The Prevalence of Knee Osteoarthritis in Elderly Community Residents in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Anyang, Korea. kimha@hallym.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Social and Preventive Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1779263
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.293
Abstract
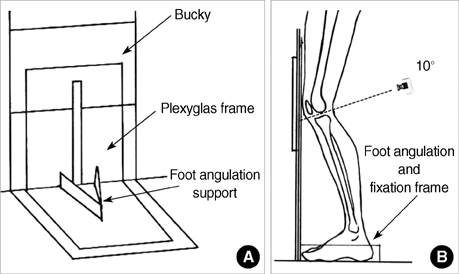
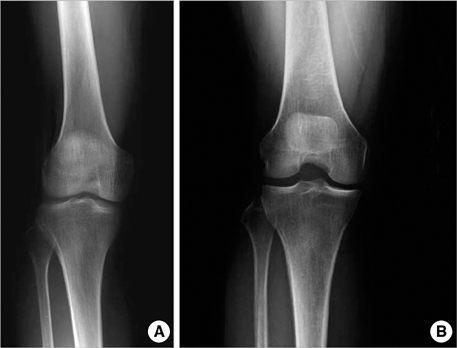
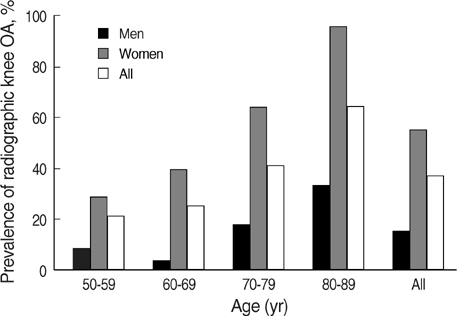
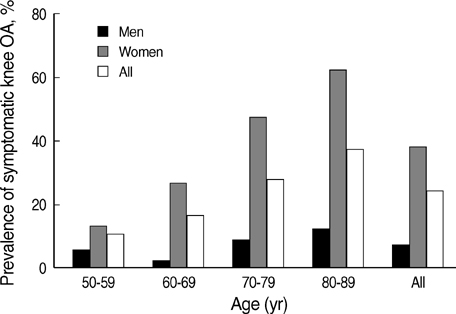
- The purpose of this study was to estimate the prevalence of radiographic and symptomatic knee osteoarthritis (OA) among community residents and to elucidate the relevant risk factors. This prospective, population-based study was conducted on residents over 50 yr of age in Chuncheon. Subjects completed an interview based on a standardized questionnaire and clinical evaluation including standardized weight bearing semiflexed knee A-P radiographs. We defined a subject with the Kellgren and Lawrence grade > or =2 as having radiographic knee OA (ROA). Symptomatic knee OA (SOA) was defined by the presence of both ROA and knee pain. We obtained symptom information and radiographs from 504 subjects. The prevalence of ROA and SOA was 37.3% and 24.2%, respectively. The prevalence of both ROA and SOA was significantly higher among women than among men. Multivariate analysis revealed that the presence of hypertension, and a manual occupation were significantly associated with the presence of ROA and SOA. Lower level of education was significantly associated with the presence of ROA, and female sex with the presence of SOA. In conclusion, both ROA and SOA are common in the aged adult population of Korea, with preponderance for women.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Female
Humans
Hypertension/complications
Interviews as Topic
Male
Middle Aged
Multivariate Analysis
Osteoarthritis, Knee/complications/*epidemiology/radiography
Pain/epidemiology
Population Surveillance
Prevalence
Prospective Studies
Questionnaires
Republic of Korea/epidemiology
Risk Factors
Sex Factors
Urban Health
Figure
Cited by 11 articles
-
Work-related musculoskeletal disorders in Korean farmers
Chul Gab Lee
J Korean Med Assoc. 2012;55(11):1054-1062. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2012.55.11.1054.Estimation of the prevalence of Korean adults aged 50 years or more with knee osteoarthritis based on the data from fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Dong Wook Shin, Sujeong Nam, Yun Sic Bang, Jong-Yeon Lee
J Korean Med Assoc. 2013;56(5):431-436. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2013.56.5.431.Utilization of Hyaluronate and Incidence of Septic Knee Arthritis in Adults: Results from the Korean National Claim Registry
Young-Kyun Lee, Ki-Choul Kim, Yong-Chan Ha, Kyung-Hoi Koo
