Yonsei Med J.
2009 Dec;50(6):845-847. 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.6.845.
A Case of Dysplastic Nevus of the External Auditory Canal Presenting with Conductive Hearing Loss
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Hallym University, Seoul, Korea. kcw5088@dreamwiz.com
- 2Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1777101
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2009.50.6.845
Abstract
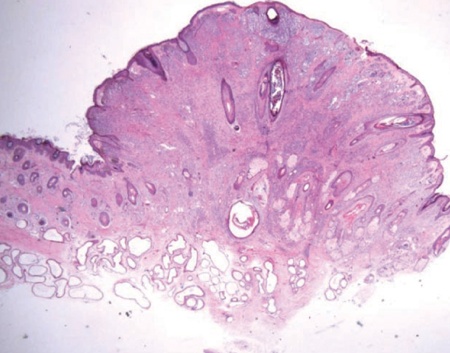
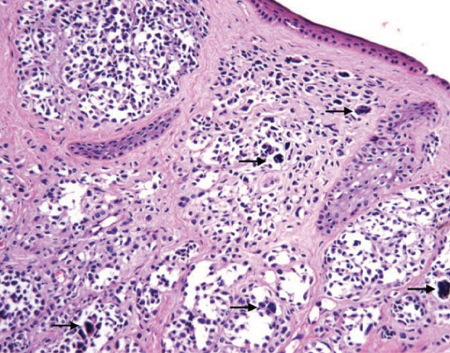
- A nevus which is a benign melanocytic neoplasm rarely occurs within the external auditory canal (EAC). A dysplastic nevus presents atypical features both clinically and histologically, and is important as a potential precursor for melanoma. We present a case of a 33-year-old female patient with a dysplastic nevus in her EAC. Physical examination revealed a protruding mass arising from the posterior wall of the left cartilaginous EAC. The mass showed clinically characteristic findings of a melanocytic nevus. The patient underwent excisional biopsy via a transcanal approach under local anesthesia. Histopathological examination revealed an intradermal nevus with atypical melanocytes without pleomorphism. There was no evidence of recurrence two years after surgical excision.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee FP. Pigmented nevus of the external auditory canal. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006. 135:124–128.
Article2. Youngs R, Hawke M, Kwok P. Intradermal nevus of the ear canal. J Otolaryngol. 1988. 17:241–243.3. Deguine C, Pulec JL. Benign nevus of the external auditory canal. Ear Nose Throat J. 1998. 77:448.
Article4. Bothwell NE, Willard CC, Sorensen DM, Downey TJ. A rare case of a sebaceous nevus in the external auditory canal. Ear Nose Throat J. 2003. 82:38–41.
Article5. Kazikdas KC, Onal K, Kuehnel TS, Ozturk T. An intradermal nevus of the external auditory meatus. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2006. 263:253–255.
Article6. Farrahi F, Egbert BM, Swetter SM. Histologic similarities between lentigo maligna and dysplastic nevus: importance of clinicopathologic distinction. J Cutan Pathol. 2005. 32:405–412.
Article7. Elder DE. Precursors to melanoma and their mimics: nevi of special sites. Mod Pathol. 2006. 19:S4–S20.
Article8. Naeyaert JM, Brochez L. Clinical practice. Dysplastic nevi. N Engl J Med. 2003. 349:2223–2240.9. Marghoob AA, Blum R, Nossa R, Busam KJ, Sachs D, Halpern A. Agminated atypical (dysplastic) nevi: case report and review of the literature. Arch Dermatol. 2001. 137:917–920.10. Tsao H, Bevona C, Goggins W, Quinn T. The transformation rate of moles (melanocytic nevi) into cutaneous melanoma: a population-based estimate. Arch Dermatol. 2003. 139:282–288.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Intradermal Nevus of the External Auditory Canal
- A Case of Compound Nevus of the External Auditory Canal
- A Case of Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis involving the External Auditory Canal
- Compound Nevus Occurring Near External Auditory Canal: Successful Treatment by CO2 Laser Abrasion
- Irritated Seborrheic Keratosis of the External Auditory Canal which Caused Conductive Hearing Loss