Korean J Radiol.
2002 Mar;3(1):16-23. 10.3348/kjr.2002.3.1.16.
The Usefulness of MR Imaging of the Temporal Bone in the Evaluation of Patients with Facial and Audiovestibular Dysfunction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. hyungkim@inha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Otolaryngology, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1758442
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2002.3.1.16
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the clinical utility of MR imaging of the temporal bone in patients with facial and audiovestibular dysfunction with particular emphasis on the importance of contrast enhancement.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the MR images of 179 patients [72 men, 107 women; average age, 44 (range, 1-77) years] who presented with peripheral facial palsy (n=15), audiometrically proven sensorineural hearing loss (n=104), vertigo (n=109), or tinnitus (n=92). Positive MR imaging findings possibly responsible for the patients' clinical manifestations were categorized according to the anatomic sites and presumed etiologies of the lesions. We also assessed the utility of contrast-enhanced MR imaging by analyzing its contribution to the demonstration of lesions which would otherwise not have been apparent. All MR images were interpreted by two neuroradiologists, who reached their conclusions by consensus.
RESULTS
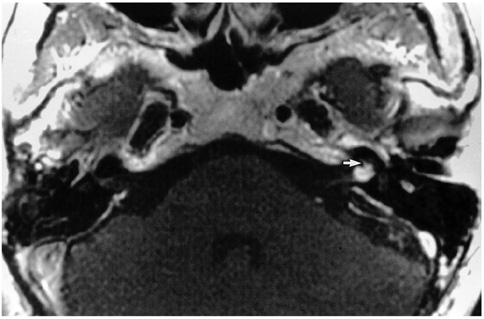
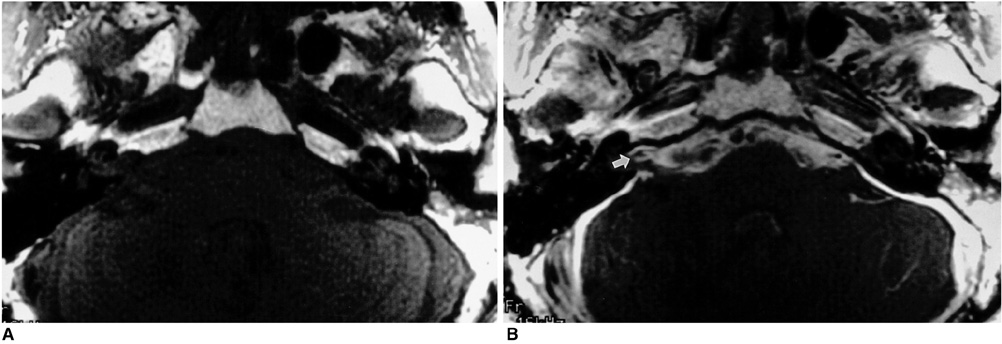
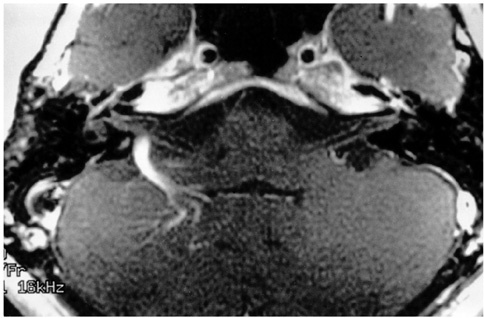
MR images demonstrated positive findings, thought to account for the presenting symptoms, in 78 (44%) of 179 patients, including 15 (100%) of 15 with peripheral facial palsy, 43 (41%) of 104 with sensorineural hearing loss, 40 (37%) of 109 with vertigo, and 39 (42%) of 92 with tinnitus. Thirty (38%) of those 78 patients had lesions that could be confidently recognized only at contrastenhanced MR imaging.
