Epidemiology of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome in Korea, 2001-2010
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul, Korea. ischoi@konkuk.ac.kr
- 2Veterinary Science Research Institute, College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1777698
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.10.1552
Abstract
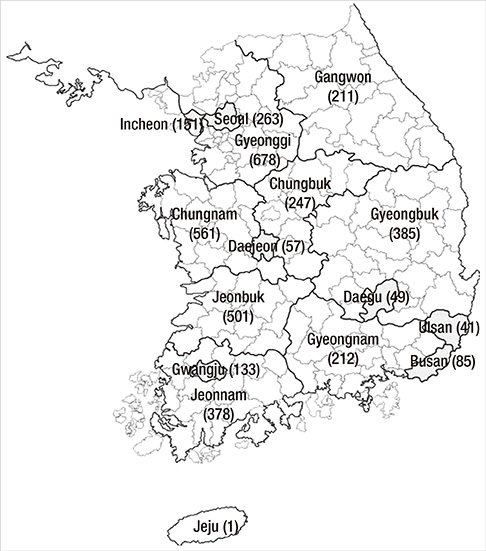
- This study describes the epidemiology of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) in the past 10 yr (2001-2010) in Korea. During this period, a total of 3,953 HFRS patients and an average prevalence rate of 0.81 per 100,000 population were recorded, with a total of 40 fatal cases, corresponding to a case fatality rate of 1.01%. More HFRS cases were found in men than in women (57% vs 43%), and a higher prevalence rate of HFRS was observed in patients older than 40 yr (82.1%). The highest numbers of HFRS cases were found amongst farmers (35.6%). The majority of HFRS cases (71.3%) occurred in the last quarter of the calendar year (October to December). More HFRS cases occurred in the western part than in the eastern part of Korea (68.9% vs 31.1%). The incidence of HFRS was significantly higher (P < 0.001) in rural areas than in urban areas (80.3% vs 19.7%). HFRS still occurs commonly among men, in autumn, and in western rural area of Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Recent Increase of Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis and Co-Infection with Scrub Typhus or Korean Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome in Korea
Dae-Hyuk Heo, Joo-Hee Hwang, Seung Hee Choi, Mir Jeon, Ju-Hyung Lee, Jae-Hoon Lee, Seon-Do Hwang, Kyeong-Ah Lee, Seung-Hun Lee, Chang-Seop Lee
J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(11):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e87.Absence of a Seasonal Variation of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome in Yeoncheon Compared to Nationwide Korea
Yo Han Park
Infect Chemother. 2018;50(2):120-127. doi: 10.3947/ic.2018.50.2.120.Clinical Score System to Differentiate Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Patients from Patients with Scrub Typhus or Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome in Korea
Dae-Hyuk Heo, Yu Min Kang, Kyoung-Ho Song, Jun-Won Seo, Jeong-Han Kim, June Young Chun, Kang Il Jun, Chang Kyung Kang, Song Mi Moon, Pyoeng Gyun Choe, Wan Beom Park, Ji Hwan Bang, Eu Suk Kim, Hong Bin Kim, Sang-Won Park, Won Sup Oh, Nam Joong Kim, Myoung-don Oh
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(11):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e77.
Reference
-
1. Jonsson CB, Figueiredo LT, Vapalahti O. A global perspective on hantavirus ecology, epidemiology, and disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010; 23:412–441.2. Lee HW, Lee PW, Johnson KM. Isolation of the etiologic agent of Korean Hemorrhagic fever. J Infect Dis. 1978; 137:298–308.3. Lee HW, van der Groen G. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Prog Med Virol. 1989; 36:62–102.4. Smadel JE. Epidemic hemorrhagic fever. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1953; 43:1327–1330.5. Park K, Kim CS, Moon KT. Protective effectiveness of hantavirus vaccine. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004; 10:2218–2220.6. Song JW, Moon SS, Gu SH, Song KJ, Baek LJ, Kim HC, Kijek T, O'Guinn ML, Lee JS, Turell MJ, et al. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in 4 US soldiers, South Korea, 2005. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009; 15:1833–1836.7. Song JY, Chun BC, Kim SD, Baek LJ, Kim SH, Sohn JW, Cheong HJ, Kim WJ, Park SC, Kim MJ. Epidemiology of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in endemic area of the Republic of Korea, 1995-1998. J Korean Med Sci. 2006; 21:614–620.8. Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome: statistical system of the national notifiable disease surveillance system (2001-2010). Available at http://www.cdc.go.kr.9. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (MHW, ROK). Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome, Incidence for communicable diseases (category III). Yearbook of Health and Welfare Statistics (2001-2010). Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare;2010.10. Lim MY, Ryou J, Kim SY, Shin EH, Yoo YJ, Yun SM, Noh YT, Han MG, Ju YR. Seroprevalence of hantaviruses in small wild mammals trapped in South Korea from 2005 to 2010. J Vector Ecol. 2012; 37:97–101.11. Ryou J, Lee HI, Yoo YJ, Noh YT, Yun SM, Kim SY, Shin EH, Han MG, Ju YR. Prevalence of hantavirus infection in wild rodents from five provinces in Korea, 2007. J Wildl Dis. 2011; 47:427–432.12. Klein SL, Marks MA, Li W, Glass GE, Fang LQ, Ma JQ, Cao WC. Sex differences in the incidence and case fatality rates from hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in China, 2004-2008. Clin Infect Dis. 2011; 52:1414–1421.