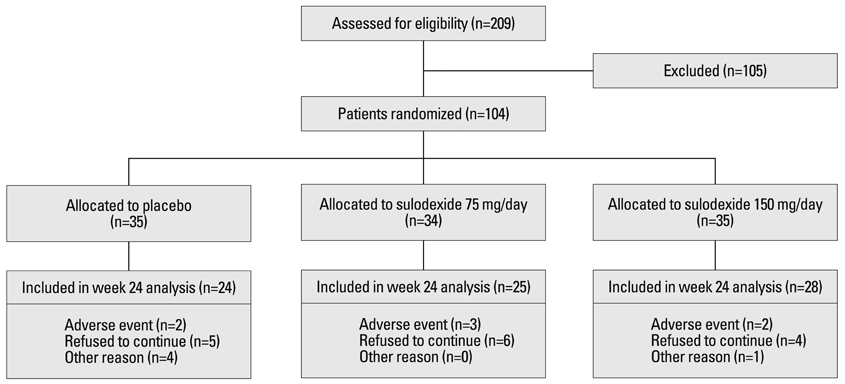
Yonsei Med J.
2011 Jul;52(4):588-594. 10.3349/ymj.2011.52.4.588.
Anti-Proteinuric Effect of Sulodexide in Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji University of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Clinical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Transplantation Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Transplantation Research Institute, Seoul, Korea. khoh@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1727990
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2011.52.4.588
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We conducted a multi-center randomized double-blind study to determine the effects of 6-month therapy with sulodexide on urinary protein excretion in patients with idiopathic Immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of seventy-seven patients participated in the study. They were randomly allocated to one of three groups: sulodexide 75 mg or 150 mg daily or the placebo for 6 months. The primary end point was the achievement, at 6 months, of at least 50% reduction in urine protein/creatinine ratio (UPCR) from the baseline value.
RESULTS
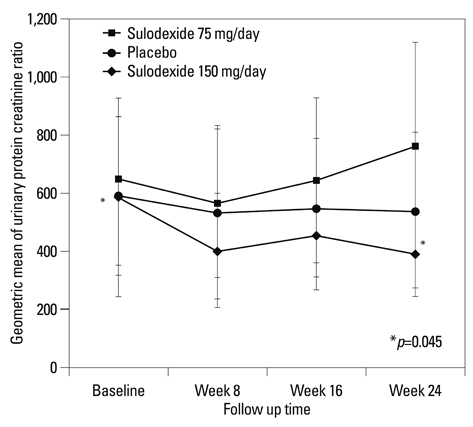
At 6 months, the primary end point was achieved by 12.5% of the patients assigned to the placebo, 4.0% of the patients assigned to sulodexide 75 mg daily and 21.4% of those assigned to 150 mg (p=0.308). Treatment with sulodexide 150 mg daily for 6 months significantly reduced log UPCR from 6.38+/-0.77 at baseline to 5.98+/-0.94 at 6 months (p=0.045), while treatment with sulodexide 75 mg daily and placebo did not.
CONCLUSION
A 6-month treatment with sulodexide did not achieve 50% reduction of urinary protein excretion in IgA nephropathy patients, but showed a tendency to increase the time-dependent anti-proteinuric effect. Therefore, long-term clinical trials on a larger scale are warranted to elucidate the hypothesis that sulodexide affords renal protection in IgA nephropathy patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. D'Amico G. The commonest glomerulonephritis in the world: IgA nephropathy. Q J Med. 1987. 64:709–727.2. Julian BA, Waldo FB, Rifai A, Mestecky J. IgA nephropathy, the most common glomerulonephritis worldwide. A neglected disease in the United States? Am J Med. 1988. 84:129–132.3. Varis J, Rantala I, Pasternack A, Oksa H, Jantti M, Paunu ES, et al. Immunoglobulin and complement deposition in glomeruli of 756 subjects who had committed suicide or met with a violent death. J Clin Pathol. 1993. 46:607–610.
Article4. Schena FP. A retrospective analysis of the natural history of primary IgA nephropathy worldwide. Am J Med. 1990. 89:209–215.
Article5. Velo M, Lozano L, Egido J, Gutierrez-Millet V, Hernando L. Natural history of IgA nephropathy in patients followed-up for more than ten years in Spain. Semin Nephrol. 1987. 7:346–350.6. Droz D. Natural history of primary glomerulonephritis with mesangial deposits of IgA. Contrib Nephrol. 1976. 2:150–157.
Article7. Radford MG Jr, Donadio JV Jr, Bergstralh EJ, Grande JP. Predicting renal outcome in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997. 8:199–207.
Article8. Velussi M, Cernigoi AM, Dapas F, De Monte A. Glycosaminoglycans oral therapy reduces microalbuminuria, blood fibrinogen levels and limb arteriopathy clinical signs in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Diab Nutr Metab. 1996. 9:53–58.9. Gambaro G, Venturini AP, Noonan DM, Fries W, Re G, Garbisa S, et al. Treatment with a glycosaminoglycan formulation ameliorates experimental diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1994. 46:797–806.
Article10. Ceol M, Nerlich A, Baggio B, Anglani F, Sauer U, Schleicher E, et al. Increased glomerular alpha 1 (IV) collagen expression and deposition in long-term diabetic rats is prevented by chronic glycosaminoglycan treatment. Lab Invest. 1996. 74:484–495.11. Ceol M, Gambaro G, Sauer U, Baggio B, Anglani F, Forino M, et al. Glycosaminoglycan therapy prevents TGF-beta1 overexpression and pathologic changes in renal tissue of long-term diabetic rats. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2000. 11:2324–2336.
Article12. Skrha J, Perusicova J, Pont'uch P, Oksa A. Glycosaminoglycan sulodexide decreases albuminuria in diabetic patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1997. 38:25–31.
Article13. Sorrenti G, Grimaldi M, Canova N, Palazzini E, Melchionda N. Glycosaminoglycans as a possible tool for micro- and macroalbuminuria in diabetic patients. A pilot study. J Int Med Res. 1997. 25:81–86.
Article14. Solini A, Vergnani L, Ricci F, Crepaldi G. Glycosaminoglycans delay the progression of nephropathy in NIDDM. Diabetes Care. 1997. 20:819–823.
Article15. Gambaro G, Kinalska I, Oksa A, Pont'uch P, Hertlova M, Olsovsky J, et al. Oral sulodexide reduces albuminuria in microalbuminuric and macroalbuminuric type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients: the DiNAS randomized trial. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002. 13:1615–1625.
Article16. Szelachowska M, Poplawska A, Topolska J, Kinalska I, Grimaldi M. A pilot study of the effect of the glycosaminoglycan sulodexide on microalbuminuria in type I diabetic patients. Curr Med Res Opin. 1997. 13:539–545.
Article17. Velussi M. CADFdMA. A randomized, controlled study of sulodexide therapy for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Nutr Metab. 1996. 9:53–58.18. Oksa A, Pontuch P, Kratochvilova H. [The effect of glycosaminoglycan sulodexide on albuminuria in patients with diabetes mellitus]. Bratisl Lek Listy. 1999. 100:486–489.19. Dedov I, Shestakova M, Vorontzov A, Palazzini E. A randomized, controlled study of sulodexide therapy for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1997. 12:2295–2300.
Article20. Poplawska A, Szelachowska M, Topolska J, Wysocka-Solowie B, Kinalska I. Effect of glycosaminoglycans on urinary albumin excretion in insulin-dependent diabetic patients with micro- or macroalbuminuria. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1997. 38:109–114.
Article21. Achour A, Kacem M, Dibej K, Skhiri H, Bouraoui S, El May M. One year course of oral sulodexide in the management of diabetic nephropathy. J Nephrol. 2005. 18:568–574.22. Gambaro G, Venturini AP, Noonan DM, Fries W, Re G, Garbisa S, et al. Treatment with a glycosaminoglycan formulation ameliorates experimental diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1994. 46:797–806.
Article23. Gambaro G, Cavazzana AO, Luzi P, Piccoli A, Borsatti A, Crepaldi G, et al. Glycosaminoglycans prevent morphological renal alterations and albuminuria in diabetic rats. Kidney Int. 1992. 42:285–291.
Article24. Ofosu FA. Pharmacological actions of sulodexide. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1998. 24:127–138.
