J Korean Surg Soc.
2010 Apr;78(4):219-224. 10.4174/jkss.2010.78.4.219.
Clinicopathologic Characteristics of Anal Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. stoh@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1750733
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2010.78.4.219
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was performed to evaluate clinicopathologic features in anal canal carcinoma.
METHODS
Among the 43 patients who were diagnosed with anal cancer at Kangnam St. Mary's Hospital, from June 1990 to June 2008, 31 patients were analyzed retrospectively. Concurrent chemoradiotherapy was performed on twenty-one patients with anal cancer. Chemotherapy with 5-FU/mitomycin and radiotherapy were started at the same time. An external beam radiation dose to the primary lesion and pelvis was modified from 4,500 to 6,000 cGy.
RESULTS
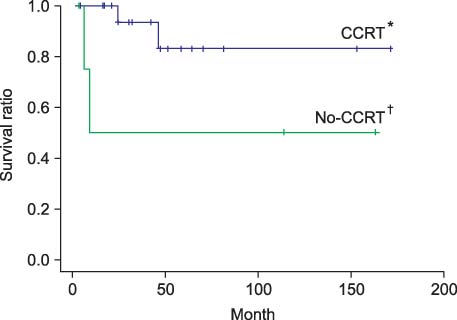
Among the 31 patients with anal cancer, the dominant histologic type was squamous cell carcinoma (n=25), followed by adenocarcinoma (n=6). Twenty-nine (93.5%) of these cancers were located in the anal canal and 2 (6.5%) in the anal margin. Among the 25 patients with squamous cell carcinoma, 20 cases were treated by concurrent chemoradiotherapy. The 5-year survival rate among squamous cell carcinoma cases was 83.3% for the concurrent chemoradiation group and 50.0% for the no concurrent chemoradiation group, which was statistically significant (P=0.05). Among the squamous cell carcinoma patients, there was no significant difference in survival rates between concurrent chemoradiation group (n=17) and concurrent chemoradiation with surgical resection group (n=8) (87.5% vs 68.8%; P=0.596).
CONCLUSION
In the squamous cell carcinoma treatment, concurrent chemoradiation therapy can offer better outcomes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Rectal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mistaken for Rectal Adenocarcinoma
Jung Ik Park, Ung Seok Yang, Sung Won Moon, Oun Ouk Nam, Hyo Jong Kim, Jeong Seok Lee, San Gyu Oh
Kosin Med J. 2014;29(2):157-160. doi: 10.7180/kmj.2014.29.2.157.
Reference
-
1. Nigro ND, Vaitkevicius VK, Considine B Jr. Combined therapy for cancer of the anal canal: a preliminary report. Dis Colon Rectum. 1974. 17:354–356.2. Whiteford MH, Stevens KR Jr, Oh S, Deveney KE. The evolving treatment of anal cancer: how are we doing? Arch Surg. 2001. 136:886–891.3. Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs. Annual Report of Cancer Incidence (2003) in Korea. 2008.4. Deans GT, McAleer JJ, Spence RA. Malignant anal tumours. Br J Surg. 1994. 81:500–508.5. Adam YG, Efron G. Current concepts and controversies concerning the etiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of malignant tumors of the anus. Surgery. 1987. 101:253–266.6. Holmes F, Borek D, Owen-Kummer M, Hassanein R, Fishback J, Behbehani A, et al. Anal cancer in women. Gastroenterology. 1988. 95:107–111.7. Kim TJ, Joo JH, Kim HR, Kim DY. Human papillomavirus infection in anal carcinoma, anal condylomata and rectal. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 1997. 13:7–14.8. Edwards AT, Morus LC, Foster ME, Griffith GH. Anal cancer: the case for earlier diagnosis. J R Soc Med. 1991. 84:395–397.9. Foust RL, Dean PJ, Stoler MH, Moinuddin SM. Intraepithelial neoplasia of the anal canal in hemorrhoidal tissue: a study of 19 cases. Hum Pathol. 1991. 22:528–534.10. Cataldo PA, MacKeigan JM. The necessity of routine pathologic evaluation of hemorrhoidectomy specimens. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1992. 174:302–304.11. Grinnell RS. An analysis of fortynine cases of squamous cell carcinoma of the anus. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1954. 98:29–39.12. Doci R, Zucali R, Bombelli L, Montalto F, Lamonica G. Combined chemoradiation therapy for anal cancer. A report of 56 cases. Ann Surg. 1992. 215:150–156.13. Beck DE, Karulf RE. Combination therapy for epidermoid carcinoma of the anal canal. Dis Colon Rectum. 1994. 37:1118–1125.14. Papillon J, Montbarbon JF. Epidermoid carcinoma of the anal canal. A series of 276 cases. Dis Colon Rectum. 1987. 30:324–333.15. Cho CC, Taylor CW 3rd, Padmanabhan A, Arnold MW, Aguilar PS, Meesig DM, et al. Squamous-cell carcinoma of the anal canal: management with combined chemo-radiation therapy. Dis Colon Rectum. 1991. 34:675–678.16. Rich TA, Ajani JA, Morrison WH, Ota D, Levin B. Chemoradiation therapy for anal cancer: radiation plus continuous infusion of 5-fluorouracil with or without cisplatin. Radiother Oncol. 1993. 27:209–215.17. Cummings BJ. Concomitant radiotherapy and chemotherapy for anal cancer. Semin Oncol. 1992. 19:102–108.18. Nigro ND. Multidisciplinary management of cancer of the anus. World J Surg. 1987. 11:446–451.19. Knecht BH. Combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy for carcinomas of the anus. Am J Surg. 1990. 159:518–521.20. Dougherty BG, Evans HL. Carcinoma of the anal canal: a study of 79 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985. 83:159–164.21. Sischy B. The use of radiation therapy combined with chemotherapy in the management of squamous cell carcinoma of the anus and marginally resectable adenocarcinoma of the rectum. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1985. 11:1587–1593.22. Bartelink H, Roelofsen F, Eschwege F, Rougier P, Bosset JF, Gonzalez DG, et al. Concomitant radiotherapy and chemotherapy is superior to radiotherapy alone in the treatment of locally advanced anal cancer: results of a phase III randomized trial of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Radiotherapy and Gastrointestinal Cooperative Groups. J Clin Oncol. 1997. 15:2040–2049.23. Flam M, John M, Pajak TF, Petrelli N, Myerson R, Doggett S, et al. Role of mitomycin in combination with fluorouracil and radiotherapy, and of salvage chemoradiation in the definitive nonsurgical treatment of epidermoid carcinoma of the anal canal: results of a phase III randomized intergroup study. J Clin Oncol. 1996. 14:2527–2539.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long-term Oncologic Outcome and Its Relevant Factors in Anal Cancer in Korea: A Nationwide Data Analysis
- Characteristics and Survival of Korean Anal Cancer From the Korea Central Cancer Registry Data
- Two Cases of Anal Cancer in Patient with Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome Infected by Human Papillomavirus
- A Case of Early-stage Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Anal Canal Diagnosed by Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
- Double Primary Cancer Patient with Sigmoid Colon Adenocarcinoma and Anal Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Rectal Mucosal Metastasis A case report