CONCLUSION
Even though its use led to positive findings in less than half of these patients, MR imaging of the temporal bone is a useful diagnostic procedure in the evaluation of those with facial and audiovestibular dysfunction. Because it was only at contrast-enhanced MR imaging that a significant number of patients showed positive imaging findings which explained their clinical manifestations, the use of contrast material is highly recommended.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
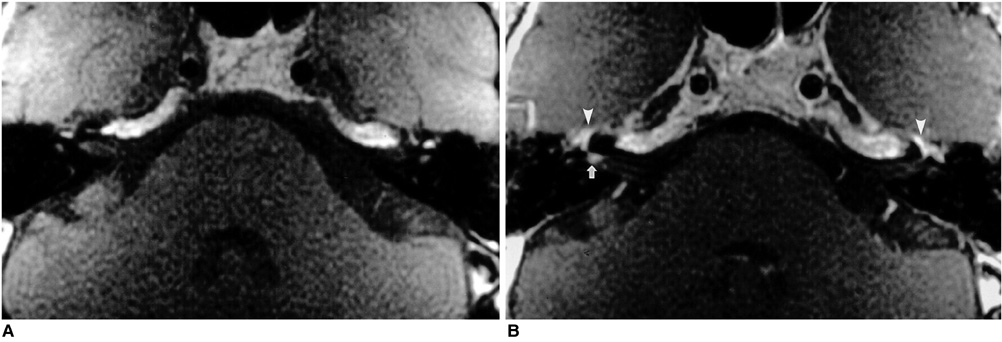
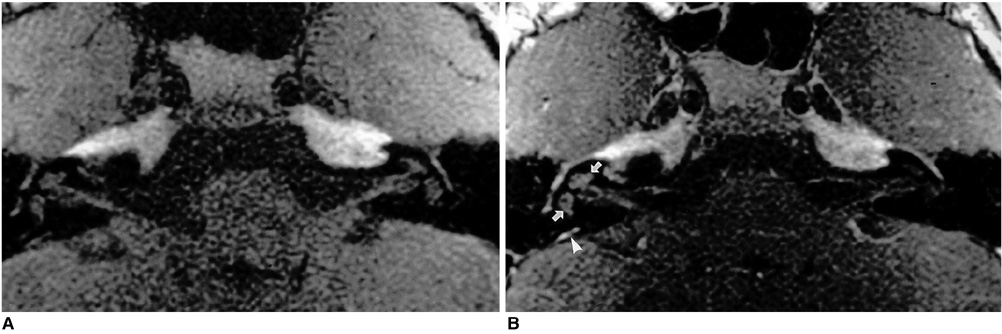
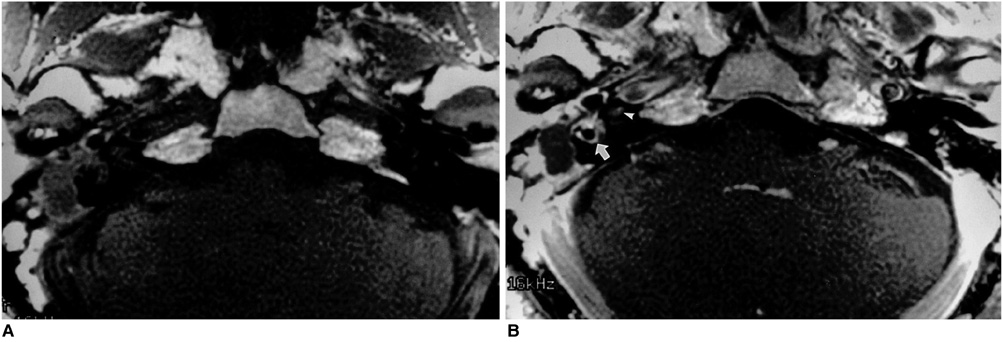
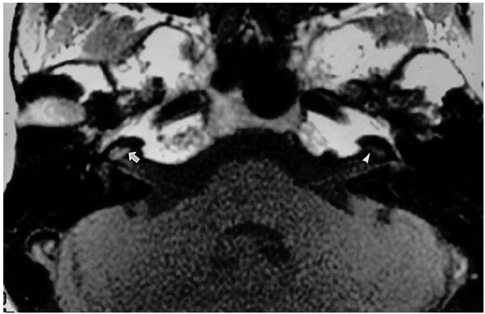
Figure
Reference
-
1. Casselman JW. Temporal bone imaging. Neuroimag Clin N Am. 1996. 6:265–289.2. Swartz JD, Harnsberger HR, Mukherji SK. The temporal bone: contemporary diagnostic dilemma. Radiol Clin North Am. 1998. 36:819–853.3. Lane JI. Facial nerve disorders. Neuroimag Clin N Am. 1993. 3:129–151.4. Mark AS. Vestibulocochlear system. Neuroimag Clin N Am. 1993. 3:153–170.5. Mark AS, Seltzer S, Harnsberger HR. Sensorineural hearing loss: more than meets the eye? AJNR. 1993. 14:37–45.6. Mark A. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of the temporal bone. Neuroimag Clin N Am. 1994. 4:117–131.7. Burgio DL, Siddique S, Haupert M, Meleca RJ. Magnetic resonance imaging of the facial nerve in children with idiopathic facial paralysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000. 122:556–559.8. Sartoretti-Schefer S, Kollias S, Wichmann W, Valavanis A. T2-weighted three-dimensional fast spin-echo MR in inflammatory peripheral facial nerve palsy. AJNR. 1998. 19:491–495.9. Saatci I, Sahinturk F, Sennaroglu L, Boyvat F, Gursel B, Besim A. MRI of the facial nerve in idiopathic facial palsy. Eur Radiol. 1996. 6:631–636.10. Gebarski SS, Telian SA, Niparko JK. Enhancement along the normal facial nerve in the facial canal: MR imaging and anatomic correlation. Radiology. 1992. 183:391–394.11. Levy RA, Arts AH. Predicting neuroradiologic outcome in patients referred for audiovestibular dysfunction. AJNR. 1996. 