J Korean Med Assoc.
2004 Mar;47(3):214-225. 10.5124/jkma.2004.47.3.214.
Alcoholic Drinking
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, College of Medicine, St. Vincent Hospital, Korea. jmyang@vincent.cuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 1723794
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2004.47.3.214
Abstract
- Alcohol abuse is one of the most significant healthrelated drug problems in many countries. Although cocaine and other illegal drugs receive much more attention from governments and news media, these drugs affect far fewer people and cause far less health problems than alcohol. Excessive alcohol consumptionis also associated with many social and family problems. In addition, alcohol abuse is linked to a long list of medical, psychological, and social problems. Long-term heavy drinking can affect the immune, endocrine, digestive, and reproductive functions and can cause various neurological problems, including dementia, blackouts, seizures, hallucinations, and peripheral neuropathy. Alcoholism can severely disrupt marital and family relationships. One family member's drinking problem can put stress on all the other members, imposing them of mental and emotional suffering sand sometimes financial hardships. According to WHO, our country ranked the second in the total amount of alcohol consumption over the last 35 years. So alcohol abuse is apparently the major drug problem in Korea. In developed countries, the goal of alcoholic policy is the regulation of the total alcohol consumption, improving the alcohol quality and regulation of social advertisements of alcohol. However, our country's regulation of alcohol is limited to drunk driving and alcohol consumption by adolescents. Rather, we should be more concerned about public health problems of alcohol.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
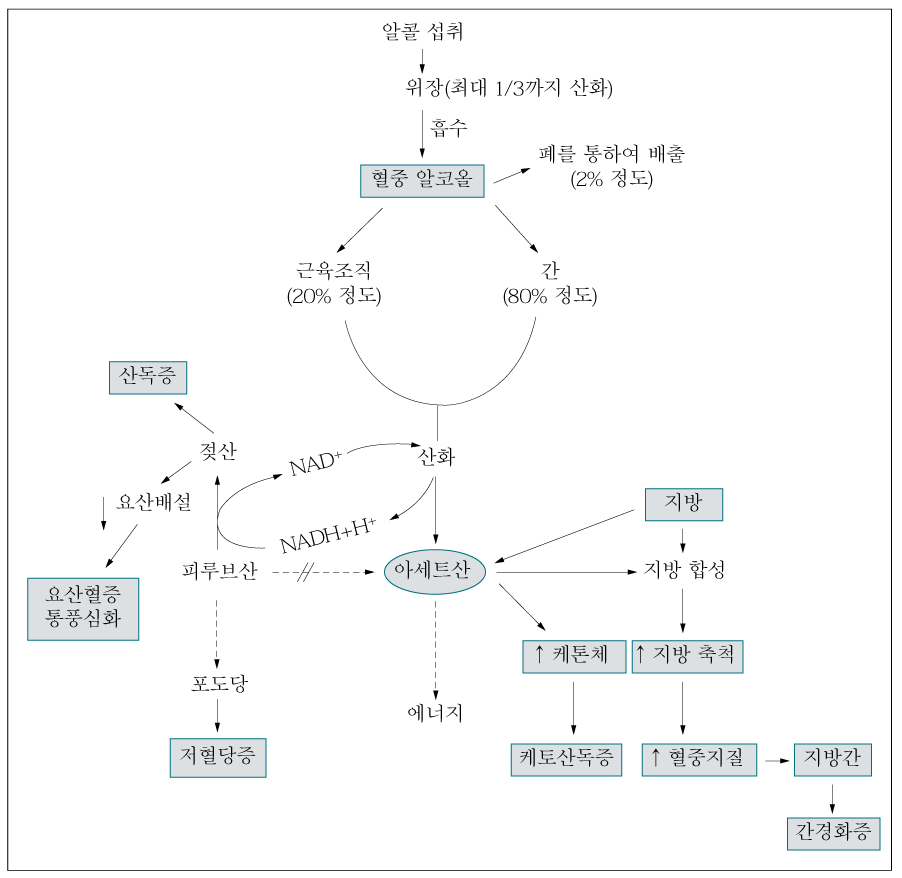
