J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Apr;24(2):326-329. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.2.326.
Erosive Arthropathy with Osteolysis As a Typical Feature in Polyfibromatosis Syndrome: A Case Report and a Review of the Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. jychoe@cu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Dankook University School of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- KMID: 1779139
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.2.326
Abstract
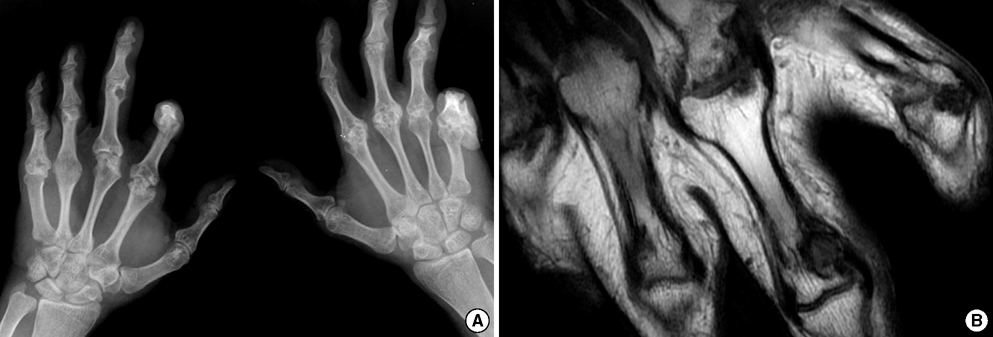
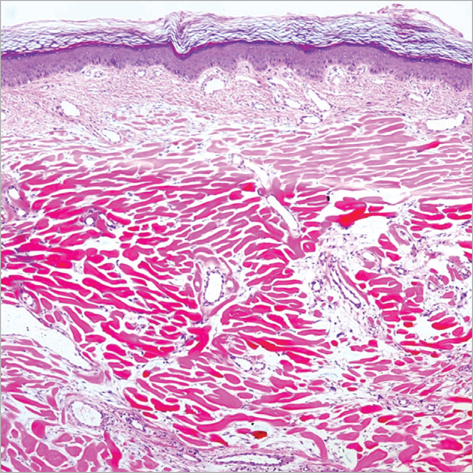
- Polyfibromatosis syndrome is a rare disease entity that is characterized by various clinical features such as palmar, plantar, and penile fibromatoses, keloid formations of the skin, and erosive arthropathy. Its precise pathophysiology or etiology remains unclear. In addition to distinctive diverse skin manifestations, patients with polyfibromatosis have been previously reported to show erosive arthropathy with significant limitation of movement at affected joints. However, the presence of erosive polyarthropathy in polyfibromatosis has not emphasized in previous cases. Here, we report a case of polyfibromatosis syndrome combined with painless massive structural destruction of hand and foot joints, and review the characteristics of erosive arthropathy in previous cases.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pierard GE, Lapiere CM. Phenytoin dependent fibrosis in polyfibromatosis syndrome. Br J Dermatol. 1979. 100:335–341.
Article2. Gonzalez-Martínez R, Marín-Bertolín S, Amorrortu-Velayos J. Association of knuckle pads and palmo-plantar and penile contracture as clinical manifestations of polyfibromatosis. Eur J Plast Surg. 1998. 21:101–102.3. Touraine A, Ruel H. La polyfibromatose héréditaire. Ann dermat et syph. 1945. 5:1–5.4. Fenton DA, Yates DA, Black MM. Aggressive polyfibromatosis. J R Soc Med. 1986. 79:482–483.
Article5. Lee YC, Chan HH, Black MM. Aggressive polyfibromatosis: a 10 year follow-up. Australas J Dermatol. 1996. 37:205–207.
Article6. Montgomery E, Lee JH, Abraham SC, Wu TT. Superficial fibromatoses are genetically distinct from deep fibromatoses. Mod Pathol. 2001. 14:695–701.
Article7. Pierard GE, Lapiere CM. Physiopathological variations in the mechanical properties of skin. Arch Dermatol Res. 1977. 260:231–239.
Article8. Chen DL, Chong AH, Green J, Orchard D, Williams R, Clemens L. A novel case of polyfibromatosis and interstitial granulomatous dermatitis with arthritis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006. 55:Suppl 2. S32–S37.
Article9. Qian A, Meals RA, Rajfer J, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF. Comparison of gene expression profiles between Peyronie's disease and Dupuytren's contracture. Urology. 2004. 64:399–404.
Article10. Jemec B, Grobbelaar AO, Wilson GD, Smith PJ, Sanders R, McGrouther DA. Is Dupuytren's disease caused by an imbalance between proliferation and cell death? J Hand Surg [Br]. 1999. 24:511–514.
Article11. Meek RM, McLellan S, Reilly J, Crossan JF. The effect of steroids on Dupuytren's disease: role of programmed cell death. J Hand Surg [Br]. 2002. 27:270–273.12. Luo S, Benathan M, Raffoul W, Panizzon RG, Egloff DV. Abnormal balance between proliferation and apoptotic cell death in fibroblasts derived from keloid lesions. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001. 107:87–96.
Article13. Gravallese EM, Manning C, Tsay A, Naito A, Pan C, Amento E, Goldring SR. Synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis is a source of osteoclast differentiation factor. Arthritis Rheum. 2000. 43:250–258.
Article14. Manisali M, Ozaksoy D. Gorham disease: correlation of MR findings with histopathologic changes. Eur Radiol. 1998. 8:1647–1650.
Article15. Al-Mayouf SM, Majeed M, Hugosson C, Bahabri S. New form of idiopathic osteolysis: nodulosis, arthropathy and osteolysis (NAO) syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 2000. 93:5–10.
Article