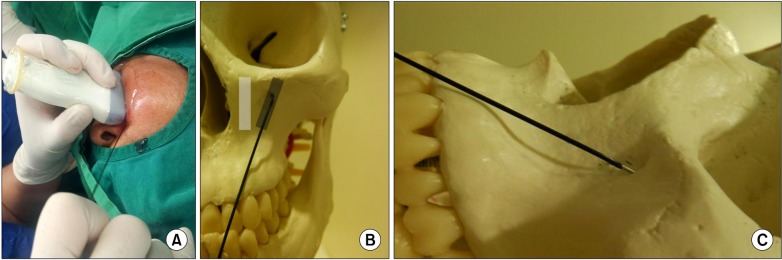
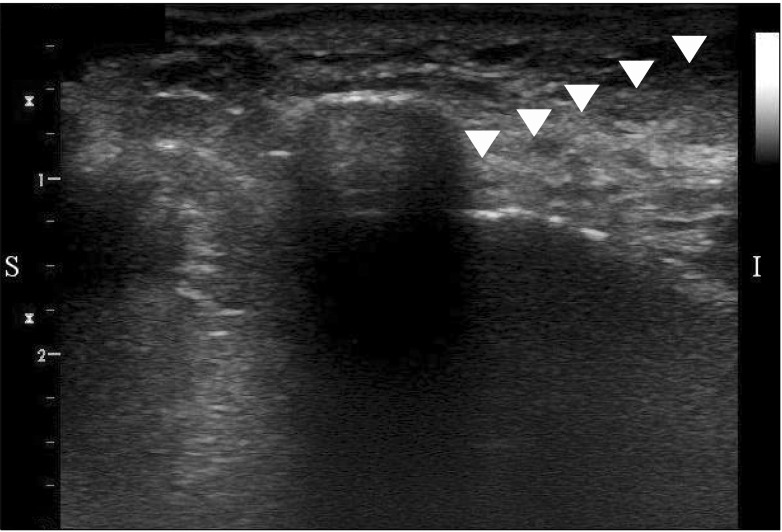
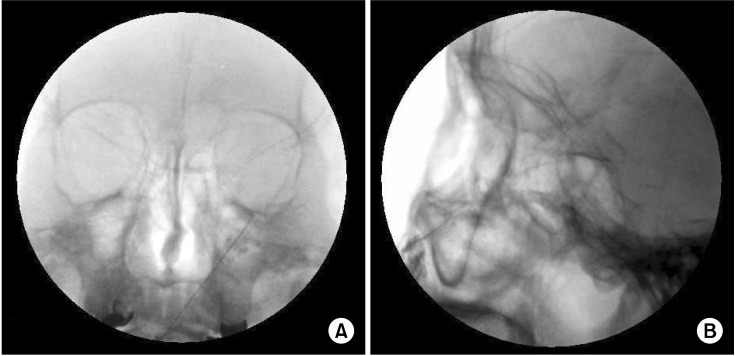
Ultrasound-Guided Infraorbital Nerve Pulsed Radiofrequency Treatment for Intractable Postherpetic Neuralgia: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, College of Medicine, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea. pain@cau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1779031
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.1.84
Abstract
- A 60-year-old man presented with pain on the left cheek and lateral nose. The patient had been diagnosed with facial herpes zoster in the left V2 area 6 months previously. Medical treatment was prescribed for 6 months but it had little effect. We blocked the left infraorbital nerve under ultrasound guidance, but pain relief was short term. Therefore, we performed pulsed radiofrequency treatment on the left infraorbital nerve under ultrasound guidance. Six months after the procedure, the reduction of pain was still maintained, and there was no need for further management.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Medications in Treatment of Postherpetic Neuralgia
Sang Wook Shin
Korean J Pain. 2014;27(1):1-2. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.1.Ultrasound-Assisted Mental Nerve Block and Pulsed Radiofrequency Treatment for Intractable Postherpetic Neuralgia: Three Case Studies
Hae Gyun Park, Pyung Gul Park, Won Joong Kim, Yong Hee Park, Hyun Kang, Chong Wha Baek, Yong Hun Jung, Young Cheol Woo, Gill Hoi Koo, Hwa Yong Shin
Korean J Pain. 2014;27(1):81-85. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.81.Reduction in mechanical allodynia in complex regional pain syndrome patients with ultrasound-guided pulsed radiofrequency treatment of the superficial peroneal nerve
Won Soek Chae, Sang Hyun Kim, Sung Hwan Cho, Joon Ho Lee, Mi Sun Lee
Korean J Pain. 2016;29(4):266-269. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.4.266.
Reference
-
1. Hashizume K. Herpes zoster and post-herpetic neuralgia. Nihon Rinsho. 2001; 59:1738–1742. PMID: 11554045.2. Fashner J, Bell AL. Herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia: prevention and management. Am Fam Physician. 2011; 83:1432–1437. PMID: 21671543.3. Nguyen M, Wilkes D. Pulsed radiofrequency V2 treatment and intranasal sphenopalatine ganglion block: a combination therapy for atypical trigeminal neuralgia. Pain Pract. 2010; 10:370–374. PMID: 20492576.
Article4. Rahman M, Richter EO, Osawa S, Rhoton AL Jr. Anatomic study of the infraorbital foramen for radiofrequency neurotomy of the infraorbital nerve. Neurosurgery. 2009; 64:423–427. PMID: 19404120.
Article5. Tsui BC. Ultrasound imaging to localize foramina for superficial trigeminal nerve block. Can J Anaesth. 2009; 56:704–706. PMID: 19504162.
Article6. Schmid T, Pautex S, Lang PO. Acute and postherpetic neuralgia in the elderly: analysis of evidence for therapeutic options. Rev Med Suisse. 2012; 8:1374–1378. 1380–1382. PMID: 22872936.7. Haridas A, Mathewson C, Eljamel S. Long-term results of 405 refractory trigeminal neuralgia surgeries in 256 patients. Zentralbl Neurochir. 2008; 69:170–174. PMID: 18666055.
Article8. Hall GC, Carroll D, McQuay HJ. Primary care incidence and treatment of four neuropathic pain conditions: a descriptive study, 2002-2005. BMC Fam Pract. 2008; 9:26. PMID: 18460194.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasound-guided pulsed radiofrequency treatment for postherpetic neuralgia of supraorbital nerve: A case report
- Ultrasound-Assisted Mental Nerve Block and Pulsed Radiofrequency Treatment for Intractable Postherpetic Neuralgia: Three Case Studies
- Ultrasound-guided pudendal nerve pulsed radiofrequency in patients with refractory pudendal neuralgia: Three cases report
- Pulsed Radiofrequency Lesioning of Supraorbital and Supratrochlear Nerve in Postherpetic Neuralgia: A report of 2 cases
- Persistent idiopathic facial pain treated with botulinum toxin and pulsed radiofrequency of infraorbital nerve – a case report