J Vet Sci.
2014 Mar;15(1):45-49. 10.4142/jvs.2014.15.1.45.
Training-induced changes in clotting parameters of athletic horses
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Science, University of Messina, Polo Universitario dell'Annunziata, 98168 Messina, Italy. giuseppe.piccione@unime.it
- KMID: 1737609
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2014.15.1.45
Abstract
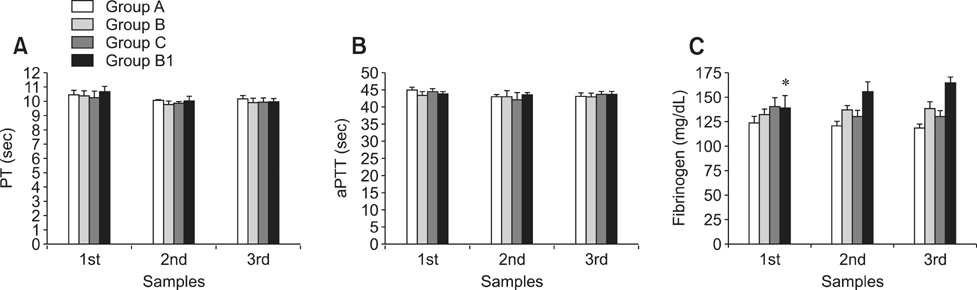
- The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of training on prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, and fibrinogen (Fb) concentrations in horses to assess potential adaptive response to training. Fifteen clinically healthy horses were enrolled in the present study and equally divided into three groups. Group A completed an intense training program, group B participated in a light training program, and group C included sedentary horses. After 5 weeks, group B was subjected to the same training program completed by group A and renamed group B1. Blood samples were collected by jugular venipuncture from each animal at rest and analyzed within 2 h after sampling. A two-way ANOVA for repeated measures showed a significant effect of training (p < 0.05) on Fb concentrations in group B1 alone during the first week after changing the training program. Our findings demonstrated that Fb is a parameter susceptible to training. Fb plasma levels increase with a more intense training program. However, Fb plasma levels decreased after the first week and returned to basel levels, suggesting that the horses had adapted to the new training program.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bayly WM, Meyers KM, Keck MT. Effects of furosemide on exercise-induced alterations in haemostatic in Thouroughbred horses exhibiting post exercise epistaxis. In : Bayly WM, Meyers KM, Keck MT, editors. Equine exercise physiology. Granta Editions. England: Cambridge;1983. p. 64–70.2. Bayly WM, Meyers KM, Keck MT, Huston LJ, Grant BD. Exercise-induced alterations in haemostatic in Thouroughbred horses. In : Snow DH, Persson SGB, Rose RJ, editors. Equine exercise physiology. Granta Editions. England: Cambridge;1983. p. 336–343.3. Casella S, Giannetto C, Fazio F, Giudice E, Piccione G. Assessment of prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, and fibrinogen concentration on equine plasma samples following different storage conditions. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2009; 21:674–678.
Article4. Domina F, Giudice E, Catarsini O. Behaviour of blood coagulation in athletic horses during progressive training. SIDI. 1998; 4:35–37.5. Fazio F, Assenza A, Tosto F, Casella S, Piccione G, Caola G. Modifications of some acute phase proteins and the white blood cell count in thoroughbreds during training. Vet Rec. 2010; 167:370–372.
Article6. Ferguson EW, Bernier LL, Banta GR, Yu-Yahiro J, Schoomaker EB. Effects of exercise and conditioning on clotting and fibrinolytic activity in men. J Appl Physiol. 1987; 62:1416–1421.
Article7. Hong S, Adler KA, Von Känel R, Nordberg J, Ziegler MG, Mills PJ. Prolonged platelet activation in individuals with elevated blood pressure in response to a moderate exercise challenge. Psychophysiology. 2009; 46:276–284.
Article8. Hurlen M, Seljeflot I, Arnesen H. Increased platelet aggregability during exercise in patients with previous myocardial infarction. Lack of inhibition by aspirin. Thromb Res. 2000; 99:487–494.
Article9. Li N, He S, Blombäck M, Hjemdahl P. Platelet activity, coagulation, and fibrinolysis during exercise in healthy males: effects of thrombin inhibition by argatroban and enoxaparin. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007; 27:407–413.
Article10. Marsh NA, Gaffney PJ. Some observation on the release of extrinsic and intrinsic plasminogen activators during exercise in man. Haemostasis. 1980; 9:238–247.
Article11. McKeever KH, Hinchcliff KW, Kociba GJ, Reed SM, Muir WW. Changes in coagulation and fibrinolysis in horses during exercise. Am J Vet Res. 1990; 51:1335–1339.12. Montgomery HE, Clarkson P, Nwose OM, Mikailidis DP, Jagroop IA, Dollery C, Moult J, Benhizia F, Deanfield J, Jubb M, World M, McEwan JR, Winder A, Humphries S. The acute rise in plasma fibrinogen concentration with exercise is influenced by the G-453-A polymorphism of the β-fibrinogen gene. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1996; 16:386–391.
Article13. Piccione G, Arcigli A, Costa A, Fazio F, Caola G. Changes in clotting times and fibrinogen concentrations in horses during a showjump. Slov Vet Res. 2004; 41:41–45.14. Piccione G, Fazio F, Giudice E, Grasso F, Caola G. Exercise-induced changes in the clotting times and fibrinolytic activity during official 1600 and 2000 meters trot races in standardbred horses. Acta Vet Brno. 2005; 74:509–514.
Article15. Prisco D, Francalanci I, Filippini M, Hagi MI. Physical exercise and hemostasis. Int J Clin Lab Res. 1994; 24:125–131.
Article16. Takizawa Y, Hobo S. Usefulness of plasma fibrinogen concentration measurement in diagnosis of respiratory disorders in Thoroughbred racehorses. J Equine Sci. 2006; 17:27–32.
Article17. Thrall MA, Baker DC, Lassen DE, Campbell TW, DeNicola D, Fettman MJ, Rebar A, Weiser G. Veterinary Hematology and Clinical Chemistry. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2004. p. 194–196.18. Van den Burg PJM, Hospers JEH, Mosterd WL, Bouma BN, Huisveld IA. Aging, physical conditioning and exerciseinduced changes in haemostatic factors and reaction products. J Appl Physiol. 2000; 88:1558–1564.
Article19. Wang JS. Exercise prescription and thrombogenesis. J Biomed Sci. 2006; 13:753–761.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasound and clinical findings in the metacarpophalangeal joint assessment of show jumping horses in training
- A novel biomarker of exercise-induced stress in horses
- Peripheral serotoninergic response to physical exercise in athletic horses
- Stress response as a contributing factor in horses with laminitis
- Rate of return to race after arthroscopic surgeries in Thoroughbred racehorses (2005~2010)