J Korean Med Sci.
2011 Sep;26(9):1244-1246. 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.9.1244.
Dopa-responsive Dystonia with a Novel Initiation Codon Mutation in the GCH1 Gene Misdiagnosed as Cerebral Palsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. changski@skku.edu
- KMID: 1779403
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2011.26.9.1244
Abstract
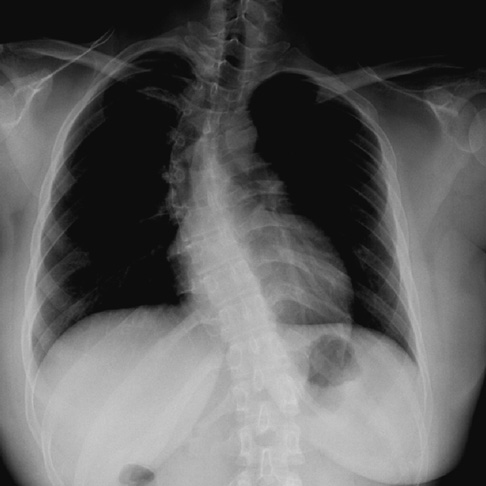
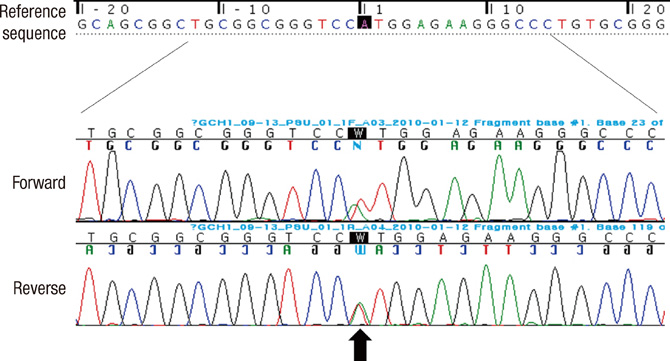
- Dopa-responsive dystonia (DRD) is a clinical syndrome characterized by childhood-onset dystonia and a dramatic response to relatively low doses of levodopa. However, patients with DRD can be misdiagnosed as cerebral palsy or spastic diplegia due to phenotypic variation. Here we report a young woman with DRD who were severely disabled and misdiagnosed as cerebral palsy for over 10 yr. A small dose of levodopa restored wheelchair-bound state to normality. However, thoracolumbar scoliosis has remained as a sequel due to late detection of DRD. Genetic analysis by using PCR-direct sequencing revealed a novel initiation codon mutation (c.1A>T; p.Met1Leu) in GTP cyclohydrolase 1 (GCH1) gene. Although it is known that DRD can be misdiagnosed as cerebral palsy, this case reinforces the importance of differential diagnosis of DRD from cerebral palsy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Segawa M, Hosaka A, Miyagawa F, Nomura Y, Imai H. Hereditary progressive dystonia with marked diurnal fluctuation. Adv Neurol. 1976. 14:215–233.2. Hagenah J, Saunders-Pullman R, Hedrich K, Kabakci K, Habermann K, Wiegers K, Mohrmann K, Lohnau T, Raymond D, Vieregge P, Nygaard T, Ozelius LJ, Bressman SB, Klein C. High mutation rate in dopa-responsive dystonia: detection with comprehensive GCHI screening. Neurology. 2005. 64:908–911.3. Ichinose H, Ohye T, Takahashi E, Seki N, Hori T, Segawa M, Nomura Y, Endo K, Tanaka H, Tsuji S, Fujita K, Nagatsu T. Hereditary progressive dystonia with marked diurnal fluctuation caused by mutations in the GTP cyclohydrolase I gene. Nat Genet. 1994. 8:236–242.4. Furukawa Y. Pagon RA, Bird TD, Dolan CR, Stephens K, editors. GTP cyclohydrolase 1-deficient dopa-responsive dystonia. GeneReviews. 1993. Seattle: University of Washington, Seattle.5. Hong KM, Kim YS, Paik MK. A novel nonsense mutation of the GTP cyclohydrolase I gene in a family with dopa-responsive dystonia. Hum Hered. 2001. 52:59–60.6. Kang JH, Kang SY, Kang HK, Koh YS, Im JH, Lee MC. A novel missense mutation of the GTP cyclohydrolase I gene in a Korean family with hereditary progressive dystonia/dopa-responsive dystonia. Brain Dev. 2004. 26:287–291.7. Kim YS, Choi YB, Lee JH, Yang SH, Cho JH, Shin CH, Lee SD, Paik MK, Hong KM. Predisposition of genetic disease by modestly decreased expression of GCH1 mutant allele. Exp Mol Med. 2008. 40:271–275.8. Yum MS, Ko TS, Yoo HW, Chung SJ. Autosomal-dominant guanosine triphosphate cyclohydrolase I deficiency with novel mutations. Pediatr Neurol. 2008. 38:367–369.9. Jeon BS. Dopa-responsive dystonia: a syndrome of selective nigrostriatal dopaminergic deficiency. J Korean Med Sci. 1997. 12:269–279.10. Jeon BS, Jeong JM, Park SS, Kim JM, Chang YS, Song HC, Kim KM, Yoon KY, Lee MC, Lee SB. Dopamine transporter density measured by [123I] beta-CIT single-photon emission computed tomography is normal in dopa-responsive dystonia. Ann Neurol. 1998. 43:792–800.11. Segawa M, Nomura Y, Nishiyama N. Autosomal dominant guanosine triphosphate cyclohydrolase I deficiency (Segawa disease). Ann Neurol. 2003. 54:Suppl 6. S32–S45.12. Tamaru Y, Hirano M, Ito H, Kawamura J, Matsumoto S, Imai T, Ueno S. Clinical similarities of hereditary progressive/dopa responsive dystonia caused by different types of mutations in the GTP cyclohydrolase I gene. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998. 64:469–473.13. Cao L, Zheng L, Tang WG, Xiao Q, Zhang T, Tang HD, He SB, Wang XJ, Ding JQ, Chen SD. Four novel mutations in the GCH1 gene of Chinese patients with dopa-responsive dystonia. Mov Disord. 2010. 25:755–760.14. Nygaard TG, Marsden CD, Fahn S. Dopa-responsive dystonia: long-term treatment response and prognosis. Neurology. 1991. 41:174–181.15. Tsirikos AI, Carr LJ, Noordeen HH. Variability of clinical expression and evolution of spinal deformity in a family with late detection of dopa-responsive dystonia. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2004. 46:128–137.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Dopa-responsive Dystonia with a Mutation in the GCH1 Gene Misdiagnosed as Cerebral Palsy for 2 Years
- Dopa-Responsive Dystonia: A Male Patient Inherited a Novel GCH1 Deletion from an Asymptomatic Mother
- Dopa-responsive dystonia with additional unusual clinical features: A case report confirmed by molecular genetics
- Dopa-responsive Dystonia Misdiagnosed as Cerebral Palsy and Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia 2 Cases: Two cases report
- Juvenile Parkinsonism with PARK2 Gene Mutation Misdiagnosed as Dopa-responsive Dystonia: a Case Report