J Korean Med Sci.
2011 Jan;26(1):42-46. 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.1.42.
Parasitemia Characteristics of Plasmodium vivax Malaria Patients in the Republic of Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Incheon, Korea.
- 7Department of Microbiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Incheon, Korea. jw.moses.park@gmail.com
- KMID: 1777974
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2011.26.1.42
Abstract
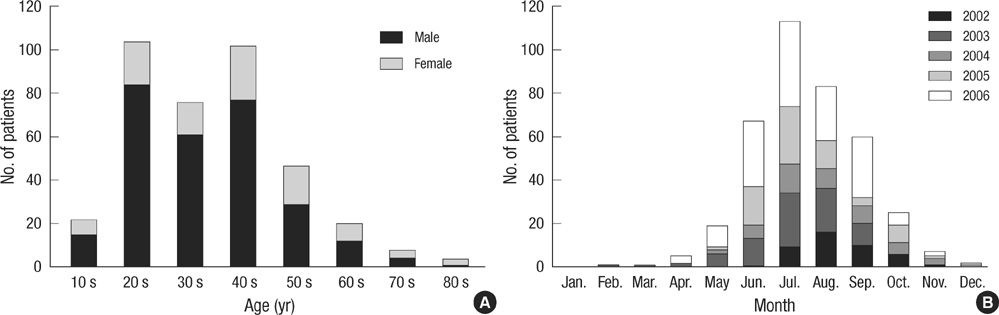
- Parasitemia characteristics of Plasmodium vivax malaria in temperate regions may differ from those in tropical zones. However, most parasitological and clinical features of P. vivax malaria have been investigated in the latter. In this study, we investigated 383 malaria patients to clarify the parasitemia characteristics of a P. vivax strain in the Republic of Korea (ROK). The mean parasitemia (8,396/microL) was less than half of tropical P. vivax malaria, and multiple invasions of erythrocytes were not rare (53.5% of the patients, 2.4% of the total investigated RBCs), but less than the observations in tropical zones. The intervals between the first symptom onset and diagnosis were significantly longer in gametocyte (+) patients than in gametocyte (-) patients. Only half of the total patients had both genders of gametocytes (191 of 353), and the male gametocyte density (169/microL) was lower than that of P. vivax strains of a previous study. Multiple invasions of erythrocytes and gametocytemia were coincident factors of the degree of anemia in P. vivax malaria. The present findings demonstrate the P. vivax strain in ROK reveals relatively low parasitemia and low male to female gametocyte ratio. The low ratio may be related with low transmission efficacy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sachs J, Malaney P. The economic and social burden of malaria. Nature. 2002. 415:680–685.2. Price RN, Tjitra E, Guerra CA, Yeung S, White NJ, Anstey NM. Vivax malaria: neglected and not benign. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007. 77:6 Suppl. 79–87.3. Hasegawa Y. Malaria in Korea. Chosun Igakkai Zasshi. 1913. 4:53–69.4. Hankey DD, Jones R Jr, Coatney GR, Alving AS, Coker WG, Garrison PL, Donovan WLWN. Korean vivax malaria. I. Natural history and response to chloroquine. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1953. 2:958–969.5. Paik YH, Ree HI, Shim JC. Malaria in Korea. Jpn J Exp Med. 1988. 58:55–66.6. Park JW, Klein TA, Lee HC, Pacha LA, Ryu SH, Yeom JS, Moon SH, Kim TS, Chai JY, Oh MD, Choe KW. Vivax malaria: a continuing health threat to the Republic of Korea. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003. 69:159–167.7. Ree HI. Unstable vivax malaria in Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 2000. 38:119–138.8. Jun G, Yeom JS, Hong JY, Shin EH, Chang KS, Yu JR, Oh S, Chung H, Park JW. Resurgence of Plasmodium vivax malaria in the Republic of Korea during 2006-2007. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009. 81:605–610.9. Yeom JS, Ryu SH, Oh S, Lee WJ, Kim TS, Kim KH, Kim YA, Ahn SY, Cha JE, Park JW. Status of Plasmodium vivax malaria in the Republic of Korea during 2001-2003. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005. 73:604–608.10. Yeom JS, Kim TS, Oh S, Sim JB, Barn JS, Kim HJ, Kim YA, Ahn SY, Shin MY, Yoo JA, Park JW. Plasmodium vivax malaria in the Republic of Korea during 2004-2005: changing patterns of infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007. 76:865–868.11. Eaton P. Susceptibility of red cells to malaria. Am J Trop Med. 1934. 14:431–437.12. McKenzie FE, Jeffery GM, Collins WE. Plasmodium vivax blood-stage dynamics. J Parasitol. 2002. 88:521–535.13. McKenzie FE, Jeffery GM, Collins WE. Gametocytemia and fever in human malaria infections. J Parasitol. 2007. 93:627–633.14. Simpson JA, Silamut K, Chotivanich K, Pukrittayakamee S, White NJ. Red cell selectivity in malaria: a study of multiple-infected erythrocytes. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1999. 93:165–168.15. Yeom JS, Ryu SH, Oh S, Choi DH, Song KJ, Oh YH, Lee JH, Kim YA, Ahn SY, Yang HY, Cha JE, Park JW. Evaluation of anti-malarial effects of mass chemoprophylaxis in the Republic of Korea Army. J Korean Med Sci. 2005. 20:707–712.16. Oh MD, Shin H, Shin D, Kim U, Lee S, Kim N, Choi MH, Chai JY, Choe K. Clinical features of vivax malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001. 65:143–146.17. Collins WE, Sullivan JS, Jeffery GM, Williams A, Galland GG, Nace D, Williams T, Barnwell JW. The Chesson strain of Plasmodium vivax in humans and different species of Aotus monkeys. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009. 80:152–159.18. Sinden RE, Gilles HM. Warrell DA, Gilles HM, editors. The malaria parasites. Essential Malariology. 2002. 4th ed. London: Arnold;8–34.19. Boyd MF, Kitchen SF. On the infectiousness of patients infected with Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med. 1937. 17:253–262.20. Smalley ME, Sinden RE. Plasmodium falciparum gametocytes: their longevity and infectivity. Parasitology. 1977. 74:1–8.21. Park JW. Changing transmission pattern of Plasmodium vivax malaria in the Republic of Korea: Relationship with climate change. Environ Health Toxicol. 2011. 26:in press.22. Hommel M. Warrell DA, Gilles HM, editors. Diagnostic methods in malaria. Essential Malariology. 2002. 4th ed. London: Arnold;35–58.23. Wang CC. Multiple invasion of erythrocyte by malaria parasites. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1970. 64:268–270.24. Prasad RN, Prasad H, Virk KJ, Sharma VP. Detection of multiple invasion of erythrocytes by Plasmodium vivax. Trop Med Parasitol. 1990. 41:437–438.25. Hingst HE. Erythrocyte susceptibility to Plasmodium vivax Grassi and Feletti, 1890. Am J Trop Med. 1938. 18:361–372.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Retinal Hemorrhage in an Adult with P. vivax Malaria
- Three cases of vivax malaria showing atypical clinical course
- A Case of Asymptomatic Plasmodium vivax Malaria Mimicking Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
- Appearance Characteristics of the Atypical Lymphocytes in the Blood of the Plasmodium vivax Malarial Patients
- Evaluation of LG Malaria Anti-PvTM for Diagnosis of Plasmodium vivax Malaria in the Republic of Korea