J Korean Med Sci.
2004 Apr;19(2):177-185. 10.3346/jkms.2004.19.2.177.
Periodic Explosive Expansion of Human Retroelements Associated with the Evolution of the Hominoid Primate
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. rhyumung@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1733474
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2004.19.2.177
Abstract
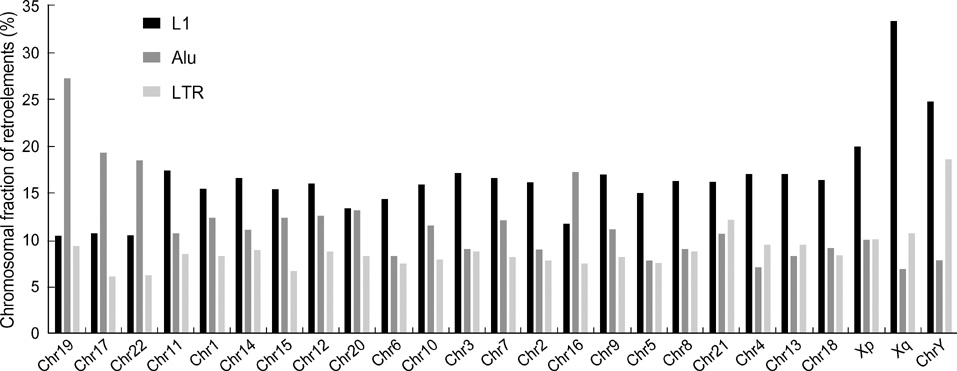
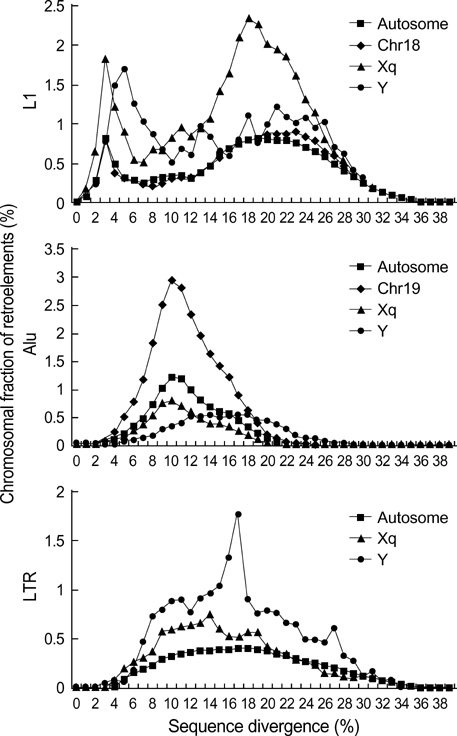
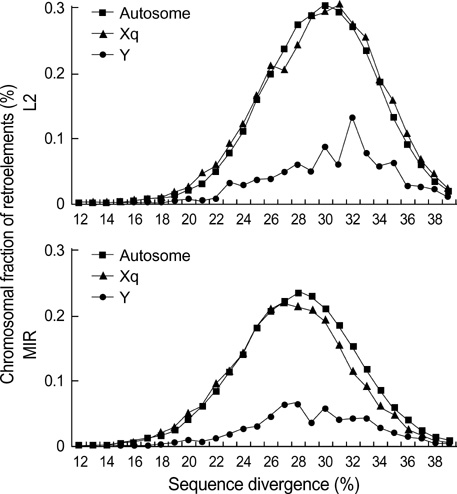
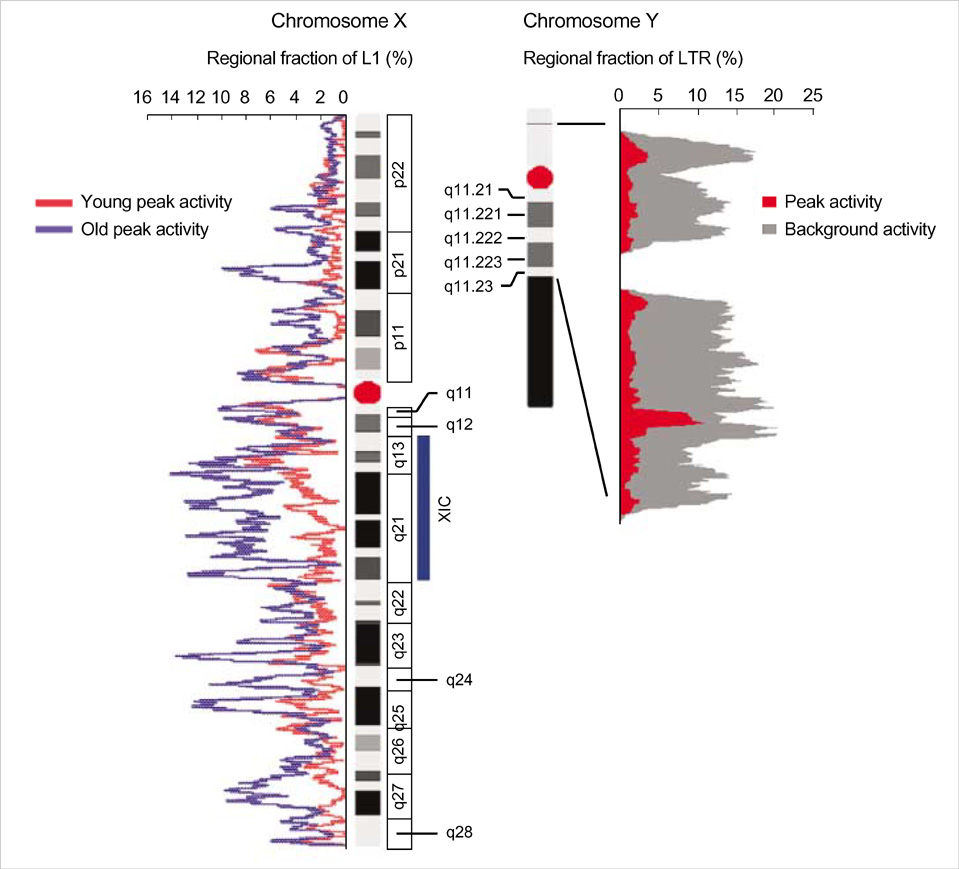
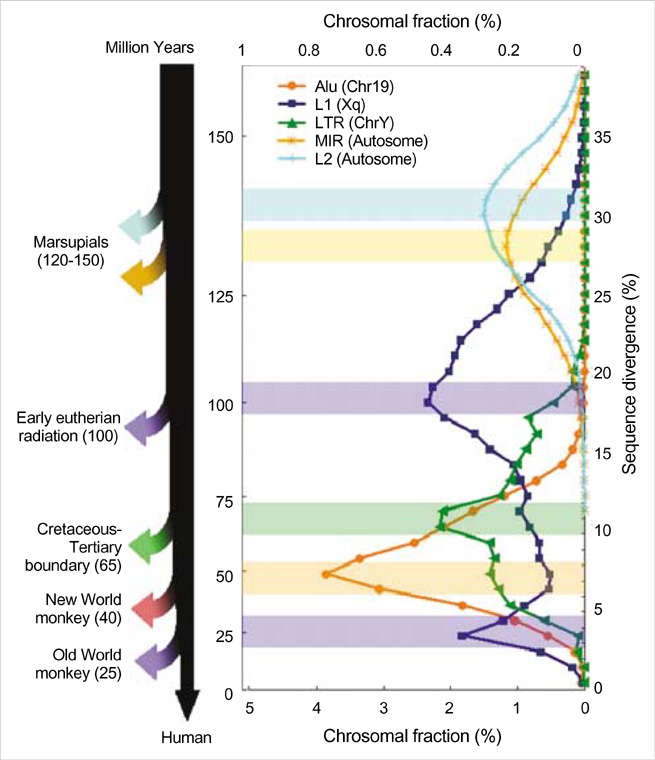
- Five retroelement families, L1 and L2 (long interspersed nuclear element, LINE), Alu and MIR (short interspersed nuclear element, SINE), and LTR (long terminal repeat), comprise almost half of the human genome. This genome-wide analysis on the time-scaled expansion of retroelements sheds light on the chronologically synchronous amplification peaks of each retroelement family in variable heights across human chromosomes. Especially, L1s and LTRs in the highest density on sex chromosomes Xq and Y, respectively, disclose peak activities that are obscured in autosomes. The periods of young L1, Alu, LTR, and old L1 peak activities calibrated based on sequence divergence coincide with the divergence of the three major hominoid divergence as well as early eutherian radiation while the amplification peaks of old MIR and L2 account for the marsupial-placental split. Overall, the peaks of autonomous LINE (young and old L1s and L2s) peaks and non-autonomous SINE (Alus and MIRs) have alternated repeatedly for 150 million years. In addition, a single burst of LTR parallels the Cretaceous-Tertiary (K-T) boundary, an exceptional global event. These findings suggest that the periodic explosive expansions of LINEs and SINEs and an exceptional burst of LTR comprise the genome dynamics underlying the macroevolution of the hominoid primate lineage.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Smit AF. The origin of interspersed repeats in the human genome. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996. 6:743–748.