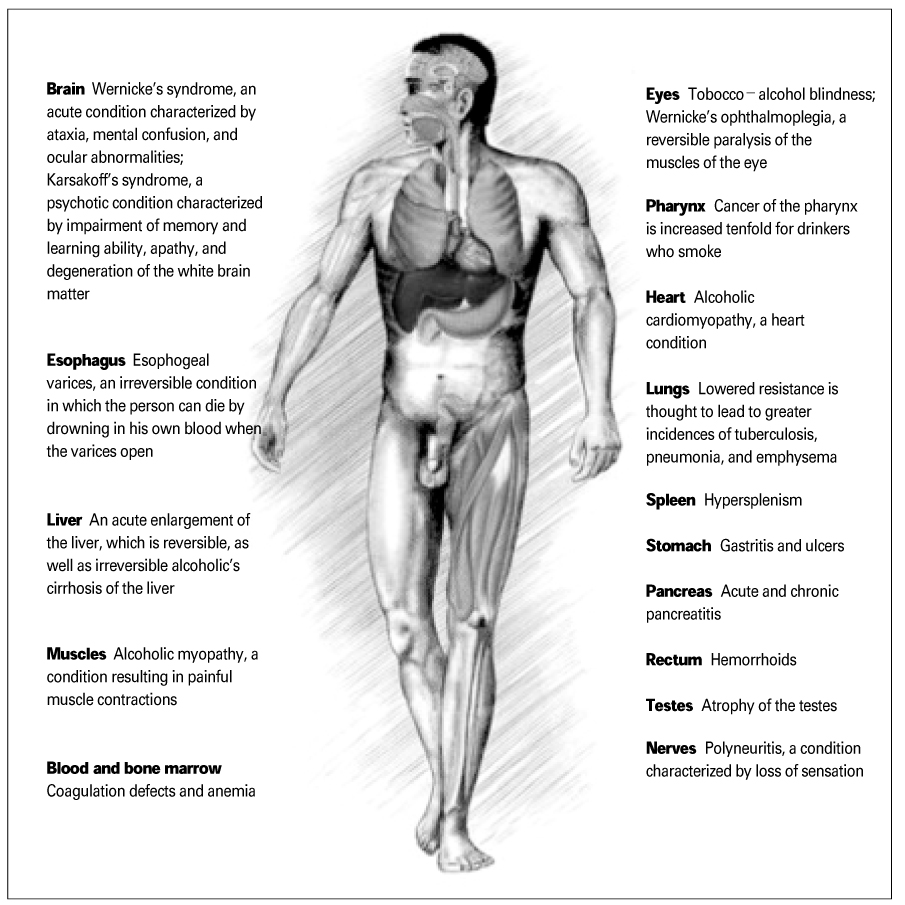
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Physician's Awareness and Education for Patient on Life Style Modification and Home Blood Pressure Monitoring Recommended in Hypertension Guideline
Do Young Kim, Sung Hea Kim, Hyun-Joong Kim, Sang Man Jung, Kyu-Hyung Ryu
J Korean Soc Hypertens. 2012;18(3):97-104. doi: 10.5646/jksh.2012.18.3.97.
Reference
-
1. Tuma DJ, Sorrell MF. Collins MA, editor. Convalent binding of acetaldehyde to hepatic proteins: role in alcoholic liver injury. Aldehyde adducts in alcoholism. 1985. New York: Alan R. Liss;3–17.2. Catilo T, Koop DR, Kamimura S, Triadafilopoulos G, Tsukamoto H. Role of cytochrome P450E1 in ethanol-, carbon tetrachloride-, and iron-dependent microsomal lipid peroxidation. Hepatology. 1992. 16:992–996.
Article3. Matsuoka M, Tsukamoto H. Stimulation of hepatic lipocyte collagen production by Kupffer cell-drived transforming growth factor b:implication for a pathogenetic role in alcoholic liver fibrogenesis. Hepatology. 1990. 11:599–605.
Article6. Drummond L. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome: what every woman should know. Pa Nurse. 1998. 53:7.7. Edlin G, Golanty E, Brown KM. Health and Wellness. 2002. 7th ed. Sudbury: Jones and Bartlett Publishers;384–398.8. Bagnardi V, Blangiardo M, La Vecchia C, Corrao G. Alcohol consumption and the risk of cancer. A meta-analysis. Alcohol Res Health. 2001. 25:263–267.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Psychosocial Characteristics of Patients with Alcoholic Liver Disease
- KASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Alcoholic Liver Disease
- Survey of Alcoholic and Non-alcoholic Beverage Preference in College Students of the Chonnam Area
- A Cross-Cultural Study of Drinking Behaviors and Perceptions in Korean and Chinese Students
- Type of Alcoholic Beverage and High Risk Drinking for Acute Harm