration
- Medullary Carcinoma of Thyroid Gland with Co-existing Papillary Carcinoma