J Korean Med Sci.
2004 Oct;19(5):647-651. 10.3346/jkms.2004.19.5.647.
Intratumoral Injection of (188)Re labeled Cationic Polyethylenimine Conjugates: A Preliminary Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nuclear Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
- 2Wonkwang University Institute of Medical Science, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
- 4Department of Nuclear Medicine, Chonnam National University School of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 1733502
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2004.19.5.647
Abstract
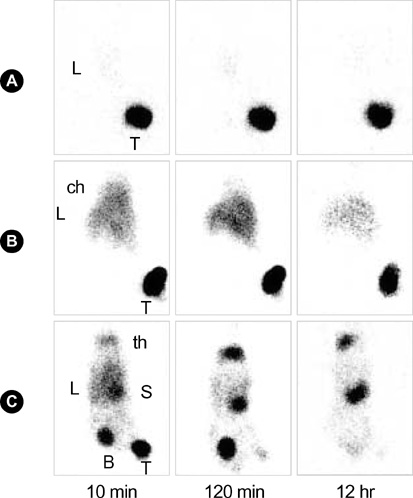
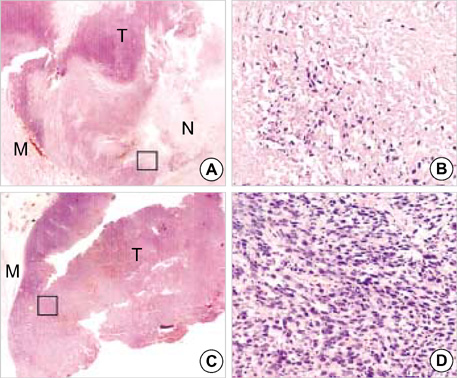
- (188)Re(Rhenium) is easily obtained from an in-house (188)W/(188)Re generator that is similar to the current (99)Mo/(99m)Tc generator, making it very convenient for clinical use. This characteristic makes this radionuclide a promising candidate as a therapeutic agent. Polyethylenimine (PEI) is a cationic polymer and has been used as a gene delivery vector. Positively charged materials interact with cellular blood components, vascular endothelium, and plasma proteins. In this study, the authors investigated whether intratumoral injection of (188)Re labeled transferrin (Tf)-PEI conjugates exert the effect of radionuclide therapy against the tumor cells. When the diameters of the Ramos lymphoma (human Burkitt's lymphoma) xenografted tumors reached approximately 1 cm, 3 kinds of (188)Re bound compounds (HYNIC-PEI-Tf, HYNIC-PEI, (188)Re perrhenate) were injected directly into the tumors. There were increases in the retention of (188)Re inside the tumor when PEI was incorporated with (188)Re compared to the use of free 188Re. The (188)Re HYNIC-Tf-PEI showed the most retention inside the tumor (retention rate=approximately 97%). H&E stain of isolated tumor tissues showed that (188)Re labeled HYNIC-PEI-Tf caused extensive tumor necrosis. These results support (188)Re HYNIC-PEI-Tf as being a useful radiopharmaceutical agent to treat tumors when delievered by intratumoral injection.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Knapp FF Jr, Beets AL, Guhlke S, Zamora PO, Bender H, Palmedo H, Biersack HJ. Availability of rhenium-188 from the alumina-based tungsten-188/rhenium-188 generator for preparation of rhenium-188-labeled radiopharmaceuticals for cancer treatment. Anticancer Res. 1997. 17:1783–1795.2. Hsieh BT, Hsieh JF, Tsai SC, Lin WY, Huang HT, Ting G, Wang SJ. Rhenium-188-Labeled DTPA: a new radiopharmaceutical for intravascular radiation therapy. Nucl Med Biol. 1999. 26:967–972.
Article3. Li S, Liu J, Zhang H, Tian M, Wang J, Zheng X. Rhenium-188 HEDP to treat painful bone metastases. Clin Nucl Med. 2001. 26:919–922.
