Yonsei Med J.
2013 May;54(3):726-731. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.3.726.
Loss of Lordosis and Clinical Outcomes after Anterior Cervical Fusion with Dynamic Rotational Plates
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Medical College of Hallym University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Medical College of Hallym University, Anyang, Korea. amhangpark@gmail.com
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Medical College of Hallym University, Hwaseong, Korea.
- KMID: 1727890
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.3.726
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The cervical dynamic rotational plating system may induce bone graft subsidence, so it may cause loss of cervical lordosis. However there were few studies for alignments of cervical spines influencing the clinical results after using dynamic rotational plates. The purpose is to evaluate the effect of graft subsidence on cervical alignments due to the dynamic rotational cervical plates and correlating it with the clinical outcomes of patients undergoing anterior cervical fusion.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty-three patients with disease or fracture underwent anterior cervical decompression and fusion using a dynamic rotational plate. The presence and extent of implant complications, graft subsidence, loss of lordosis were identified and Visual Analog Scale score (VAS score), Japanese Orthopaedic Association score (JOA score), clinical outcomes based on Odom's criteria were recorded.
RESULTS
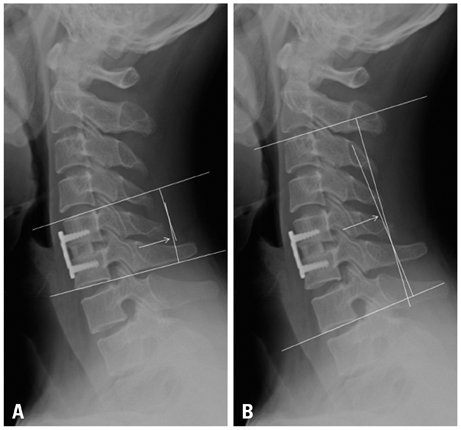
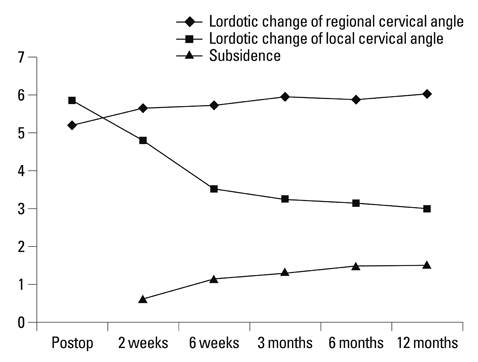
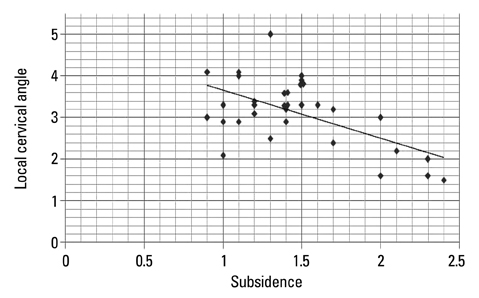
Fusion was achieved without implant complications in all cases. The mean graft subsidence at 6 months after the surgery was 1.46 mm. The lordotic changes in local cervical angles were 5.85degrees which was obtained postoperatively. VAS score for radicular pain was improved by 5.19 and the JOA score was improved by 3. Clinical outcomes based on Odom's criteria showed sixteen excellent, ten good and two satisfactory results. There was no significant relationship between clinical outcomes and changes in the cervical angles.
CONCLUSION
Dynamic rotational anterior cervical plating provides comparable clinical outcomes to that of the reports of former static cervical platings. The loss of lordosis is related to the amount of graft settling but it is not related to the clinical outcomes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Alters Whole-Spine Sagittal Alignment
Jang Hoon Kim, Jeong Yoon Park, Seong Yi, Kyung Hyun Kim, Sung Uk Kuh, Dong Kyu Chin, Keun Su Kim, Yong Eun Cho
Yonsei Med J. 2015;56(4):1060-1070. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.4.1060.
Reference
-
1. Böhler J, Gaudernak T. Anterior plate stabilization for fracture-dislocations of the lower cervical spine. J Trauma. 1980. 20:203–205.
