J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Mar;25(3):505-508. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.3.505.
Neurotoxic Manifestations of an Overdose Intrathecal Injection of Gadopentetate Dimeglumine
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea. isbrzw@sch.ac.kr
- KMID: 1778054
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.3.505
Abstract
- The intravenous administration of gadopentetate dimeglumine (GD) is relatively safe and rarely causes systemic toxicity in the course of routine imaging studies. However, the general safety of intrathecal GD has not been established. We report a very rare case of an overdose intrathecal GD injection presenting with neurotoxic manifestations, including a decreased level of consciousness, global aphasia, rigidity, and visual disturbance.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aphasia/etiology/pathology/physiopathology
Brain/drug effects/pathology
*Contrast Media/administration & dosage/toxicity
*Gadolinium DTPA/administration & dosage/toxicity
Humans
*Injections, Spinal
Male
Muscle Rigidity/etiology/pathology/physiopathology
*Neurotoxicity Syndromes/etiology/pathology/physiopathology
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Vision Disorders/etiology/pathology
Contrast Media
Gadolinium DTPA
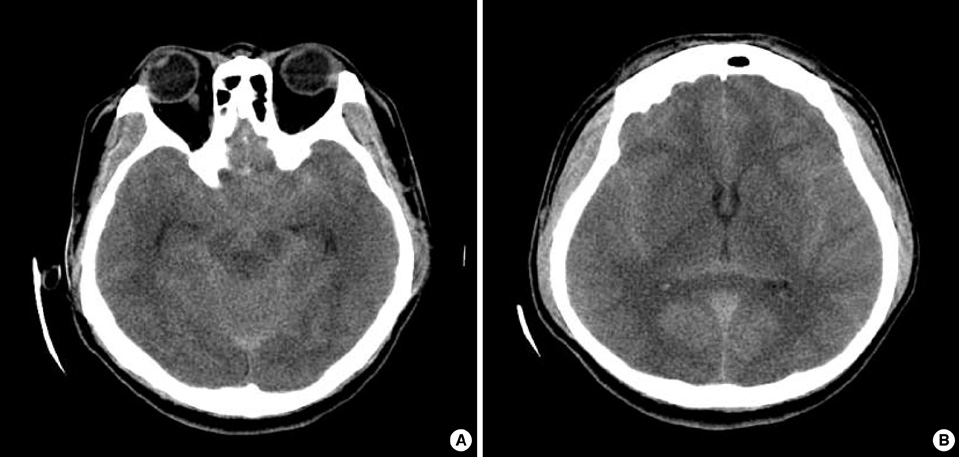
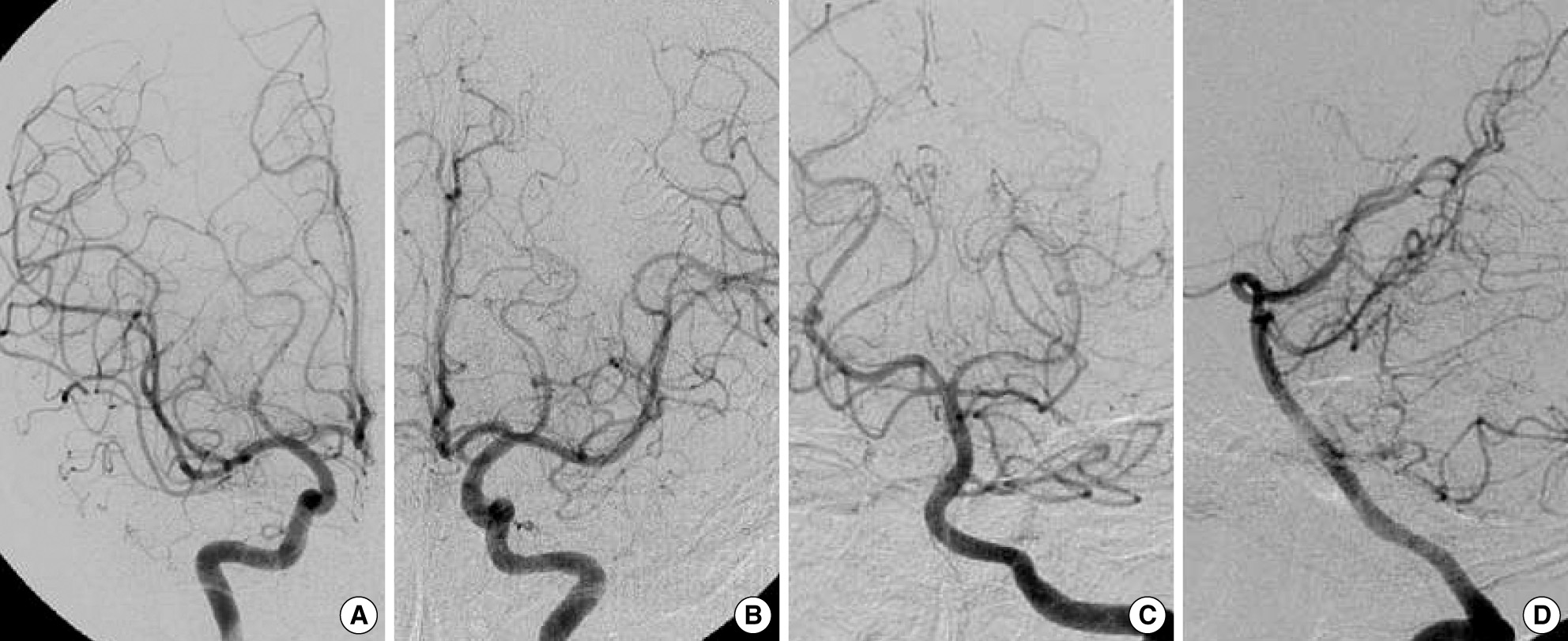
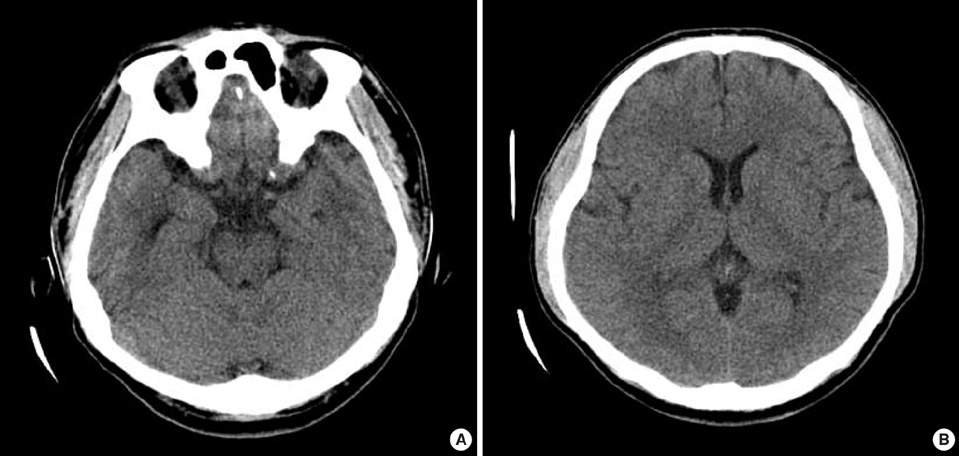
Figure
Reference
-
1. Maramattom BV, Manno EM, Wijdicks EF, Lindell EP. Gadolinium encephalopathy in a patient with renal failure. Neurology. 2005. 64:1276–1278.
Article2. Tali ET, Ercan N, Krumina G, Rudwan M, Mironov A, Zeng QY, Jinkins JR. Intrathecal gadolinium (gadopentetate dimeglumine) enhanced magnetic resonance myelography and cisternography: results of a multicenter study. Invest Radiol. 2002. 37:152–159.3. Niendorf HP, Haustein J, Cornelius I, Alhassan A, Clauss W. Safety of gadolinium-DTPA: extended clinical experience. Magn Reson Med. 1991. 22:222–228.
Article4. Goldstein HA, Kashanian FK, Blumetti RF, Holyoak WL, Hugo FP, Blumenfield DM. Safety assessment of gadopentetate dimeglumine in U.S. clinical trials. Radiology. 1990. 174:17–23.