Article4. Buchmann I, Bunjes D, Kotzerke J, Martin H, Glatting G, Seitz U, Rattat D, Buck A, Dohner H, Reske SN. Myeloablative radioimmunotherapy with Re-188-anti-CD66-antibody for conditioning of highrisk leukemia patients prior to stem cell transplantation: biodistribution, biokinetics and immediate toxicities. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2002. 17:151–163.
Article5. Boussif O, Lezoualc'h F, Zanta MA, Mergny MD, Scherman D, Demeneix B, Behr JP. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995. 92:7297–7301.
Article6. Kobayashi S, Hiroishi K, Tokunoh M, Saegusa T. Chelating properties of linear and branched poly (ethylenimines). Macromolecules. 1987. 20:1496–1500.7. Rivas BL, Geckeler KE. Synthesis and metal complexation of poly (ethylenimine) and derivatives. Adv Polym Sci. 1992. 102:173–183.8. Zanta MA, Boussif O, Adib A, Behr JP. In vitro gene delivery to hepatocytes with galactosylated polyethylenimine. Bioconjug Chem. 1997. 8:839–844.9. Sagara K, Kim SW. A new synthesis of galactose-poly (ethylene glycol)-polyethylenimine for gene delivery to hepatocytes. J Control Release. 2002. 79:271–281.10. Kunath K, von Harpe A, Fischer D, Kissel T. Galactose-PEI-DNA complex for targeted gene delivery: degree of substitution affects complex size and transfection efficiency. J Control Release. 2003. 88:159–172.11. Ogris M, Steinlein P, Carotta S, Brunner S, Wagner E. DNA/polyethylenimine transfection particles: influence of ligands, polymer size, and PEGylation on internalization and gene expression. AAPS PharmSci. 2001. 3:E21.
Article12. Hildebrandt IJ, Iyer M, Wagner E, Gambhir SS. Optical imaging of transferrin targeted PEI/DNA complexes in living subjects. Gene Ther. 2003. 10:758–764.
Article13. Ogris M, Wagner E. Tumor-targeted gene transfer with DNA polyplexes. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 2002. 27:85–95.14. Qian ZM, Li H, Sun H, Ho K. Targeted drug delivery via the transferrin receptor-mediated endocytosis pathway. Pharmacol Rev. 2002. 54:561–587.
Article15. Xu L, Pirollo KF, Chang EH. Transferrin-liposome-mediated p53 sensitization of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck to radiation in vitro. Hum Gene Ther. 1997. 8:467–475.
Article16. Kircheis R, Kichler A, Wallner G, Kursa M, Ogris M, Felzmann T, Buchberger M, Wagner E. Coupling of cell-binding ligands to polyethylenimine for targeted gene delivery. Gene Ther. 1997. 4:409–418.
Article17. Stabin MG. MIRDOSE: personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med. 1996. 37:538–546.18. Ogris M, Brunner S, Schuller S, Kircheis R, Wagner E. PEGylated DNA/transferrin-PEI complexes: reduced interaction with blood components, extended circulation in blood and potential for systemic gene delivery. Gene Ther. 1999. 6:595–605.
Article19. Oupicky D, Konak C, Dash PR, Seymour LW, Ulbrich K. Effect of albumin and polyanion on the structure of DNA complexes with polycation containing hydrophilic nonionic block. Bioconjug Chem. 1999. 10:764–772.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- In Vitro Properties and Biodistribution of Tc-99m and Re-188 Labeled Monoclonal Antibody CEA79.4
- Labeling and Biodistribution of Re-188-DTPA ( Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid )
- Biodistribution and Hepatic Metabolism of Galactosylated 111In-Antibody-Chelator Conjugates: Comparison with 111In-Antibody-Chelator Conjugates
- Dosimetry and MIRD for Re-188 Liquid Balloons
- Chondrosarcoma with Intratumoral Hemorrhage: Case Report