J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Apr;24(2):350-353. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.2.350.
Loss of Distal Femur Combined with Popliteal Artery Occlusion: Reconstructive Arthroplasty Using Modular Segmental Endoprosthesis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Cheongju St. Mary's Hospital, Cheongju, Korea. zona413@yahoo.co.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1779145
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.2.350
Abstract
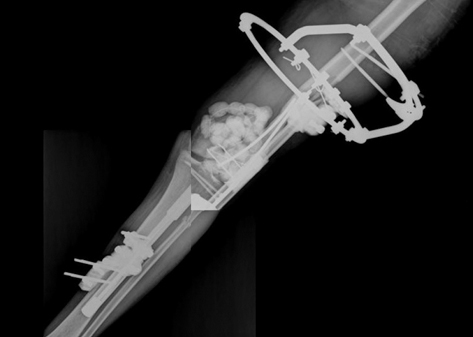
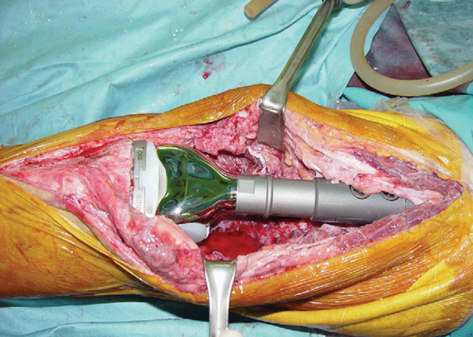
- Severe injury to the knee and the surrounding area is frequently associated with injury to ligaments of the knee joint and structures in the popliteal fossa. This case involved a popliteal artery occlusion, severe bone loss of distal femur, loss of collateral ligaments, and extensor mechanism destruction of the knee. Initially, prompt recognition and correction of associated popliteal artery injury are important for good results after treatment. After successful revascularization, treatment for severe bone loss of distal femur and injury of the knee joint must be followed. We treated this case by delayed reconstruction using modular segmental endoprosthesis after revascularization of the popliteal artery. This allowed early ambulation. At 36 months after surgery, the patient had good circulation of the lower limb and was ambulating independently.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Friedman SA, Cerruti MM, Kosmoski J, Sobel J. Isolated popliteal artery rupture caused by blunt trauma. Angiology. 1971. 22:533–537.
Article2. Lange RH. Limb reconstruction versus amputation decision making in massive lower extremity trauma. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989. 243:92–99.3. Harrison RJ Jr, Thacker MM, Pitcher JD, Temple HT, Scully SP. Distal femur replacement is useful in complex total knee arthroplasty revisions. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006. 446:113–120.
Article4. Springer BD, Sim FH, Hanssen AD, Lewallen DG. The modular segmental kinematic rotating hinge for nonneoplastic limb salvage. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. 421:181–187.
Article5. Eger M, Huler T, Hirsch M. Popliteal artery occlusion associated with dislocation of the knee-joint. Report of a case with successful surgical repair. Br J Surg. 1970. 57:315–317.
Article6. Tominaga GT, Connolly JE, Wilson SE. Bilateral popliteal artery injury from bumper crush injury. J Trauma. 1996. 40:311–313.
Article7. Frink SJ, Rutledge J, Lewis VO, Lin PP, Yasko AW. Favorable long-term results of prosthetic arthroplasty of the knee for distal femur neoplasms. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005. 438:65–70.
Article8. Dennis DA. The structural allograft composite in revision total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2002. 17:4 Suppl 1. 90–93.
Article9. Petrou G, Petrou H, Tilkeridis C, Stavrakis T, Kapetsis T, Kremmidas N, Gavras M. Medium-term results with a primary cemented rotatinghinge total knee replacement. A 7-to 15-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004. 86:813–817.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Popliteal Artery Occlusion after Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Case Report
- Popliteal Artery Occlusion after Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Case Report
- Popliteal Artery Occlusion after Total Knee Replacement Arthroplasty: A Case Report
- Reconstruction of Knee Joint with Total Elbow Endoprosthesis in Eight Years Old Osteosarcoma of Distal Femur: A Case Report
- Posterior Thigh Compartment Syndrome as a Result of Pseudoaneurysm of the Popliteal Artery in the Distal Femoral Fracture: A Case Report