Clin Orthop Surg. 2015;7(3):318-322. doi: 10.4055/cios.2015.7.3.318.Arthroscopic Partial Meniscectomy versus Physical Therapy for Degenerative Meniscal Tear: a Systematic Review
Miyoung Choi, Su Jung Lee, Chan Mi Park, Seungeun Ryoo, Sunghyun Kim, Ju Yeon Jang, Hyun Ah Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(45):e292. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e292.Analysis of Tertiary Hospital Utilization in Pediatric Orthopaedics: a Study Using Nationwide Sample Data from Korea
Kunhyung Bae, Soo-Sung Park, Jinhee Park, Michael Seungcheol Kang
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(45):e289. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e289.Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs-sparing Effect of Symptomatic Slow-acting Drugs for Osteoarthritis in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients
Soo-Kyung Cho, Hyoungyoung Kim, Ha-Rim Park, Wooseok Choi, Seongmi Choi, Sun-Young Jung, Eun Jin Jang, Yoon-Kyoung Sung
J Rheum Dis. 2019;26(3):179-185. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2019.26.3.179.Factors Associated with Knee Pain with Different Grades of Knee Osteoarthritis among Korean Adults Aged 50 Years or More
Eun Young Choi, Min Jeong Kim
Korean J Health Promot. 2016;16(3):145-152. doi: 10.15384/kjhp.2016.16.3.145.Effects of the Off-Loading Brace on the Activation of Femoral Muscles -A Preliminary Study-
Eun-Hi Choi, Keon-Koo Kim, Ah-Young Jun, Eun-Hye Choi, Sung-Won Choi, Ka-Young Shin
Ann Rehabil Med. 2011;35(6):887-896. doi: 10.5535/arm.2011.35.6.887.Factors Related to Standing Balance in Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis
Hye Jeong Park, Saebyuk Ko, Hyeon Mi Hong, Eunjae Ok, Jong In Lee
Ann Rehabil Med. 2013;37(3):373-378. doi: 10.5535/arm.2013.37.3.373.Effects of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy in Chronic Stroke Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Study
Sung Jun Cho, Ja Ryung Yang, Hee Seung Yang, Hea-Eun Yang
Ann Rehabil Med. 2016;40(5):862-870. doi: 10.5535/arm.2016.40.5.862.Osteoarthritis – Insights From Recent Research
Hyun Ah Kim
J Rheum Dis. 2022;29(3):132-139. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2022.29.3.132.
Reference
-
1. Guccione AA, Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Anthony JM, Zhang Y, Wilson PW, Kelly-Hayes M, Wolf PA, Kreger BE, Kannel WB. The effects of specific medical conditions on the functional limitations of elders in the Framingham Study. Am J Public Health. 1994. 84:351–358.
Article2. Felson DT, Zhang Y. An update on the epidemiology of knee and hip osteoarthritis with a view to prevention. Arthritis Rheum. 1998. 41:1343–1355.
Article3. Cho NH, Kim S, Kim HA, Seo YI. The prevalence and risk factors of knee and hand osteoarthritis in Korea. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2007. 14:354–362.
