J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2008 Sep;15(3):190-193. 10.4184/jkss.2008.15.3.190.
Paraparesis due to Posterior Migration of Ruptured Disc in the Adjacent Segment after Spinal Fusion: Unusual Junctional Problem
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Guri, Korea. hyparkys@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Guri, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1747203
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2008.15.3.190
Abstract
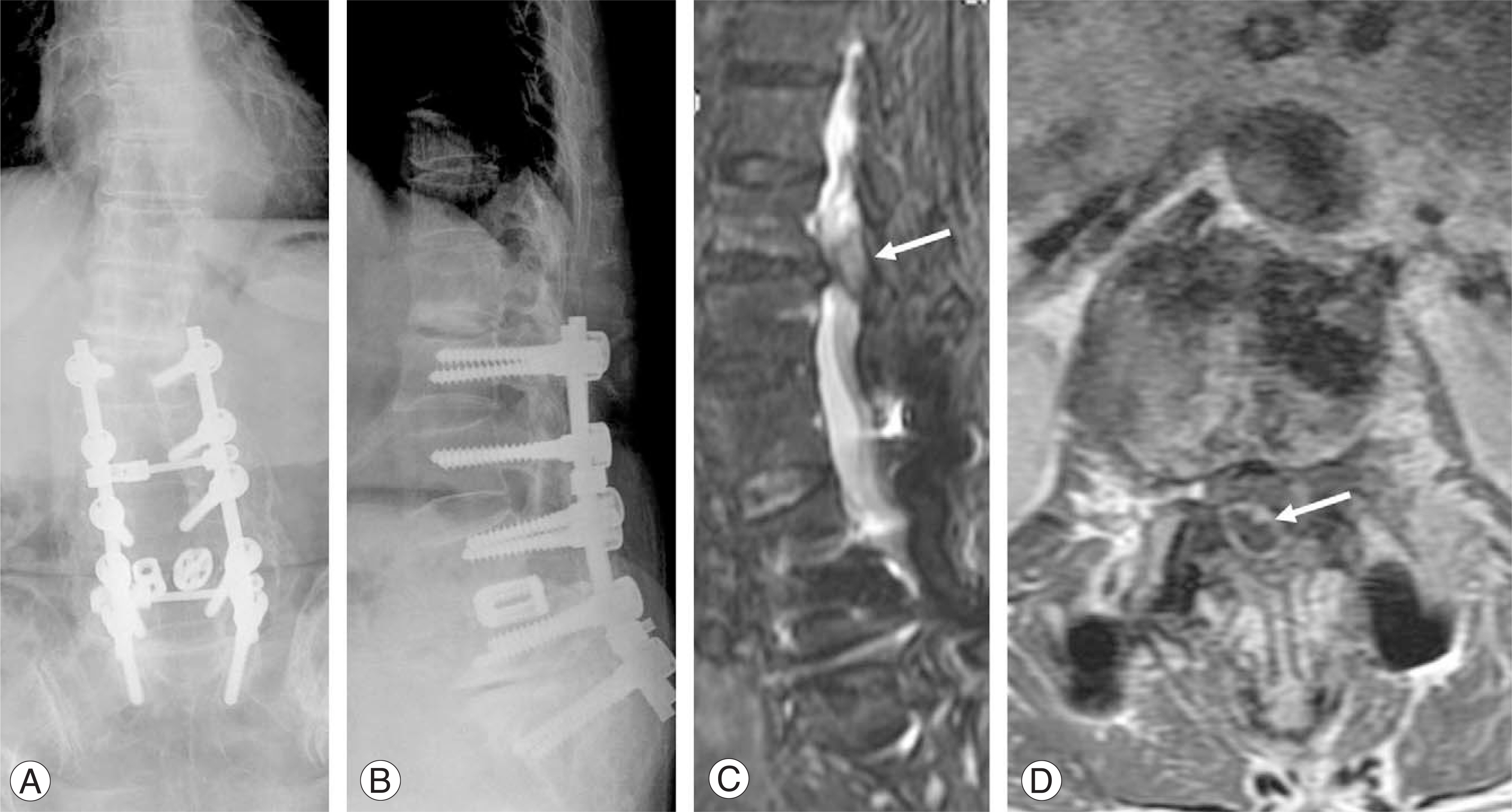
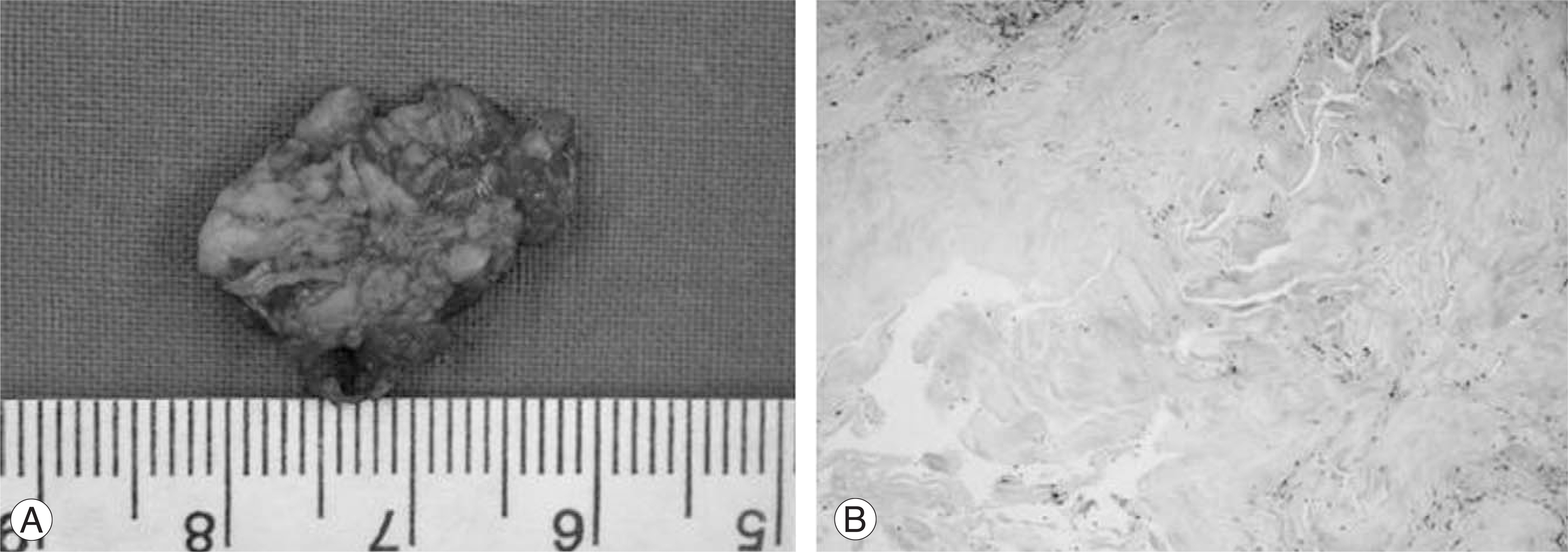
- Posterior epidural migration of sequestered lumbar disc fragments is an uncommon event. We present here an especially uncommon case involving a patient with paraparesis that was due to posterior migration of a ruptured disc in the adjacent segment after spinal fusion. The patient had a herniated lumbar disc in a diseased spinal junction with sequestered fragments that were located posterior to the thecal sac.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Bonaroti EA, Welch WC. Posterior epidural migration of an extruded lumbar disc fragment causing cauda equina syndrome. Clinical and magnetic resonance imaging evaluation. Spine. 1998; 23:378–381.2). Manabe S, Tateishi A. Epidural migration of extruded cervical disc and its surgical treatment. Spine. 1986; 11:873–878.
Article3). Giannini C, Scheithauer BW, Wenger DE, Unni KK. Pigmented villonodular synovitis of the spine: a clinical, radiological and morphological study of 12 cases. J Neurosurg. 1996; 84:592–597.
