Yonsei Med J.
2013 May;54(3):788-790. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.3.788.
Cardiac Tamponade Complicated by Acupuncture: Hemopericardium due to Shredded Coronary Artery Injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea. yhkim02@kangwon.ac.kr
- 2Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, School of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Emergency Medicine, School of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1727899
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.3.788
Abstract
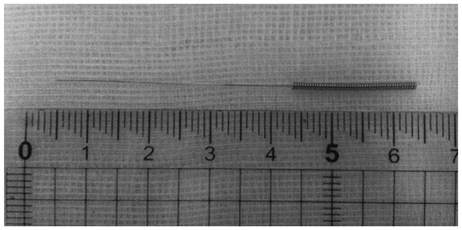
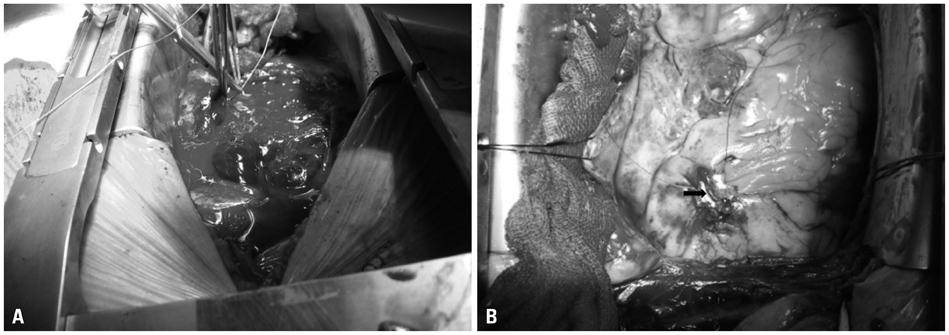
- We report a case of 62-year-old man with cardiac tamponade due to coronary artery injury after acupuncture into the substernum. After resuscitation of cardiac arrest, we performed emergent pericardiocentesis. Nevertheless, the cardiac arrest recurred, and the emergent operation on cardiopulmonary bypass was performed. We identified hemopericardium due to shredded acute marginal branch of right coronary artery, and it was ligated leading to termination of bleeding. The patient was discharged without any other complications.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. WHO. WHO traditional medicine strategy 2002-2005. 2002. Geneva: World Health Organisation;74.2. White A. A cumulative review of the range and incidence of significant adverse events associated with acupuncture. Acupunct Med. 2004. 22:122–133.3. Yamashita H, Tsukayama H, White AR, Tanno Y, Sugishita C, Ernst E. Systematic review of adverse events following acupuncture: the Japanese literature. Complement Ther Med. 2001. 9:98–104.4. Ernst E, Pittler MH, Wider B, Boddy K. The desktop guide to complementary and alternative medicine. 2006. 2nd ed. Edinburgh: Elsevier Mosby.5. Hunt KJ, Coelho HF, Wider B, Perry R, Hung SK, Terry R, et al. Complementary and alternative medicine use in England: results from a national survey. Int J Clin Pract. 2010. 64:1496–1502.
Article6. Ernst E, Zhang J. Cardiac tamponade caused by acupuncture: a review of the literature. Int J Cardiol. 2011. 149:287–289.
Article7. LeWinter MM, Tischler MD. Braunwald E, editor. Pericardial disease. Heart disease: a textbook of cardiovascular medicine. 2012. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders;1651–1661.8. Leung PC, Zhang L, Cheng KF. Acupuncture: complications are preventable not adverse events. Chin J Integr Med. 2009. 15:229–232.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cardiac Tamponade Associated with Acupuncture
- A Case of Cardiac Tamponade due to Penetration of the Right Ventricule by an Acupunture Needle
- Cardiac Tamponade Caused by Epigastric Acupuncture: A Case Report
- A Case of Right Atrial Sarcoma Complicated with Hemopericardium and Cardiac Tamponade
- Guidewire-Induced Perforation of Distal Circumflex Artery Treated with Transcatheter Embolization of Polyvinyl Alcohol Form