Article2. Brodke DS, Gollogly S, Alexander Mohr R, Nguyen BK, Dailey AT, Bachus AK. Dynamic cervical plates: biomechanical evaluation of load sharing and stiffness. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001. 26:1324–1329.3. Brodke DS, Klimo P Jr, Bachus KN, Braun JT, Dailey AT. Anterior cervical fixation: analysis of load-sharing and stability with use of static and dynamic plates. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. 88:1566–1573.4. Fogel GR, Li Z, Liu W, Liao Z, Wu J, Zhou W. In vitro evaluation of stiffness and load sharing in a two-level corpectomy: comparison of static and dynamic cervical plates. Spine J. 2010. 10:417–421.
Article5. Ferch RD, Shad A, Cadoux-Hudson TA, Teddy PJ. Anterior correction of cervical kyphotic deformity: effects on myelopathy, neck pain, and sagittal alignment. J Neurosurg. 2004. 100:1 Suppl Spine. 13–19.
Article6. Katsuura A, Hukuda S, Saruhashi Y, Mori K. Kyphotic malalignment after anterior cervical fusion is one of the factors promoting the degenerative process in adjacent intervertebral levels. Eur Spine J. 2001. 10:320–324.
Article7. Matsunaga S, Onishi T, Sakou T. Significance of occipitoaxial angle in subaxial lesion after occipitocervical fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001. 26:161–165.
Article8. Barsa P, Suchomel P. Factors affecting sagittal malalignment due to cage subsidence in standalone cage assisted anterior cervical fusion. Eur Spine J. 2007. 16:1395–1400.
Article9. DuBois CM, Bolt PM, Todd AG, Gupta P, Wetzel FT, Phillips FM. Static versus dynamic plating for multilevel anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. Spine J. 2007. 7:188–193.
Article10. Okawa A, Sakai K, Hirai T, Kato T, Tomizawa S, Enomoto M, et al. Risk factors for early reconstruction failure of multilevel cervical corpectomy with dynamic plate fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011. 36:E582–E587.
Article11. Smith GW, Robinson RA. The treatment of certain cervical-spine disorders by anterior removal of the intervertebral disc and interbody fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1958. 40-A:607–624.
Article12. Bose B. Anterior cervical arthrodesis using DOC dynamic stabilization implant for improvement in sagittal angulation and controlled settling. J Neurosurg. 2003. 98:1 Suppl. 8–13.
Article13. Ghahreman A, Rao PJ, Ferch RD. Dynamic plates in anterior cervical fusion surgery: graft settling and cervical alignment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009. 34:1567–1571.14. Pitzen TR, Chrobok J, Stulik J, Ruffing S, Drumm J, Sova L, et al. Implant complications, fusion, loss of lordosis, and outcome after anterior cervical plating with dynamic or rigid plates: two-year results of a multi-centric, randomized, controlled study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009. 34:641–646.15. Goldberg G, Albert TJ, Vaccaro AR, Hilibrand AS, Anderson DG, Wharton N. Short-term comparison of cervical fusion with static and dynamic plating using computerized motion analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007. 32:E371–E375.
Article16. Nunley PD, Jawahar A, Kerr EJ 3rd, Cavanaugh DA, Howard C, Brandao SM. Choice of plate may affect outcomes for single versus multilevel ACDF: results of a prospective randomized single-blind trial. Spine J. 2009. 9:121–127.
Article17. Stulik J, Pitzen TR, Chrobok J, Ruffing S, Drumm J, Sova L, et al. Fusion and failure following anterior cervical plating with dynamic or rigid plates: 6-months results of a multi-centric, prospective, randomized, controlled study. Eur Spine J. 2007. 16:1689–1694.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Total Cervical Disc Replacement using Artificial Disc in Cervical Disc Herniations
- Cervical Foraminal and Discal Height after Dynamic Rotational Plating in the Cervical Discectomy and Fusion
- Outcome Analysis of the Patients with and without Anterior Plating in Multi-Level Degenerative Cervical Diseases
- Clinical Results from Subsidence and Loss of Lordosis after Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion
- Comparative Study of Clinical Outcomes of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Using Autobone Graft or Cage with Bone Substitute