Article25. Nader HB, Buonassisi V, Colburn P, Dietrich CP. Heparin stimulates the synthesis and modifies the sulfation pattern of heparan sulfate proteoglycan from endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1989. 140:305–310.
Article26. Caenazzo C, Garbisa S, Ceol M, Baggio B, Borsatti A, Marchi E, et al. Heparin modulates proliferation and proteoglycan biosynthesis in murine mesangial cells: molecular clues for its activity in nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1995. 10:175–184.27. Lewis EJ, Xu X. Abnormal glomerular permeability characteristics in diabetic nephropathy: implications for the therapeutic use of low-molecular weight heparin. Diabetes Care. 2008. 31:Suppl 2. S202–S207.28. Goldshmidt O, Zcharia E, Cohen M, Aingorn H, Cohen I, Nadav L, et al. Heparanase mediates cell adhesion independent of its enzymatic activity. FASEB J. 2003. 17:1015–1025.
Article29. Gambaro G, Kong NC. Glycosaminoglycan treatment in glomerulonephritis? An interesting option to investigate. J Nephrol. 2010. 23:244–252.30. Donadio JV Jr, Grande JP. Immunoglobulin A nephropathy: a clinical perspective. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997. 8:1324–1332.
Article31. Callas DD, Hoppensteadt DA, Jeske W, Iqbal O, Bacher P, Ahsan A, et al. Comparative pharmacologic profile of a glycosaminoglycan mixture, Sulodexide, and a chemically modified heparin derivative, Suleparoide. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1993. 19:Suppl 1. 49–57.32. Andriuoli G, Mastacchi R, Barbanti M. Antithrombotic activity of a glycosaminoglycan (sulodexide) in rats. Thromb Res. 1984. 34:81–86.
Article33. Calabro A, Rossi A, Baiocchi MR, Coscetti G, Fellin R, Crepaldi G. [Effect of sulodexide on hemorheological parameters in a group of patients with peripheral arteriosclerotic vascular disease]. Ric Clin Lab. 1985. 15:Suppl 1. 455–463.34. Crepaldi G, Rossi A, Coscetti G, Abbruzzese E, Calveri U, Calabro A. Sulodexide oral administration influences blood viscosity and fibrinolysis. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1992. 18:189–195.35. Coccheri S, Scondotto G, Agnelli G, Palazzini E, Zamboni V. Arterial Arm of the Suavis (Sulodexide Arterial Venous Italian Study) group. Sulodexide in the treatment of intermittent claudication. Results of a randomized, double-blind, multicentre, placebo-controlled study. Eur Heart J. 2002. 23:1057–1065.
Article36. Condorelli M, Chiariello M, Dagianti A, Penco M, Dalla Volta S, Pengo V, et al. IPO-V2: a prospective, multicenter, randomized, comparative clinical investigation of the effects of sulodexide in preventing cardiovascular accidents in the first year after acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994. 23:27–34.
Article37. Koblik T, Sieradzki J, Sendur R, Biernat J, Czarnobilski K, Gryz E, et al. The effect of insulin and sulodexide (Vessel Due F) on diabetic foot syndrome: pilot study in elderly patients. J Diabetes Complications. 2001. 15:69–74.
Article38. Kanwar YS, Farquhar MG. Presence of heparan sulfate in the glomerular basement membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979. 76:1303–1307.
Article39. Kanwar YS, Rosenzweig LJ, Jakubowski ML. Distribution of de novo synthesized sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the glomerular basement membrane and mesangial matrix. Lab Invest. 1983. 49:216–225.40. Taniguchi Y, Yorioka N, Masaki T, Asakimori Y, Yamashita K, Yamakido M. Localization of transforming growth factors beta1 and beta2 and epidermal growth factor in IgA nephropathy. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1999. 33:243–247.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Use of low-dose sulodexide in IgA nephropathy patients on renin-angiotensin system blockades
- Sulodexide-induced Hyperkalemia: A Case Report
- Sulodexide in IgA nephropathy
- Effect of Combined Treatment of Steroid and Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker (ARB) in Proteinuric IgA Nephropathy
- Concurrent Anti-glomerular Basement Membrane Nephritis and IgA Nephropathy