J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Mar;25(3):481-484. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.3.481.
Primary T-cell Lymphoma of the Thyroid Associated with Hashimoto's Thyroiditis, Histologically Mimicking MALT-Lymphoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yhko310@skku.edu
- 3Department of Surgery, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1778048
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.3.481
Abstract
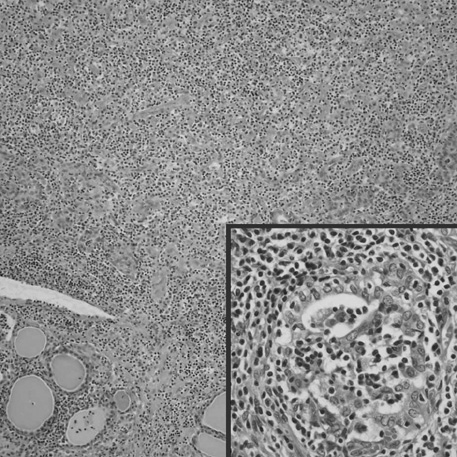
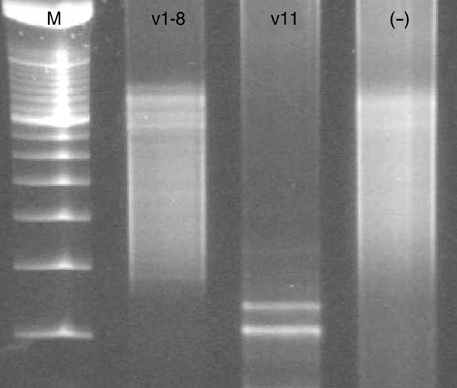
- Most of thyroid lymphomas are B-lineage, and T-cell lymphomas are rare. Here, we report a case of primary thyroid T-cell lymphoma associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. A 48-yr-old woman presented with incidentally found neck mass. Histologically, the resected right lobe of the thyroid was replaced by monomorphic small atypical lymphoid cells with lymphoepithelial lesion-like change, most of which were immunoreactive for CD3, CD8, betaF-1, and TIA-1. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, unspecified, was finally diagnosed after molecular study for TCR-gamma gene rearrangement. This is the second case of cytotoxic T-cell lymphoma reported in the thyroid gland so far. Unique association between thyroid follicles and neoplastic lymphocytes may be characteristic feature of this type of T-cell lymphoma.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Abbondanzo S, Aozasa K, Boerner S, Thompson LDR. DeLellis RA, Lloyd RV, Heitz PU, Eng C, editors. Primary lymphoma and plasmacytoma. World Health Organization classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics of tumours of endocrine organs. 2004. Lyon: IARC Press;109–111.2. Singer JA. Primary lymphoma of the thyroid. Am Surg. 1998. 64:334–337.3. Ansell SM, Grant CS, Habermann TM. Primary thyroid lymphoma. Semin Oncol. 1999. 26:316–323.4. Motoi N, Ozawa Y. Malignant T-cell lymphoma of the thyroid gland associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Pathol Int. 2005. 55:425–430.
Article5. Koida S, Tsukasaki K, Tsuchiya T, Harasawa H, Fukushima T, Yamada Y, Ohshima K, Kamihira S, Kikuchi M, Tomonaga M. Primary T-cell lymphoma of the thyroid gland with chemokine receptors of Th1 phenotype complicating autoimmune thyroiditis. Haematologica. 2007. 92:e37–e40.
Article6. Raftopoulos I, Vanuno D, Kouraklis G. Two unusual sites of colon cancer metastases and a rare thyroid lymphoma. Case 3. Primary T-cell lymphoma of the thyroid arising in a background of Hashimoto's thyroiditis. J Clin Oncol. 2001. 19:3576–3580.7. Yamaguchi M, Ohno T, Kita K. gamma/delta T-cell lymphoma of the thyroid gland. N Engl J Med. 1997. 336:1391–1392.8. Torlakovic E, Cherwitz DL, Jessurun J, Scholes J, McGlennen R. B-cell gene rearrangement in benign and malignant lymphoid proliferations of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue and lymph nodes. Hum Pathol. 1997. 28:166–173.
Article9. Jaffe ES. Surgical pathology of the lymph nodes and related organs. 1995. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company.10. Hyjek E, Isaacson PG. Primary B cell lymphoma of the thyroid and its relationship to Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Hum Pathol. 1988. 19:1315–1326.
Article11. Isaacson PG. Knoweles DM, editor. Gastrointestinal lymphomas and lymphoid hyperplasias. Neoplastic hematology. 2001. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;1235–1261.12. Födinger M, Buchmayer H, Schwarzinger I, Simonitsch I, Winkler K, Jäger U, Knobler R, Mannhalter C. Multiplex PCR for rapid detection of T-cell receptor-gamma chain gene rearrangements in patients with lymphoproliferative diseases. Br J Haematol. 1996. 94:136–139.
Article13. Matsuzuka F, Fukata S, Kuma K, Miyauchi A, Kakudo K, Sugawara M. Gene rearrangement of immunoglobulin as a marker of thyroid lymphoma. World J Surg. 1998. 22:558–561.
Article14. Signoretti S, Murphy M, Cangi MG, Puddu P, Kadin ME, Loda M. Detection of Clonal T-Cell Receptor gamma gene rearrangements in paraffin-embedded tissue by polymerase chain reaction and nonradioactive single-strand conformational polymorphism analysis. Am J Pathol. 1999. 154:67–75.15. Miller TP, Dahlberg S, Cassady JR, Adelstein DJ, Spier CM, Grogan TM, LeBlanc M, Carlin S, Chase E, Fisher RI. Chemotherapy alone compared with chemotherapy plus radiotherapy for localized high-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1998. 339:21–26.16. Coltrera MD. Primary T-cell lymphoma of the thyroid. Head Neck. 1999. 21:160–163.
Article17. Okamoto A, Namura K, Uchiyama H, Kajita Y, Inaba T, Nakamura S, Shimazaki C. Cytotoxic T-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the thyroid gland. Am J Hematol. 2005. 80:77–78.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Thyroid MALT Lymphoma Associated with Thyroid Papillary Cancer
- Malignant Lymphoma Associated with Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- A Case of Primary Thyroid Lymphoma Associated with Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- Synchronous Occurrence of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma: a Single Case Report
- Three Cases of Primary Thyroid Lymphoma at a Single Institution