Article4. Park NG, Kim WK, Shin DH, Choi YM, Lee YJ, Lee EB, Kim HA, Kim YK, Park BJ, Hong SC, Song YW. Prevalence of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis in two communities in Korea. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2003. 10:151–157.5. Yun SH, Kang PS, Kim SB, Lee KS. Prevalence and related factors of knee osteoarthritis in rural woman. Korean J Prev Med. 2001. 34:331–336.6. Min BH, Kim HS, Kim HW, Lee SY, Park JW, Kang SY. Epidemiology for Korean knee osteoarthritis: results from the health and nutritional survey in Kuri city. J Korean Knee Soc. 2000. 12:214–221.7. Kellgren JH, editor. Atlas of standard radiographs of arthritis. 1963. Vol II. Oxford, England: Blackwell Scientific;15–33.8. Korean Census. Korean Statistical Office, The Republic of Korean Government. 2000. accessed 11 July 2007. Available at http://www.kosis.kr/index.html .9. Bellamy N, Buchanan WW, Goldsmith CH, Campbell J, Stitt LW. Validation study of WOMAC: a health status instrument for measuring important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip and knee. J Rheumatol. 1988. 15:1833–1840.10. Nevitt MC, Peterfy C, Guermazi A, Felson DT, Duryea J, Woodworth T, Chen H, Kwoh K, Harris TB. Longitudinal performance evaluation and validation of fixed-flexion radiography of the knee for detection of joint space loss. Arthritis Rheum. 2007. 56:1512–1520.
Article11. Kothari M, Guermazi A, von Ingersleben G, Miaux Y, Sieffert M, Block JE, Stevens R, Peterfy CG. Fixed-flexion radiography of the knee provides reproducible joint space width measurements in osteoarthritis. Eur Radiol. 2004. 14:1568–1573.
Article12. Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS. Radiological assessment of osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957. 16:494–502.13. Altman RD, Hochberg M, Murphy WA Jr, Wolfe F, Lequesne M. Atlas of individual radiographic features in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1995. 3:Suppl A. 3–70.14. Zhang Y, Xu L, Nevitt MC, Aliabadi P, Yu W, Qin M, Lui LY, Felson DT. Comparison of the prevalence of knee osteoarthritis between the elderly Chinese population in Beijing and whites in the United States: the Beijing Osteoarthritis Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2001. 44:2065–2071.
Article15. Yoshida S, Aoyagi K, Felson DT, Aliabadi P, Shindo H, Takemoto T. Comparison of the prevalence of radiographic osteoarthritis of the knee and hand between Japan and the United States. J Rheumatol. 2002. 29:1454–1458.16. Hur NW, Choi CB, Uhm WS, Bae SC. The prevalence and trend of arthritis in Korea: results from Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2008. 15:11–26.
Article17. Kim HA, Kim S, Seo YI, Choi HJ, Seong SC, Song YW, Hunter D, Zhang Y. The epidemiology of total knee replacement in South Korea: national registry data. Rheumatology. 2008. 47:88–91.
Article18. Yau WP, Tang WM, Ng TP, Chiu KY. Factors leading to blood transfusion among Chinese patients undergoing total knee replacements: a retrospective study. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2004. 12:153–157.
Article19. Mitsuyasu S, Hagihara A, Horiguchi H, Nobutomo K. Relationship between total arthroplasty case volume and patient outcome in an acute care payment system in Japan. J Arthroplasty. 2006. 21:656–663.
Article20. Hart DJ, Doyle DV, Spector TD. Association between metabolic factors and knee osteoarthritis in women: the Chingford Study. J Rheumatol. 1995. 22:1118–1123.21. Szebenyi B, Hollander AP, Dieppe P, Quilty B, Duddy J, Clarke S, Kirwan JR. Associations between pain, function, and radiographic features in osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. 54:230–235.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study on Nutrition and Health Evaluation of Osteoarthritis Elderly in Community
- The Prevalence and Risk Factors of Knee and Hand Osteoarthritis in Korea
- Prevalence of Radiographic Knee Osteoarthritis in Elderly Koreans
- Prevalence of Knee Pain and Its Influence on Quality of Life and Physical Function in the Korean Elderly Population: A Community Based Cross-Sectional Study
- Prevalence of Osteoporosis in Female Patients with Advanced Knee Osteoarthritis Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty