Yonsei Med J.
2011 May;52(3):445-453. 10.3349/ymj.2011.52.3.445.
Overexpressions of Cyclin B1, cdc2, p16 and p53 in Human Breast Cancer: The Clinicopathologic Correlations and Prognostic Implications
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. idavidkim@yahoo.co.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1777016
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2011.52.3.445
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The molecular mechanisms that are responsible for the initiation and progression of breast cancers are largely unknown. This study was to analyze the cyclin B1, cdc2, p53 and p16 tumor suppressor genes in human breast cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
To investigate the role of cyclin B1, cdc2, p53 and p16 in the pathogenesis and progression of breast carcinomas, 98 cases of breast cancers were examined by immunohistochemical method. The correlations of cyclin B1, cdc2, p53 and p16 expression with various clinico-pathologic findings were analysed.
RESULTS
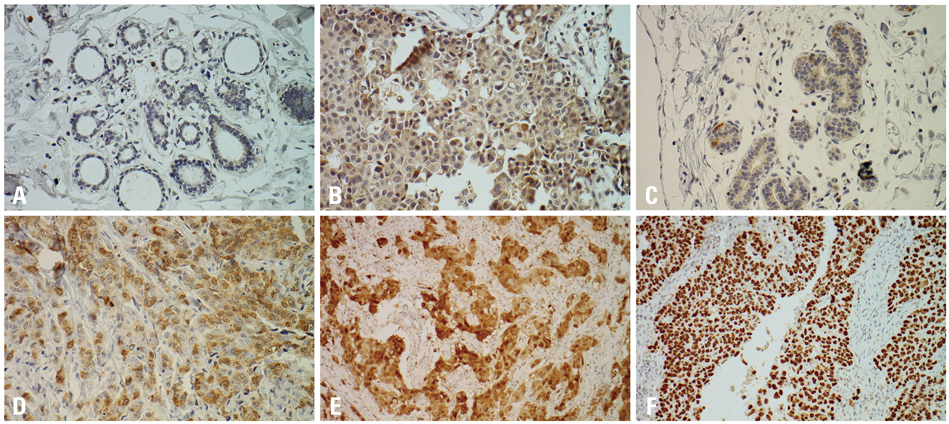
In the normal breast tissues, cyclin B1, cdc2 and p16 were weakly expressed, while p53 was not expressed. On the other hand, cyclin B1, cdc2, p53 and p16 were overexpressed in breast cancer, showing correlation between the expression of cyclin B1 and cdc2 and breast cancers (p=0.00). The overexpressions of cdc2 and p16 were correlated with an infiltrative tumor border pattern and this was statistically significant (p<0.05). In addition, the overexpression of cdc2 was correlated with histologic high grade carcinomas (p=0.00).
CONCLUSION
Cyclin B1 and cdc2 appeared to be involved in the genesis or progression of breast cancers. In addition, the overexpressions of p16 and p53 may play important roles in more aggressive tumor and the overexpression of cdc2 is associated with progression of tumor to a higher grade of breast carcinomas. The deranged overexpressions of cyclin B1, cdc2, p16 and p53 may play an important role in human breast carcinogenesis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Breast Neoplasms/*genetics/metabolism/pathology
Cyclin B/*genetics/metabolism
Cyclin B1/*genetics/metabolism
Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor p16/*genetics/metabolism
Female
Gene Expression Regulation, Neoplastic
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
Middle Aged
Tumor Suppressor Protein p53/*genetics/metabolism
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jung KW, Won YJ, Park S, Kong HJ, Sung J, Shin HR, et al. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality and survival in 2005. J Korean Med Sci. 2009. 24:995–1003.
Article2. Ohta T, Okamoto K, Isohashi F, Shibata K, Fukuda M, Yamaguchi S, et al. T-loop deletion of CDC2 from breast cancer tissues eliminates binding to cyclin B1 and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21. Cancer Res. 1998. 58:1095–1098.3. Aaltonen K, Amini RM, Heikkilä P, Aittomäki K, Tamminen A, Nevanlinna H, et al. High cyclin B1 expression is associated with poor survival in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2009. 100:1055–1060.
Article4. Agarwal R, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Myhre S, Carey M, Lee JS, Overgaard J, et al. Integrative analysis of cyclin protein levels identifies cyclin b1 as a classifier and predictor of outcomes in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. 15:3654–3662.
Article5. Suzuki T, Urano T, Miki Y, Moriya T, Akahira J, Ishida T, et al. Nuclear cyclin B1 in human breast carcinoma as a potent prognostic factor. Cancer Sci. 2007. 98:644–651.
Article6. Yuan J, Yan R, Krämer A, Eckerdt F, Roller M, Kaufmann M, et al. Cyclin B1 depletion inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human tumor cells. Oncogene. 2004. 23:5843–5852.
Article7. Kim SJ, Nakayama S, Miyoshi Y, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y, Matsushima T, et al. Determination of the specific activity of CDK1 and CDK2 as a novel prognostic indicator for early breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2008. 19:68–72.
Article8. Kourea HP, Koutras AK, Scopa CD, Marangos MN, Tzoracoeleftherakis E, Koukouras D, et al. Expression of the cell cycle regulatory proteins p34cdc2, p21waf1, and p53 in node negative invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Mol Pathol. 2003. 56:328–335.
Article9. Dublin EA, Patel NK, Gillett CE, Smith P, Peters G, Barnes DM. Retinoblastoma and p16 proteins in mammary carcinoma: their relationship to cyclin D1 and histopathological parameters. Int J Cancer. 1998. 79:71–75.
Article10. Vallian S, Sedaghat M, Nassiri I, Frazmand A. Methylation status of p16 INK4A tumor suppressor gene in Iranian patients with sporadic breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009. 135:991–996.
Article11. Zhang J, Pickering CR, Holst CR, Gauthier ML, Tlsty TD. p16INK4a modulates p53 in primary human mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2006. 66:10325–10331.
Article12. Iwaya K, Tsuda H, Hiraide H, Tamaki K, Tamakuma S, Fukutomi T, et al. Nuclear p53 immunoreaction associated with poor prognosis of breast cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1991. 82:835–840.
Article13. Hunter T, Pines J. Cyclins and cancer. Cell. 1991. 66:1071–1074.
Article14. Nurse P. Ordering S phase and M phase in the cell cycle. Cell. 1994. 79:547–550.
Article15. Sherr CJ, Roberts JM. Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev. 1995. 9:1149–1163.
Article16. Porter LA, Donoghue DJ. Cyclin B1 and CDK1: nuclear localization and upstream regulators. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2003. 5:335–347.17. Looi K, Megliorino R, Shi FD, Peng XX, Chen Y, Zhang JY. Humoral immune response to p16, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor in human malignancies. Oncol Rep. 2006. 16:1105–1110.
Article18. Shaw PH. The role of p53 in cell cycle regulation. Pathol Res Pract. 1996. 192:669–675.
Article19. Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW. p53 function and dysfunction. Cell. 1992. 70:523–526.
Article20. American Joint Committee on Cancer. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 2010. 7th ed. New York: Springer-Verlag;347–376.21. Harris L, Fritsche H, Mennel R, Norton L, Ravdin p, Taube S, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology 2007 update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007. 25:5287–5312.
Article22. Gannon JV, Nebreda A, Goodger NM, Morgan PR, Hunt T. A measure of the mitotic index: studies of the abundance and half-life of p34cdc2 in cultured cells and normal and neoplastic tissues. Genes Cells. 1998. 3:17–27.
Article23. Murakami H, Furihata M, Ohtsuki Y, Ogoshi S. Determination of the prognostic significance of cyclin B1 overexpression in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Virchows Arch. 1999. 434:153–158.
Article24. Soria JC, Jang SJ, Khuri FR, Hassan K, Liu D, Hong WK, et al. Overexpression of cyclin B1 in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer and its clinical implication. Cancer Res. 2000. 60:4000–4004.25. Ito Y, Takeda T, Sakon M, Monden M, Tsujimoto M, Matsuura N. Expression and prognostic role of cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (cdc2) in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology. 2000. 59:68–74.
Article26. Feakins RM, Nickols CD, Bidd H, Walton SJ. Abnormal expression of pRb, p16, and cyclin D1 in gastric adenocarcinoma and its lymph node metastases: relationship with pathological features and survival. Hum Pathol. 2003. 34:1276–1282.
Article27. Lee CT, Capodieci P, Osman I, Fazzari M, Ferrara J, Scher HI, et al. Overexpression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16 is associated with tumor recurrence in human prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1999. 5:977–983.28. Halvorsen OJ, Høstmark J, Haukaas S, Høisaeter PA, Akslen LA. Prognostic significance of p16 and CDK4 proteins in localized prostate carcinoma. Cancer. 2000. 88:416–424.
Article29. Dong Y, Walsh MD, McGuckin MA, Gabrielli BG, Cummings MC, Wright RG, et al. Increased expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2 (CDKN2A) gene product P16INK4A in ovarian cancer is associated with progression and unfavourable prognosis. Int J Cancer. 1997. 74:57–63.
Article30. Gonzalez-Zulueta M, Bender CM, Yang AS, Nguyen T, Beart RW, Van Tornout JM, et al. Methylation of the 5' CpG island of the p16/CDKN2 tumor suppressor gene in normal and transformed human tissues correlates with gene silencing. Cancer Res. 1995. 55:4531–4535.31. Bartley AN, Ross DW. Validation of p53 immunohistochemistry as a prognostic factor in breast cancer in clinical practice. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2002. 126:456–458.
Article32. Wegman PP, Marcus NJ, Malakkaran BP, Wingren S. Biological significance of allele specific loss of the p53 gene in breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009. 118:15–20.
Article33. O'Hanlon DM, Kiely M, MacConmara M, Al-Azzawi R, Connolly Y, Jeffers M, et al. An immunohistochemical study of p21 and p53 expression in primary node-positive breast carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2002. 28:103–107.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of Cyclin B1 and cdc2 in Nodal Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma and its Prognostic Implications
- Prognostic Implications of Cyclin B1, p34cdc2, p27(Kip1) and p53 Expression in Gastric Cancer
- Expression of p34(cdc2), p27(Kip1), p21(WAF1/Cip1) and p53 in Human Breast Cancers
- Significance of Expression of p16, Cyclin D1, Rb, and p53 Protein and Correlation with Clinicopathologic Prognostic Factors in Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of the Breast
- Enrichment for the POLE mutated against p53 wild subtype using clinicopathologic factors and cyclin B1 immunohistochemistry in endometrial cancer