Article2. International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001. 409:860–921.3. Deininger PL, Batzer MA. Mammalian retroelements. Genome Res. 2002. 12:1455–1465.
Article4. Brookfield JF. Selection on Alu sequences? Curr Biol. 2001. 11:R900–R901.
Article5. Mighell AJ, Markham AF, Robinson PA. Alu sequences. FEBS Lett. 1997. 417:1–5.6. Brosius J. Genomes were forged by massive bombardments with retroelements and retrosequences. Genetica. 1999. 107:209–238.
Article7. Hamdi HK, Nishio H, Tavis J, Zielinski R, Dugaiczyk A. Alu-mediated phylogenetic novelties in gene regulation and development. J Mol Biol. 2000. 299:931–939.8. Sverdlov ED. Retroviruses and primate evolution. Bioessays. 2000. 22:161–171.
Article9. Ostertag EM, Kazazian HH Jr. Biology of mammalian L1 retrotransposons. Annu Rev Genet. 2001. 35:501–538.
Article10. Gu Z, Wang H, Nekrutenko A, Li WH. Densities, length proportions, and other distributional features of repetitive sequences in the human genome estimated from 430 megabases of genomic sequence. Gene. 2000. 259:81–88.
Article11. Jurka J, Kapitonov VV. Sectorial mutagenesis by transposable elements. Genetica. 1999. 107:239–248.
Article12. Chu WM, Ballard R, Carpick BW, Williams BR, Schmid CW. Potential Alu function: regulation of the activity of double-stranded RNA-activated kinase PKR. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. 18:58–68.
Article13. Erlandsson R, Wilson JF, Paabo S. Sex chromosomal transposable element accumulation and male-driven substitutional evolution in humans. Mol Biol Evol. 2000. 17:804–812.
Article14. Boissinot S, Entezam A, Furano AV. Selection against deleterious LINE-1-containing loci in the human lineage. Mol Biol Evol. 2001. 18:926–935.
Article15. Bailey JA, Carrel L, Chakravarti A, Eichler EE. Molecular evidence for a relationship between LINE-1 elements and X chromosome inactivation: the Lyon repeat hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000. 97:6634–6639.
Article16. Jurka J. Repeats in genomic DNA: mining and meaning. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998. 8:333–337.
Article17. Pavlicek A, Jabbari K, Paces J, Paces V, Hejnar JV, Bernardi G. Similar integration but different stability of Alus and LINEs in the human genome. Gene. 2001. 276:39–45.
Article18. Ovchinnikov I, Troxel AB, Swergold GD. Genomic characterization of recent human LINE-1 insertions: evidence supporting random insertion. Genome Res. 2001. 11:2050–2058.
Article19. Shukolyukov A, Lugmair GW. Isotopic evidence for the Cretaceous-Tertiary impactor and its type. Science. 1998. 282:927–929.
Article20. Jurka J. Repbase update: a database and an electronic journal of repetitive elements. Trends Genet. 2000. 16:418–420.
Article21. Smith TF, Waterman MS. Identification of common molecular subsequences. J Mol Biol. 1981. 147:195–197.
Article22. Graves JA. The origin and function of the mammalian Y chromosome and Y-borne genes--an evolving understanding. Bioessays. 1995. 17:311–320.23. Kapitonov V, Jurka J. The age of Alu subfamilies. J Mol Evol. 1996. 42:59–65.
Article24. Kjellman C, Sjogren HO, Widegren B. The Y chromosome: a graveyard for endogenous retroviruses. Gene. 1995. 161:163–170.
Article25. Rastan S. Non-random X-chromosome inactivation in mouse X-autosome translocation embryos--location of the inactivation centre. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1983. 78:1–22.
Article26. Hope RM, Cooper S, Wainwright B. Graves JA, Hope RM, Cooper DW, editors. Globin macromolecular sequences in marsupials and monotremes. Mammals from Pouches and Eggs: Genetics, Breeding and Evolution of Marsupials and Monotremes. 1990. Melbourne: CSIRO;147–172.
Article27. Springer MS, Murphy WJ, Eizirik E, O'Brien SJ. Placental mammal diversification and the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003. 100:1056–1061.
Article28. Kumar S, Hedges SB. A molecular timescale for vertebrate evolution. Nature. 1998. 392:917–920.
Article29. Smit AF. Interspersed repeats and other momentos of transposable elements in mammalian genomes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1999. 9:657–663.30. Hartl DL, Clark AG. Principles of population genetics. 1989. 2nd ed.31. Ohshima K, Hamada M, Terai Y, Okada N. The 3' ends of tRNA-derived short interspersed repetitive elements are derived from the 3' ends of long interspersed repetitive elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. 16:3756–3764.
Article32. Feng Q, Moran JV, Kazazian HH Jr, Boeke JD. Human L1 retrotransposon encodes a conserved endonuclease required for retrotransposition. Cell. 1996. 87:905–916.
Article33. Makalowski W. Genomic scrap yard: how genomes utilize all that junk. Gene. 2000. 259:61–67.
Article34. Jabbari K, Bernardi G. CpG doublets, CpG islands and Alu repeats in long human DNA sequences from different isochore families. Gene. 1998. 224:123–127.
Article35. Charlesworth B. The evolution of chromosomal sex determination and dosage compensation. Curr Biol. 1996. 6:149–162.
Article36. Bachtrog D, Charlesworth B. Reduced adaptation of a non-recombining neo-Y chromosome. Nature. 2002. 416:323–326.
Article37. Graves JA. The rise and fall of SRY. Trends Genet. 2002. 18:259–264.
Article38. Lyon MF. X-chromosome inactivation: a repeat hypothesis. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1998. 80:133–137.
Article39. Hsu SJ, Erickson RP, Zhang J, Garver WS, Heidenreich RA. Fine linkage and physical mapping suggests cross-over suppression with a retroposon insertion at the npc1 mutation. Mamm Genome. 2000. 11:774–778.
Article40. Lahn BT, Page DC. Four evolutionary strata on the human X chromosome. Science. 1999. 286:964–967.
Article41. Walsh CP, Chaillet JR, Bestor TH. Transcription of IAP endogenous retroviruses is constrained by cytosine methylation. Nat Genet. 1998. 20:116–117.
Article42. Alvareaz L, Alvarez W, Asaro F, Michel H. Extraterrestrial Cause for the Cretaceous-Tertiary Extinction. Science. 1980. 208:1095–1180.
Article43. Kerr R. Testing an Ancient Impact's Punch. Science. 1994. 263:1371–1372.
Article44. Easteal S. Molecular evidence for the early divergence of placental mammals. Bioessays. 1999. 21:1052–1058.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- PrimateDB: Development of Primate Genome DB and Web Service
- Genomic Features of Retroelements and Implications for Human Disease
- Study of Modern Human Evolution via Comparative Analysis with the Neanderthal Genome
- Structural Variation of Alu Element and Human Disease
- Non-Synteny Regions in the Human Genome