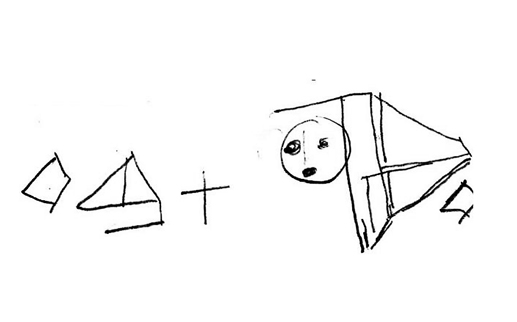Yonsei Med J.
2012 May;53(3):486-494. 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.3.486.
Lateralization of Cognitive Functions in Aphasia after Right Brain Damage
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Speech Pathology, Daegu University, Gyeongsan, Korea.
- 2The Geriatric Health Clinic and Research Institute (GHCRI), Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. rmpyun@korea.ac.kr
- 4Department of English Language, Interpretation & Translation, Dongguk University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Communication Disorders, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1776981
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.3.486
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The lateralization of cognitive functions in crossed aphasia in dextrals (CAD) has been explored and compared mainly with cases of aphasia with left hemisphere damage. However, comparing the neuropsychological aspects of CAD and aphasia after right brain damage in left-handers (ARL) could potentially provide more insights into the effect of a shift in the laterality of handedness or language on other cognitive organization. Thus, this case study compared two cases of CAD and one case of ARL.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The following neuropsychological measures were obtained from three aphasic patients with right brain damage (two cases of CAD and one case of ARL); language, oral and limb praxis, and nonverbal cognitive functions (visuospatial neglect and visuospatial construction).
RESULTS
All three patients showed impaired visuoconstructional abilities, whereas each patient showed a different level of performances for oral and limb praxis, and visuospatial neglect.
CONCLUSION
Based on the analysis of these three aphasic patients' performances, we highlighted the lateralization of language, handedness, oral and limb praxis, visuospatial neglect and visuospatial constructive ability in aphasic patients with right brain damage.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
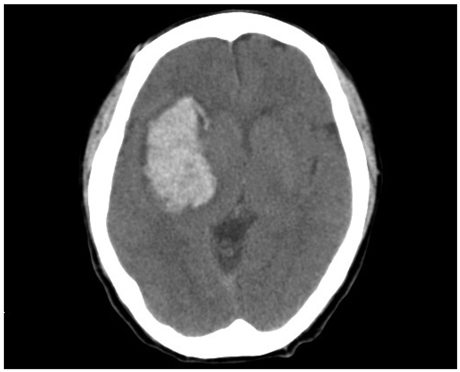
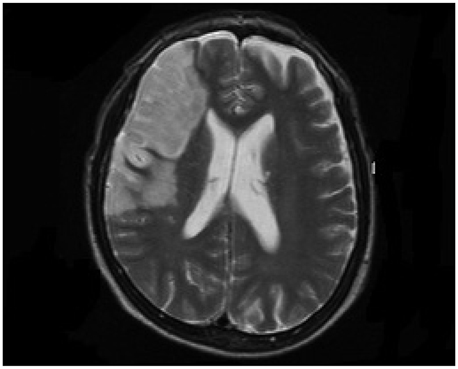
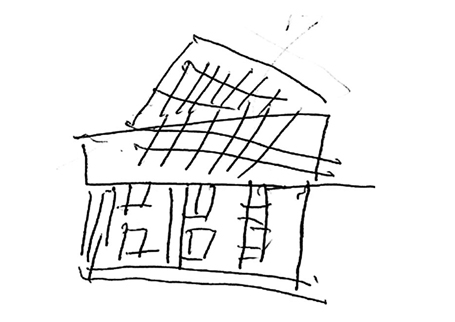
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Letter to the Editor. Re: Lateralization of Cognitive Functions in Aphasia after Right Brain Damage
Iraj Derakhshan
Yonsei Med J. 2013;54(4):1070-1071. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.4.1070.The Author Reply. Re: Lateralization of Cognitive Functions in Aphasia after Right Brain Damage
Sung-Bom Pyun
Yonsei Med J. 2013;54(4):1072-1073. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.4.1072.The Author Reply. Re: Lateralization of Cognitive Functions in Aphasia after Right Brain Damage
Sung-Bom Pyun
Yonsei Med J. 2013;54(4):1072-1073. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.4.1072.
Reference
-
1. Alexander MP. Feinberg TE, Farah MJ, editors. APhasia: Clinical and anatomic issues. Behavioral neurology and neuropsychology. 2003. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;147–164.2. Bartha L, Mariën P, Poewe W, Benke T. Linguistic and neuropsychological deficits in crossed conduction aphasia. Report of three cases. Brain Lang. 2004. 88:83–95.
Article3. Borod JC, Carper M, Naeser M, Goodglass H. Left-handed and right-handed aphasics with left hemisphere lesions compared on nonverbal performance measures. Cortex. 1985. 21:81–90.
Article4. Brown JW, Hécaen H. Lateralization and language representation. Neurology. 1976. 26:183–189.5. Brown JW, Wilson FR. Crossed aphasia in a dextral. A case report. Neurology. 1973. 23:907–911.
Article6. Coppens P, Hungerford S, Yamaguchi S, Yamadori A. Crossed aphasia: an analysis of the symptoms, their frequency, and a comparison with left-hemisphere aphasia symptomatology. Brain Lang. 2002. 83:425–463.
Article7. Lessa Mansur L, Radanovic M, Santos Penha S, Iracema Zanotto de Mendonça L, Cristina Adda C. Language and visuospatial impairment in a case of crossed aphasia. Laterality. 2006. 11:525–539.