Article4). Baker JK, Hanson GW. Cyst of the ligamentum flavum. Spine. 1994; 19:1092–1094.
Article5). Masaryk TJ, Ross JS, Modic MT, Boumphrey F, Bohlman H, Wilber G. High-resolution MR imaging of sequestered lumbar intervertebral disks. Am I Roentgenol. 1988; 150:1155–1162.
Article6). Schellinger D, Manz HJ, Vidic B, et al. Disk fragment migration. Radiology. 1990; 175:831–836.
Article7). Lutz JD, Smith RR, Jones HM. CT myelography of a fragment of a lumbar disk sequestered posterior to the thecal sac. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1990; 11:610–611.8). Bonaldi VM, Duong H, Starr MR, Sarazin L, Richardson J. Tophaceous gout of the lumbar spine mimicking an epidural abscess: MR features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996; 17:1949–1952.9). Liu SS, Williams KD, Drayer BP, Spetzler RF, Sonntag VK. Synovial cysts of the lumbosacral spine: diagnosis by MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1989; 10:1239–1242.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Cervical Myelopathy Due to Ruptured Disc During Leisure Sports Activity in Adjacent Segment
- Surgical Treatment of Adjacent Segment Degeneration after Spinal Fusion in Degenerative Lumbar Disc Disease
- Acute Paraplegia Secondary to Thoracic Disc Herniation of the Adjacent Segment Following Thoracolumbar Fusion and Instrumentation
- Revision Surgery for Spinal Stenosis Developed at the Adjacent Segment after Lumbar Fusion
- A Comparison of Adjacent Segment Diseases Above One Versus Above Two Vertebral Segment after Spinal Fusion of the Degenerative Lumbar Disease