17:1717–1724.12. Fitzgerald DC, Mark AS. Sudden hearing loss: frequency of abnormal findings on contrast-enhanced MR studies. AJNR. 1998. 19:1433–1436.13. Day JJ, Freer CE, Dixon AK. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and brainstem in elderly patients with dizziness. Age Ageing. 1990. 19:144–150.14. Casselman JW, Kuhweide R, Dehaene I, Ampe W, Devlies F. Magnetic resonance examination of the inner ear and cerebellopontine angle in patients with vertigo and/or abnormal findings at vestibular testing. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1994. 513:15–27.15. Ojala M, Ketonen L, Palo J. The value of CT and very low-field MRI in the etiological diagnosis of dizziness. Acta Neurol Scand. 1988. 78:26–29.16. Han MH, Jabour BA, Andrews JC, et al. Nonneoplastic enhancing lesions mimicking intracanalicular vestibular schwannoma on gadolinium-enhanced MR images. Radiology. 1991. 179:795–796.17. Renowden SA, Anslow P. The effective use of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of acoustic neuromas. Clin Radiol. 1993. 48:25–28.18. Freije JE, Harvey SA, Haberkamp TJ. False-negative magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of facial nerve paralysis. Laryngoscope. 1996. 106:239–242.19. Mark AS, Seltzer S, Nelson-Drake J, Chapman JC, Fitzgerald DC, Gulya AJ. Labyrinthine enhancement of gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in sudden deafness and vertigo: correlation with audiologic and electronystagmographic studies. Ann Otol Laryngol. 1992. 101:459–464.20. Swartz JD. Sensorineural hearing deficit: a systematic approach based on imaging findings. Radiographics. 1996. 16:561–574.21. Weissman JL, Curtin HD, Hirsch BE, Hirsch WL Jr. High signal from the otic labyrinth on unenhanced magnetic resonance imaging. AJNR. 1992. 13:1183–1187.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- 3 Dimensional Volume MR Imaging of Intratemporal Facial Nerve
- Vestibular Schwannoma Atypically Invading Temporal Bone
- Radiologic Characteristics in a Case of Facial Nerve with Multisegment Involvement
- Multiple Myeloma: Report of a Case Manifested as Facial Nerve Palsy
- A Case of Multiple Myeloma Involving Temporal Bone