Article8. Mariën P, Engelborghs S, Vignolo LA, De Deyn PP. The many faces of crossed aphasia in dextrals: report of nine cases and review of the literature. Eur J Neurol. 2001. 8:643–658.
Article9. Bramwell B. On "crossed" aphasia. Lancet. 1899. 1:1473–1479.10. Sheehy LM, Haines ME. Crossed Wernicke's aphasia: a case report. Brain Lang. 2004. 89:203–206.
Article11. Annett M. A single gene explanation of right and left handedness and brainedness. 1978. Coventry, UK: Lanchester Polytechnic.12. Joanette Y. Boller F, Grafman J, editors. Aphasia in left-handers and crossed aphasia. Handbook of neuropsychology. 1989. Amsterdam: Elsevier;173–183.13. Alexander MP, Annett M. Crossed aphasia and related anomalies of cerebral organization: case reports and a genetic hypothesis. Brain Lang. 1996. 55:213–239.
Article14. Oldfield RC. The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia. 1971. 9:97–113.
Article15. Kim HH, Na DL. Korean-version Western Aphasia Battery (K-WAB). 2001. Seoul: Paradise Welfare Foundation.16. Dabul BL. Apraxia battery for adults: Examiner's manual and picture plates. 1979. Austin, TX: Pro-Ed.17. Kang Y, Na DL, Hahn S. A validity study on the Korean mini-mental state examination (K-MMSE) in dementia patients. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1997. 15:300–308.18. Wilson B, Cockburn J, Halligan P. Development of a behavioral test of visuospatial neglect. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1987. 68:98–102.19. Gauthier L, Dehaut F, Joanette Y. The Bells Test: a quantitative and qualitative test for visual neglect. Int J Clin Neuropsychol. 1989. 11:49–54.20. Wechsler D. Manual for the Wechsler adult intelligence scale. 1995. New York: Psychological Corporation.21. Visser RSH. Manual of the complex figure test CFT. 1973. Amsterdam: Swets & Zeitlinger.22. Raven JC. Guide to the standard progressive matrices: sets A, B, C, D and E. 1960. London: H.K. Lewis.23. Piercy M, Hecaen H, de Ajuriaguerra . Constructional apraxia associated with unilateral cerebral lesions-left and right sided cases compared. Brain. 1960. 83:225–242.
Article24. Laeng B. Constructional apraxia after left or right unilateral stroke. Neuropsychologia. 2006. 44:1595–1606.
Article25. Marchetti C, Carey D, Della Sala S. Crossed right hemisphere syndrome following left thalamic stroke. J Neurol. 2005. 252:403–411.
Article26. Castro-Caldas A, Confraria A, Poppe P. Non-verbal disturbances in crossed aphasia. Aphasiology. 1987. 1:403–413.
Article27. Marchetti C, Della Sala S. On crossed apraxia. Description of a right-handed apraxic patient with right supplementary motor area damage. Cortex. 1997. 33:341–354.
Article28. Raymer AM, Merians AS, Adair JC, Schwartz RL, Williamson DJ, Rothi LJ, et al. Crossed apraxia: implications for handedness. Cortex. 1999. 35:183–199.
Article29. Henderson VW. Speech fluency in crossed aphasia. Brain. 1983. 106(Pt 4):837–857.
Article30. Mendez MF, Benson DF. Atypical conduction aphasia. A disconnection syndrome. Arch Neurol. 1985. 42:886–891.31. Vingerhoets G, Acke F, Alderweireldt AS, Nys J, Vandemaele P, Achten E. Cerebral lateralization of praxis in right- and left-handedness: same pattern, different strength. Hum Brain Mapp. 2012. 2011. [Epub ahead of print].
Article32. Basso A, De Renzi E, Faglioni P, Scotti G, Spinnler H. Neuropsychological evidence for the existence of cerebral areas critical to the performance of intelligence tasks. Brain. 1973. 96:715–728.
Article33. Kertesz A, McCabe P. Intelligence and aphasia: performance of aphasics on Raven's coloured progressive matrices (RCPM). Brain Lang. 1975. 2:387–395.
Article34. Maeshima S, Ueyoshi A, Matsumoto T, Boh-Oka S, Yoshida M, Itakura T. Quantitative assessment of impairment in constructional ability by cube copying in patients with aphasia. Brain Inj. 2002. 16:161–167.
Article35. Pyun SB, Yi HY, Hwang YM, Ha J, Yoo SD. Is visuospatial cognitive function preserved in aphasia? J Neurol Sci. 2009. 283:304.
Article36. Mazzocchi F, Vignolo LA. Localisation of lesions in aphasia: clinical-CT scan correlations in stroke patients. Cortex. 1979. 15:627–653.
Article37. Alexander MP. Boller F, Grafman J, editors. Clinical-anatomical correlations of aphasia following predominantly subcortical lesions. Handbook of neuropsychology. 1989. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science;46–66.38. Kleist K. Gehirnpathologie. 1934. Leipzig: Barth.39. Guérin F, Ska B, Belleville S. Cognitive processing of drawing abilities. Brain Cogn. 1999. 40:464–478.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Letter to the Editor. Re: Lateralization of Cognitive Functions in Aphasia after Right Brain Damage
- The Author Reply. Re: Lateralization of Cognitive Functions in Aphasia after Right Brain Damage
- Evaluation of Aphasia
- Characteristics of Cognitive Impairment in Patients With Post-stroke Aphasia
- Two Cases of Primary Progressive Aphasia