Article5. Zeng Q, Xiong L, Jinkins JR, Fan Z, Liu Z. Intrathecal gadolinium-enhanced MR myelography and cisternography: a pilot study in human patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999. 173:1109–1115.
Article6. Di Chiro G, Knop RH, Girton ME, Dwyer AJ, Doppman JL, Patronas NJ, Gansow OA, Brechbiel MW, Brooks RA. MR cisternography and myelography with Gd-DTPA in monkeys. Radiology. 1985. 157:373–377.
Article7. Ray DE, Cavanagh JB, Nolan CC, Williams SC. Neurotoxic effects of gadopentetate dimeglumine: behavioral disturbance and morphology after intracerebroventricular injection in rats. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996. 17:365–373.8. Ray DE, Holton JL, Nolan CC, Cavanagh JB, Harpur ES. Neurotoxic potential of gadodiamide after injection into the lateral cerebral ventricle of rats. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998. 19:1455–1462.9. Tali ET, Ercan N, Kaymaz M, Pasaoglu A, Jinkins JR. Intrathecal gadolinium (gadopentetate dimeglumine)-enhanced MR cisternography used to determine potential communication between the cerebrospinal fluid pathways and intracranial arachnoid cysts. Neuroradiology. 2004. 46:744–754.
Article10. Arlt S, Cepek L, Rustenbeck HH, Prange H, Reimers CD. Gadolinium encephalopathy due to accidental intrathecal administration of gadopentetate dimeglumine. J Neurol. 2007. 254:810–812.
Article11. Li L, Gao FQ, Zhang B, Luo BN, Yang ZY, Zhao J. Overdosage of intrathecal gadolinium and neurological response. Clin Radiol. 2008. 3:1063–1068.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum: Figure Correction
- Analysis of Signal Intensity Curve on Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Imaging of Postoperative Scars in Rabbits:Comparison of Gadopentetate Dimeglumine and 24-gadolinium-tetraazacy-clododecanetetraacetic acid (DOTA)-dendrimer
- Acute Management of Intrathecal Methotrexate Overdose in a Patient with Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
- Bilateral Renal Artery Stenosis with Renal Insufficiency: Successful Angioplasty Using Gadopentetate Dimeglumine as a Contrast Agent
- Apoptotic Effect of Radiocontrast Media on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells